国外的BSseq数据分析教程
Epigenomics Workshop 2021
Tutorials(目录)
- Setup
- DNA Methylation
- ChIPseq
- ATACseq
- Advanced ChIP methods
- Downstream Processing
- Experimental Design and Data Considerations
- Data Integration
- Nextflow & nf-core
Babraham Institute training Courses
开发了bismark、trim-galore等知名生信软件的机构
Babraham Institute: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/training.html
注:该网站不止包含BSseq数据分析教程,还包括一堆的生信相关教程,不过课程开设的年份有点早,有些软件可能已有更好的替代品。
截图上的资料我下载了,现传上来并简单分类一下:
- BS-Seq theory and QC lecture,BS-seq基础知识
BS-Seq theory and QC lecture.pptx
Basic BS-Seq processing Exercises.docx
- Differential Methylation Analysis,如何计算差异甲基化,以及相应的统计学方法选择。
Differential Methylation lecture.pptx
- Visualising and Exploring BS-Seq Data,讨论了关于如何计算位点和区域的甲基化水平
Visualising and Exploring Lecture.pptx
- 偏向于介绍seqmonk的使用,当然也介绍了其他的知识点
- Differential methylation Exercises.docx
- Visualising and exploring Exercises.docx
- SeqMonk tools for methylation analysis.pptx
RRBS数据分析流程
RRBS甲基化分析流程:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29300341/article/details/80551131
我对这个教程最感兴趣的地方是他使用R包来进行基因组区域的注释并计算其甲基化水平,代码如下:
library(GenomicRanges)library(IRanges)library(TxDb.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm10.ensGene)txdb_mm10 <- TxDb.Mmusculus.UCSC.mm10.ensGenetrans <- as.data.frame(transcripts(txdb_mm10))# 取出正链上的基因transUp <- trans[trans$strand=="+",]# 取出Tss上游200到下游1500bp内的范围grPromoterUp <- GRanges(seqnames = transUp$seqnames,strand = "+",ranges = IRanges(start = transUp$start-1500,end = transUp$start+200))# # 取出负链上的基因# transDown <- trans[trans$strand=="-",]# # 取出Tss上游200到下游1500bp内的范围# grPromoterDown <- GRanges(seqnames = transDown$seqnames,strand = "-",# ranges = IRanges(start = transDown$end-200,end = transDown$end+1500))grPromoterUp$value <- NaN #value存储每个promoter区域的甲基化程度wt01Cpg <- read.table("C:/Users/f/Desktop/wt01_CpG_filter.txt",header = TRUE)grCpG <- GRanges(seqnames = wt01Cpg$chr,ranges = IRanges(start = wt01Cpg$base, width = 1))grCpG$meth <- wt01Cpg$freqCgrCpG$coverage <- wt01Cpg$coverage#---------最重要的就是GenomicRanges包的根据基因组坐标找交集的findOverlaps函数hitObj<- findOverlaps(grPromoterUp,grCpG)promoterid<- unique(hitObj@from)for(i in 1:length(promoterid)){CpGid<- hitObj[hitObj@from==promoterid[i],]@topromoterCpG <- grCpG[CpGid]grPromoterUp[promoterid[i]]$value<- weighted.mean(promoterCpG$meth,promoterCpG$coverage) #加权平均值}grPromoterUp <- as.data.frame(grPromoterUp)grPromoterUp <- cbind(grPromoterUp,transUp$tx_id,transUp$tx_name)write.table(grPromoterUp,"wt01UpStrandPromoterMeth.txt",sep = "\t",quote = FALSE,row.names = FALSE)#Further :把负链上的基因也做一遍
表观组学 - 甲基化分析
这篇博文里面的
注意细节
是否去重
WGBS在比对完后需要去重;RRBS不需要去重;
去重指的是去除PCR引入的重复扩增的reads,但这些重复的reads其实都是来源于同一条被超声波或机械或酶学打断的序列。
bismark软件的输出文件格式
非常值得注意的一个问题是:
bismark coverage 文件格式里面记录的CpG位点数目 比 全基因组甲基化胞嘧啶报告,即后缀为.”CpG_report.txt”文件格式(就算去掉没有覆盖到的位点)数目要多一点点,这个是正常的,bismark的GitHub的常见问题里面有解答。
文库是否具有方向性/链特异性
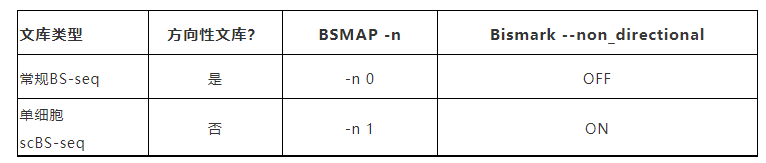
参考:单细胞甲基化测序(scBS-seq)比对率奇低?你的文库方向性参数可能没选对!
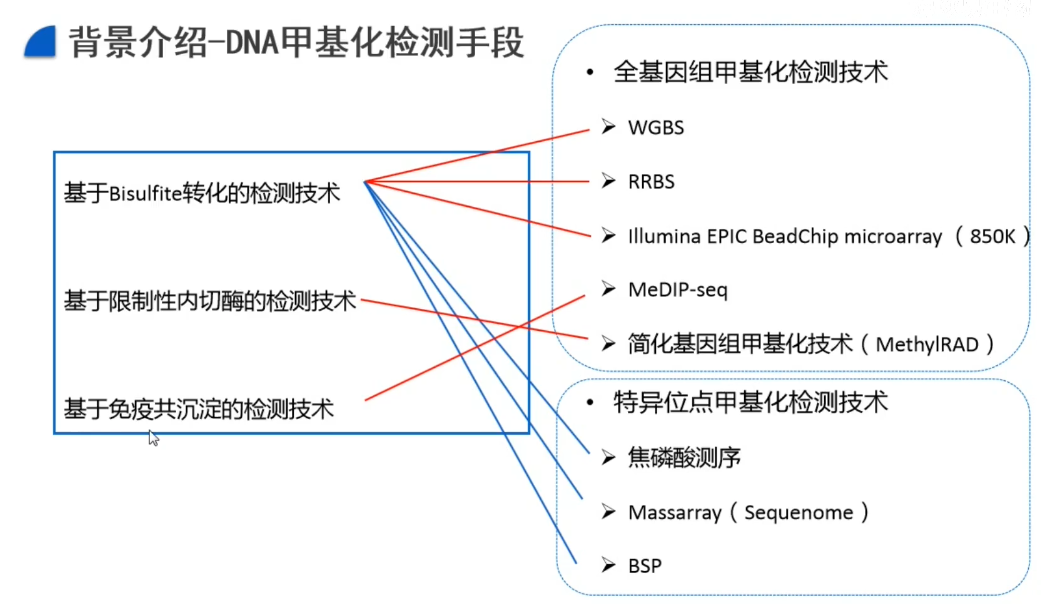
关于RRBS使用**MspI**(甲基化敏感的限制性核酸内切酶)酶切C^CGG位点的生物学小知识点:
下面的文字来自于:https://www.thermofisher.cn/order/catalog/product/cn/zh/ER0541


