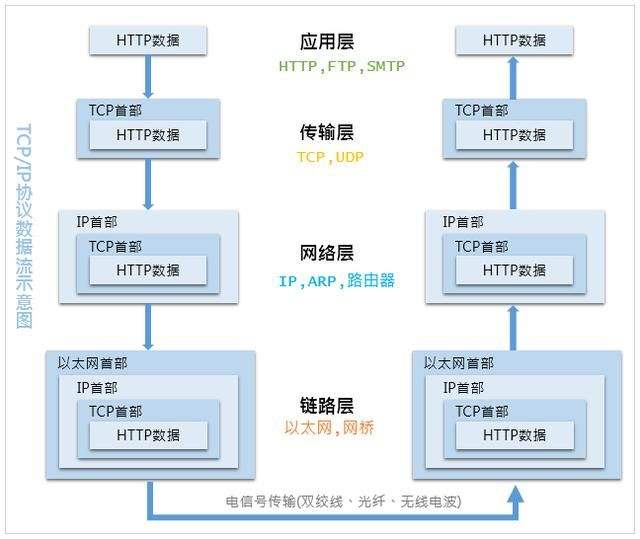
TCP/IP协议的工作原理
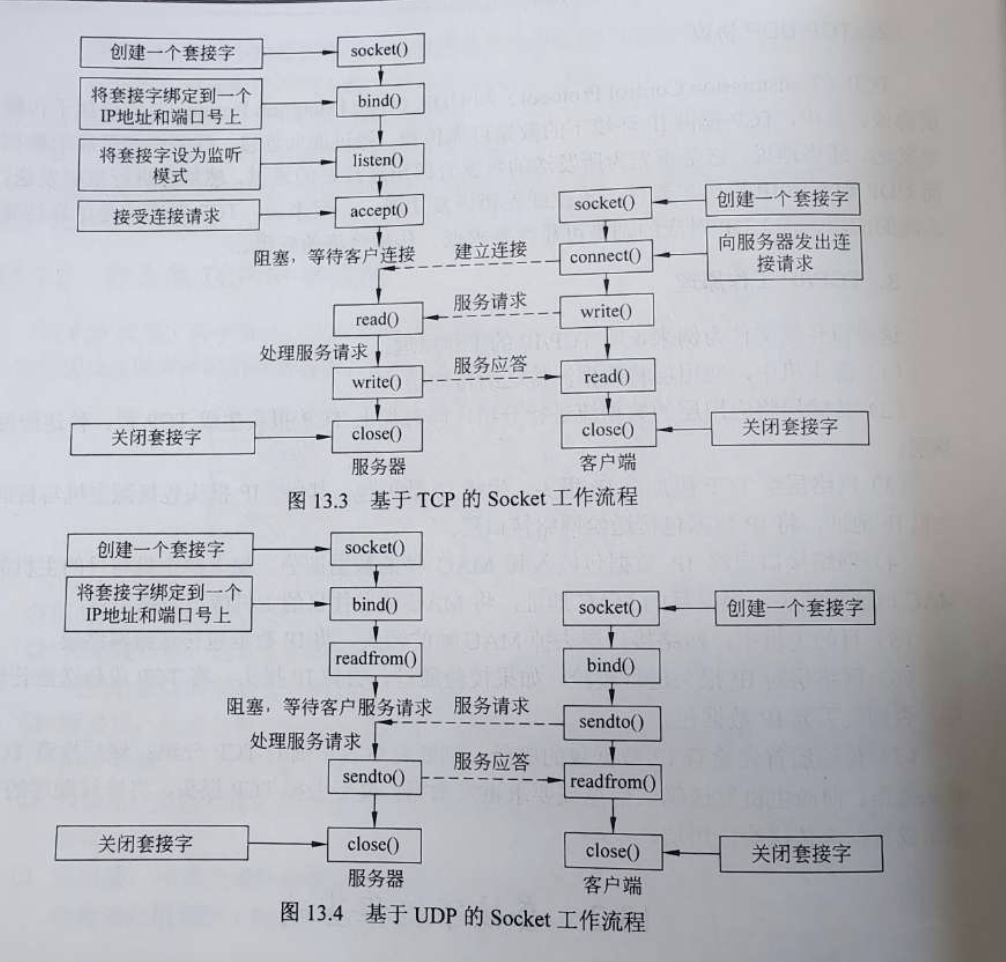
Socket
socket的主要类型有两种,数据流套接字(Stream Sockets)和数据报套接字(Datagram Sockets)两种。
数据流套接字 TCP 可靠传高
数据报套接字 UDP 可靠性低,传输经济
TCP
服务器端
端口说明及端口复用
端口号加协议标识一个“唯一端口”,TCP/IP协议的3000端口和HTTP协议的3000端口,并不会冲突,但是如果同时打开相同协议相同端口的“端口监听”时,就会端口冲突了
1.一个应用程序只能绑定一个端口(一个套接字只能绑定一个端口)
2.UDP端口和TCP端口 虽然端口号相同,但是是不同的端口
3.病毒端口复用,是先断开原来的端口,然后自己连接上去,然后是自己的数据就自己处理不是自己的就分发给其他程序
4.可以多个线程同时receive(接收)你绑定的套接字,共享你绑定的套接字
5.设置端口复用
SO_REUSEADDR可以用在以下4种情况下
5.1 当有一个socket1处于TIME_WAIT状态时,而你启动的程序socket2需要用到该地址和端口,你的程序可以用到此项。
5.2 SO_REUSEADDR允许同一个port上启动同一服务的多个实例(多个进程)。但每个实例绑定的ip地址不能相同。有多块网卡或用IP Alias技术的机器可以测试这种情况。
5.3 SO_REUSEADDR允许单个进程绑定相同的端口到多个socket上,但每个socket绑定的ip地址不同,这和5.2很相似,区别请看UNPv1
5.4 SO_REUSEADDR允许完全相同的地址和端口绑定,但这只用于UDP的多播,不能用于TCP。
注意:设置端口复用函数要在绑定之前调用,而且只要绑定到同一个端口的所有套接字都得设置复用。
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <errno.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <netinet/in.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <arpa/inet.h>/**服务器监听端口号*/#define SERV_PORT 3000/**请求队列长度*/#define LENGTH 10/**缓冲区长度*/#define SIZE 128int main(int argc, char **argv){int res;int sockfd;int clientfd;struct sockaddr_in hostAddr;struct sockaddr_in clientAddr;unsigned int addrLen;char buf[SIZE];int cnt;sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);if (sockfd == -1) {perror("套接字创建失败");exit(1);}/**套接字与IP端口绑定*/hostAddr.sin_family = AF_INET; /**TCP/IP协议*/hostAddr.sin_port = SERV_PORT; // htons(SERV_PORT); /**让系统使用一个未被占用的端口号*/hostAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; /**本机IP地址*/bzero(&(hostAddr.sin_zero), 8); /**清零*/res = bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&hostAddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr));if (res == -1) {perror("套接字绑定失败");exit(1);}/**将套接字设为监听模式,以等待连接请求*/res = listen(sockfd, LENGTH);if (res == -1) {perror("设置监听模式失败");exit(1);}printf("服务器IP:%s\n", inet_ntoa(hostAddr.sin_addr));printf("服务器端口号:%d\n", hostAddr.sin_port);printf("等待客户端请求连接。\n");// 请求到来后,接受连接请求,并接收数据while(1) {addrLen = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);clientfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &clientAddr, &addrLen);if (clientfd == -1) {perror("接受连接请求错误");continue;}printf("客户端IP:%s\n", inet_ntoa(clientAddr.sin_addr));cnt = recv(clientfd, buf, SIZE, 0);if (cnt == -1) {perror("数据接收失败");exit(1);}printf("收到数据:%s\n", buf);close(clientfd);}return 0;}
服务器端并发—多开子线程处理
注意:上面的代码以及下面的代码,使用的都是堵塞方式的套接字,使用堵塞方式的套接字,进程的效率比较低,尤其是在读写操作时,我们可以使用fcntl()或ioctl()函数来改变套接字的属性,将其设置为无堵塞方式。
在无堵塞方式下,进程调用recv,read,recvfrom函数从套接字缓冲区中读取内容时,如果缓冲区没有数据,函数立即返回,并设置相应错误码。同样写入时,send,write,sendto,如果缓冲区没有空闲空间,函数立即返回,并设置相应错误码。 将套接字设置为无阻塞模式,cpu可以通过轮询的方式同时处理多个套接字,但是这种方式会浪费大量CPU时间,从而降低系统的性能,Linux 提供了select()函数可以,有效解决这个问题。该函数用来将进程挂起,使系统内核去监听多个文件描述的状态变化,任何一个文件描述符上有时间发送时,进程都会被唤起,进而节省了CPU时间。
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <errno.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <netinet/in.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <arpa/inet.h>/**服务器监听端口号*/#define SERV_PORT 3000/**请求队列长度*/#define LENGTH 10/**缓冲区长度*/#define SIZE 128int main(int argc, char **argv){int res;int sockfd;int clientfd;int pth;struct sockaddr_in hostAddr;struct sockaddr_in clientAddr;unsigned int addrLen;char buf[SIZE];int cnt;sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);if (sockfd == -1){perror("套接字创建失败");exit(1);}/**套接字与IP端口绑定*/hostAddr.sin_family = AF_INET; /**TCP/IP协议*/hostAddr.sin_port = SERV_PORT; // htons(SERV_PORT); /**让系统使用一个未被占用的端口号*/hostAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; /**本机IP地址*/bzero(&(hostAddr.sin_zero), 8); /**清零*/res = bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&hostAddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr));if (res == -1){perror("套接字绑定失败");exit(1);}/**将套接字设为监听模式,以等待连接请求*/res = listen(sockfd, LENGTH);if (res == -1){perror("设置监听模式失败");exit(1);}printf("服务器IP:%s\n", inet_ntoa(hostAddr.sin_addr));printf("服务器端口号:%d\n", hostAddr.sin_port);printf("等待客户端请求连接。\n");// 请求到来后,接受连接请求,并接收数据while (1){addrLen = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);clientfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&clientAddr, &addrLen);if (clientfd == -1){perror("接受连接请求错误");continue;}pth = fork();if (pth == -1) {perror("进程创建失败");exit(1);}if (pth == 0) {close(sockfd); // 关闭父进程套接字printf("客户端IP:%s\n", inet_ntoa(clientAddr.sin_addr));cnt = recv(clientfd, buf, SIZE, 0);if (cnt == -1){perror("数据接收失败");exit(1);}printf("收到数据:%s\n", buf);sleep(5);close(clientfd);exit(0);}/**父亲进程关闭子进程套接字*/close(clientfd);}return 0;}
客户端
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <errno.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <netinet/in.h>#include <sys/socket.h>/**服务器监听端口号*/#define SERV_PORT 3000/**请求队列长度*/#define LENGTH 10/**缓冲区长度*/#define SIZE 128int main(int argc, char **argv){int res;int sockfd;struct sockaddr_in hostAddr;char buf[SIZE];int cnt;if (argc != 2) {perror("参数错误");exit(1);}sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);if (sockfd == -1) {perror("套接字创建失败");exit(1);}/**套接字与IP端口绑定*/hostAddr.sin_family = AF_INET; /**TCP/IP协议*/hostAddr.sin_port = SERV_PORT; // htons(SERV_PORT); /**让系统使用一个未被占用的端口号*/hostAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; /**本机IP地址*/bzero(&(hostAddr.sin_zero), 8); /**清零*/res = connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&hostAddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr));if (res == -1){perror("连接失败");exit(1);}strcpy(buf, argv[1]);cnt = send(sockfd, buf, SIZE, 0);if (cnt == -1) {perror("发送数据失败");exit(1);}printf("发送数据:%s\n", buf);close(sockfd);return 0;}
UDP
服务器端
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <errno.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <netinet/in.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <arpa/inet.h>/**服务器监听端口号*/#define SERV_PORT 3000/**请求队列长度*/#define LENGTH 10/**缓冲区长度*/#define SIZE 128int main(int argc, char **argv){int res;int sockfd;int clientfd;struct sockaddr_in hostAddr;struct sockaddr_in clientAddr;unsigned int addrLen;char buf[SIZE];int cnt;sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);if (sockfd == -1) {perror("套接字创建失败");exit(1);}/**套接字与IP端口绑定*/hostAddr.sin_family = AF_INET; /**TCP/IP协议*/hostAddr.sin_port = SERV_PORT; // htons(SERV_PORT); /**让系统使用一个未被占用的端口号*/hostAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; /**本机IP地址*/bzero(&(hostAddr.sin_zero), 8); /**清零*/res = bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&hostAddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr));if (res == -1) {perror("套接字绑定失败");exit(1);}printf("服务器IP:%s\n", inet_ntoa(hostAddr.sin_addr));printf("服务器端口号:%d\n", hostAddr.sin_port);printf("等待客户端请求连接。\n");// 请求到来后,接受连接请求,并接收数据while(1) {addrLen = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);cnt = recvfrom(sockfd, buf, SIZE, 0,(struct sockaddr *)&clientAddr, &addrLen);if (cnt == -1) {perror("数据接收失败");exit(1);}printf("客户端IP:%s\n", inet_ntoa(clientAddr.sin_addr));printf("收到数据:%s\n", buf);}close(clientfd);return 0;}
客户端
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <errno.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <netinet/in.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <arpa/inet.h>/**服务器监听端口号*/#define SERV_PORT 3000/**请求队列长度*/#define LENGTH 10/**缓冲区长度*/#define SIZE 128int main(int argc, char **argv){int res;int sockfd;struct sockaddr_in hostAddr;unsigned int addrLen;char buf[SIZE];int cnt;if (argc != 3) {perror("参数错误");exit(1);}sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);if (sockfd == -1) {perror("套接字创建失败");exit(1);}/**套接字与IP端口绑定*/hostAddr.sin_family = AF_INET; /**TCP/IP协议*/hostAddr.sin_port = SERV_PORT; // htons(SERV_PORT); /**让系统使用一个未被占用的端口号*/hostAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); // INADDR_ANY; /**本机IP地址*/bzero(&(hostAddr.sin_zero), 8); /**清零*/addrLen = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);strcpy(buf, argv[2]);cnt = sendto(sockfd, buf, SIZE, 0,(struct sockaddr *)&hostAddr, addrLen);if (cnt == -1) {perror("发送数据失败");exit(1);}printf("发送数据:%s\n", buf);close(sockfd);return 0;}
域名系统
通过域名获取主机信息
通过地址获取主机信息
获取本地主机信息
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <netinet/in.h>#include <sys/socket.h>#include <arpa/inet.h>#include <netdb.h>/**uname函数*/#include <sys/utsname.h>int main(int argc, char **argv){struct sockaddr_in addr;struct hostent *host;struct hostent *webHost;if (argc != 2) {printf("参数错误");exit(1);}char domainName[] = "www.baidu.com";webHost = gethostbyname((char *) &domainName);printf("webHost.h_name=%s\n", webHost->h_name);printf("webHost.h_aliases=%s\n", *webHost->h_aliases);/**将ip地址由字符串转换为二进制形式*/inet_aton(argv[1], &addr.sin_addr);/**查找IP对应的主机信息*/host = gethostbyaddr((char *)&addr.sin_addr, 4, AF_INET);printf("host=%s\n", host->h_name);char name[128];/**获取本地主机信息,gethostname函数调用成功返回0,否则返回-1*/gethostname((char *)&name, sizeof(name));printf("name=%s\n", name);struct utsname utsName;uname((struct utsname *)&utsName);printf("sysname=%s\n", utsName.sysname);printf("nodename=%s\n", utsName.nodename);printf("release=%s\n", utsName.release);printf("version=%s\n", utsName.version);printf("machine=%s\n", utsName.machine);return 0;}