一、什么是 Spring Boot Actuator
Spring Boot Actuator 模块提供了生产级别的功能,比如健康检查,审计,指标收集,HTTP 跟踪等,监控和管理Spring Boot 应用。这个模块是一个采集应用内部信息暴露给外部的模块,上述的功能都可以通过HTTP 和 JMX 访问。
因为暴露内部信息的特性,Actuator 也可以和一些外部的应用监控系统整合(Prometheus, Graphite, DataDog, Influx, Wavefront, New Relic等)。这些监控系统提供了出色的仪表板,图形,分析和警报,通过一个统一友好的界面,监视和管理应用程序。
Actuator使用Micrometer与这些外部应用程序监视系统集成。这样一来,只需很少的配置即可轻松集成外部的监控系统。
Micrometer 为 Java 平台上的性能数据收集提供了一个通用的 API,应用程序只需要使用 Micrometer 的通用 API 来收集性能指标即可。Micrometer 会负责完成与不同监控系统的适配工作。这就使得切换监控系统变得很容易。
对比 Slf4j 之于 Java Logger 中的定位。
二、快速开始,创建一个Spring Boot Actuator Demo
可以通过Spring Boot CLI 创建:
spring init -d=web,actuator -n=actuator-demo actuator-demo
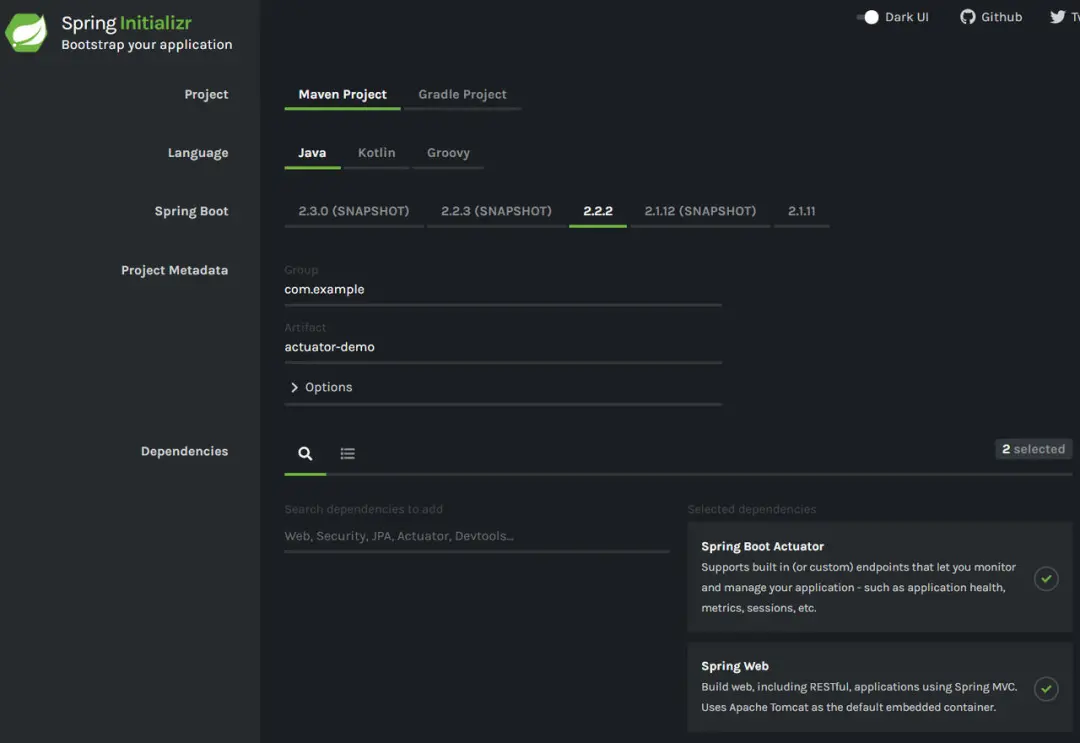
或者通过Spring Initializr 创建:
对应的maven依赖:
<dependencies>...<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId></dependency>...</dependencies>
对应的Gradle 依赖:
dependencies {compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator")}
三、Endpoints 介绍
Spring Boot 提供了所谓的 endpoints (下文翻译为端点)给外部来与应用程序进行访问和交互。
打比方来说,/health 端点 提供了关于应用健康情况的一些基础信息。metrics 端点提供了一些有用的应用程序指标(JVM 内存使用、系统CPU使用等)。
这些 Actuator 模块本来就有的端点称之为原生端点。根据端点的作用的话,大概可以分为三大类:
应用配置类: 获取应用程序中加载的应用配置、环境变量、自动化配置报告等与Spring Boot应用密切相关的配置类信息。
度量指标类:获取应用程序运行过程中用于监控的度量指标,比如:内存信息、线程池信息、HTTP请求统计等。
操作控制类:提供了对应用的关闭等操作类功能。
详细的原生端点介绍,请以官网为准,这里就不赘述徒增篇幅。
需要注意的就是:
1、每一个端点都可以通过配置来单独禁用或者启动
2、不同于Actuator 1.x,Actuator 2.x 的大多数端点默认被禁掉。Actuator 2.x 中的默认端点增加了/actuator前缀。默认暴露的两个端点为/actuator/health和 /actuator/info
四、端点暴露配置
可以通过以下配置,来配置通过JMX 和 HTTP 暴露的端点。
| Property | Default |
|---|---|
| management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.exclude |
|
| management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.include | * |
| management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude |
|
| management.endpoints.web.exposure.include | info, healt |
可以打开所有的监控点
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
也可以选择打开部分,”*” 代表暴露所有的端点,如果指定多个端点,用”,”分开
management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude=beans,trace
Actuator 默认所有的监控点路径都在/actuator/*,当然如果有需要这个路径也支持定制。
management.endpoints.web.base-path=/minitor
设置完重启后,再次访问地址就会变成/minitor/。
*现在按照如下配置:
# "*" 代表暴露所有的端点 如果指定多个端点,用","分开management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*# 赋值规则同上management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude=
启动DEMO程序,访问http://localhost:8080/actuator,查看暴露出来的端点:
上面这样显示是因为chrome 浏览器安装了 JSON-handle 插件,实际上就是返回一大段json
下面会着重介绍几个比较重要的端点。
五、重要端点解析
5.1 /health端点
/health端点会聚合程序的健康指标,来检查程序的健康情况。端点公开的应用健康信息取决于:
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
该属性可以使用以下值之一进行配置:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| never | 不展示详细信息,up或者down的状态,默认配置 |
| when-authorized | 详细信息将会展示给通过认证的用户。授权的角色可以通过management.endpoint.health.roles配置 |
| always | 对所有用户暴露详细信息 |
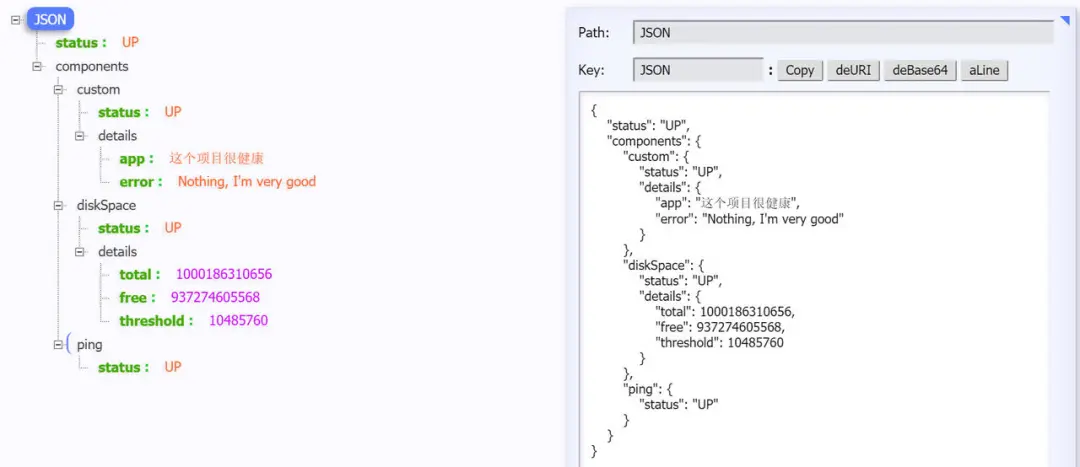
按照上述配置,配置成always之后,启动项目,访问http://localhost:8080/actuator/health端口,可以看到这样的信息:
是不是感觉好像健康信息有点少?先别急,那是因为创建的是一个最基础的Demo项目,没有依赖很多的组件。
/health端点有很多自动配置的健康指示器:如redis、rabbitmq、db等组件。当项目有依赖对应组件的时候,这些健康指示器就会被自动装配,继而采集对应的信息。如上面的 diskSpace 节点信息就是DiskSpaceHealthIndicator 在起作用。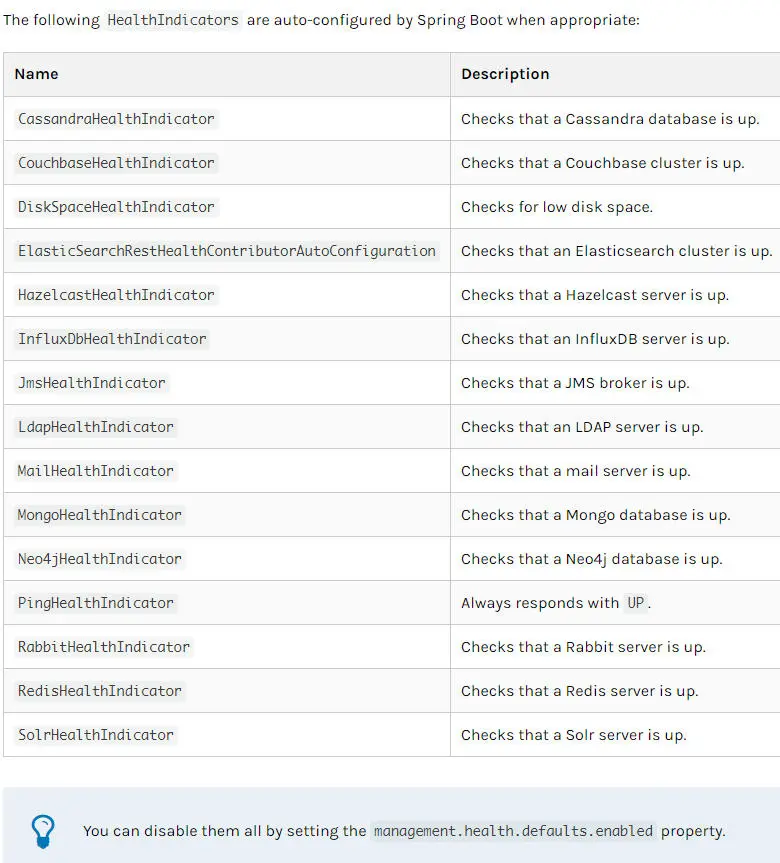
上述截图取自官方文档
这是另一个项目的/health端点信息。
当如上的组件有一个状态异常,应用服务的整体状态即为down。也可以通过配置禁用某个组件的健康监测。
management.health.mongo.enabled: false
或者禁用所有自动配置的健康指示器:
management.health.defaults.enabled: false
⭐自定义 Health Indicator
当然也可以自定义一个Health Indicator,只需要实现HealthIndicator 接口或者继承AbstractHealthIndicator类。
@Componentpublic class CustomHealthIndicator extends AbstractHealthIndicator {@Overrideprotected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {// 使用 builder 来创建健康状态信息// 如果你throw 了一个 exception,那么status 就会被置为DOWN,异常信息会被记录下来builder.up().withDetail("app", "这个项目很健康").withDetail("error", "Nothing, I'm very good");}}
5.2 /metrics端点
/metrics端点用来返回当前应用的各类重要度量指标,比如:内存信息、线程信息、垃圾回收信息、tomcat、数据库连接池等。
{"names": ["tomcat.threads.busy","jvm.threads.states","jdbc.connections.active","jvm.gc.memory.promoted","http.server.requests","hikaricp.connections.max","hikaricp.connections.min","jvm.memory.used","jvm.gc.max.data.size","jdbc.connections.max",....]}
不同于1.x,Actuator在这个界面看不到具体的指标信息,只是展示了一个指标列表。为了获取到某个指标的详细信息,可以请求具体的指标信息,像这样:
http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/{MetricName}
比如访问/actuator/metrics/jvm.memory.max,返回信息如下:
也可以用query param的方式查看单独的一块区域。比如可以访问/actuator/metrics/jvm.memory.max?tag=id:Metaspace。结果就是:
5.3/loggers端点
/loggers 端点暴露了程序内部配置的所有logger的信息。访问/actuator/loggers可以看到,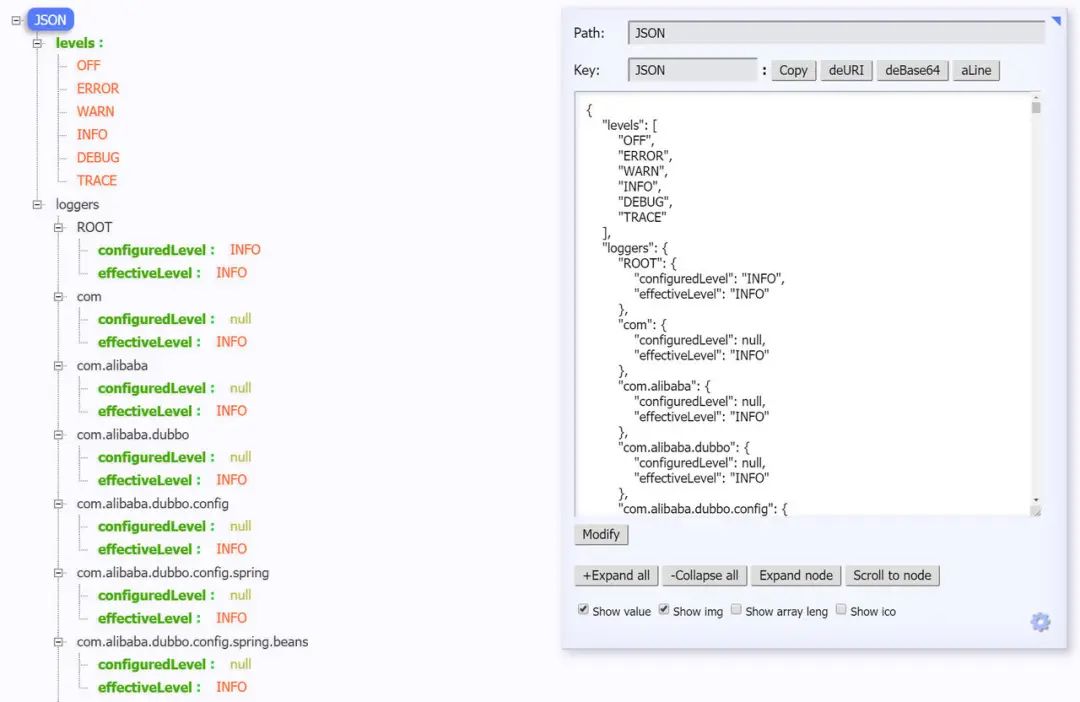
也可以通过下述方式访问单独一个logger,
http://localhost:8080/actuator/loggers/{name}
比如现在访问 root logger,http://localhost:8080/actuator/loggers/root
{"configuredLevel": "INFO","effectiveLevel": "INFO"}
⭐改变运行时的日志等级
/loggers端点最想提的就是这个功能,能够动态修改日志等级。
比如,可以通过下述方式来修改 root logger的日志等级。只需要发起一个URL 为http://localhost:8080/actuator/loggers/root的POST请求,POST报文如下:
{"configuredLevel": "DEBUG"}
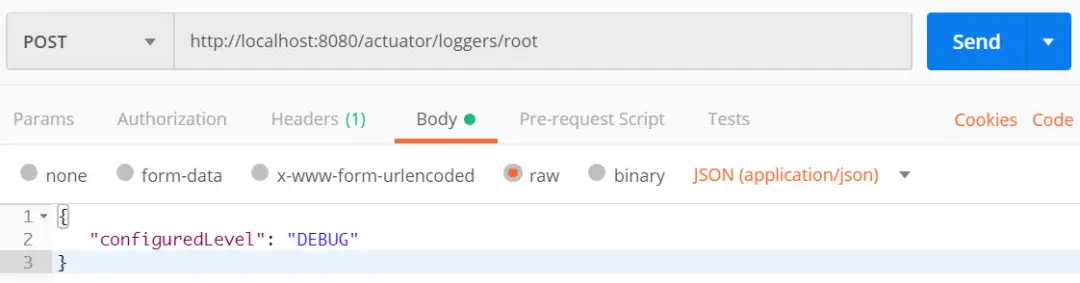
仔细想想,这个功能是不是非常有用。如果在生产环境中,要对应用输出一些Debug信息以便于诊断一些异常情况,只需要按照上述方式就可以修改,而不需要重启应用。
如果想重置成默认值,把value 改成 null
5.4 /info端点
/info端点可以用来展示程序的信息。并且可以按照自己的需求在配置文件application.properties中个性化配置(默认情况下,该端点只会返回一个空的json内容。):
info.app.name=actuator-test-demoinfo.app.encoding=UTF-8info.app.java.source=1.8info.app.java.target=1.8# 在 maven 项目中你可以直接用下列方式引用 maven properties的值# info.app.encoding=@project.build.sourceEncoding@# info.app.java.source=@java.version@# info.app.java.target=@java.version@
启动项目,访问http://localhost:8080/actuator/info:
{"app": {"encoding": "UTF-8","java": {"source": "1.8.0_131","target": "1.8.0_131"},"name": "actuator-test-demo"}}
5.5 /beans端点
/beans端点会返回Spring 容器中所有bean的别名、类型、是否单例、依赖等信息。
访问http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans,返回如下: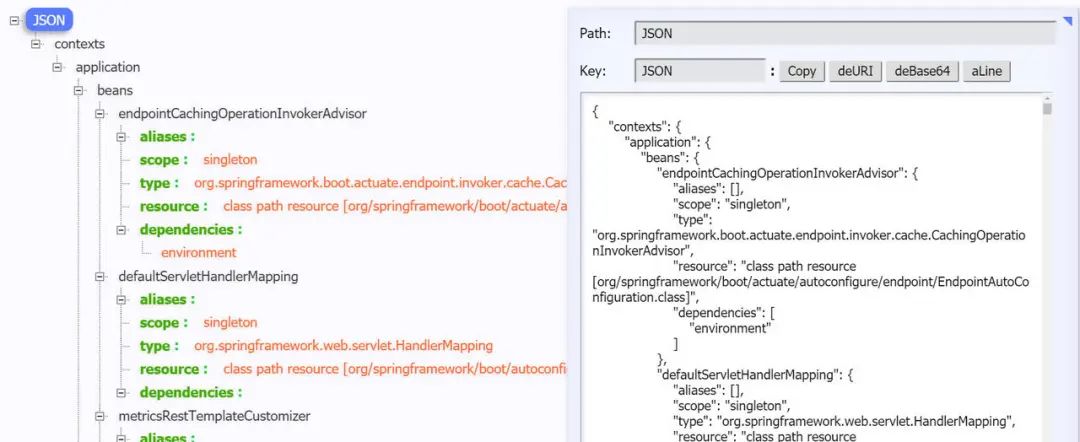
5.6 /heapdump 端点
访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/heapdump会自动生成一个 Jvm 的堆文件 heapdump。可以使用 JDK 自带的 Jvm 监控工具 VisualVM 打开此文件查看内存快照。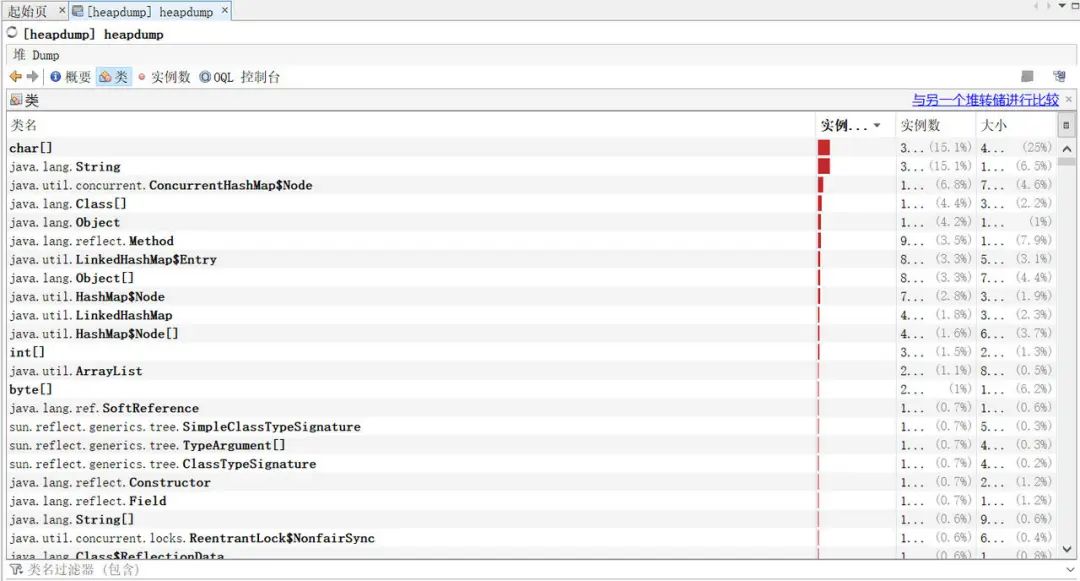
5.7 /threaddump 端点
这个端点特别有用,方便在日常定位问题的时候查看线程的情况。主要展示了线程名、线程ID、线程的状态、是否等待锁资源、线程堆栈等信息。就是可能查看起来不太直观。访问http://localhost:8080/actuator/threaddump
5.8 /shutdown端点
这个端点属于操作控制类端点,可以优雅关闭 Spring Boot 应用。要使用这个功能首先需要在配置文件中开启:
management.endpoint.shutdown.enabled=true
由于 shutdown 接口默认只支持 POST 请求,启动Demo项目,向http://localhost:8080/actuator/shutdown发起POST请求。返回信息:
{"message": "Shutting down, bye..."}
然后应用程序被关闭。
由于开放关闭应用的操作本身是一件非常危险的事,所以真正在线上使用的时候,需要对其加入一定的保护机制,比如:定制Actuator的端点路径、整合Spring Security进行安全校验等。(不是特别必要的话,这个端点不用开)
六、整合Spring Security 对端点进行安全校验
由于端点的信息和产生的交互都是非常敏感的,必须防止未经授权的外部访问。如果应用程序中存在Spring Security的依赖,则默认情况下使用基于表单的HTTP身份验证来保护端点。
如果没有,只需要增加对应的依赖即可:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId></dependency>
添加之后,需要定义安全校验规则,来覆盖Spring Security 的默认配置。
这里给出了两个版本的模板配置:
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.security.servlet.EndpointRequest;import org.springframework.boot.actuate.context.ShutdownEndpoint;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.PathRequest;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;@Configurationpublic class ActuatorSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {/** version1:* 1. 限制 '/shutdown'端点的访问,只允许ACTUATOR_ADMIN访问* 2. 允许外部访问其他的端点* 3. 允许外部访问静态资源* 4. 允许外部访问 '/'* 5. 其他的访问需要被校验* version2:* 1. 限制所有端点的访问,只允许ACTUATOR_ADMIN访问* 2. 允许外部访问静态资源* 3. 允许外部访问 '/'* 4. 其他的访问需要被校验*/@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {// version1// http// .authorizeRequests()// .requestMatchers(EndpointRequest.to(ShutdownEndpoint.class))// .hasRole("ACTUATOR_ADMIN")// .requestMatchers(EndpointRequest.toAnyEndpoint())// .permitAll()// .requestMatchers(PathRequest.toStaticResources().atCommonLocations())// .permitAll()// .antMatchers("/")// .permitAll()// .antMatchers("/**")// .authenticated()// .and()// .httpBasic();// version2http.authorizeRequests().requestMatchers(EndpointRequest.toAnyEndpoint()).hasRole("ACTUATOR_ADMIN").requestMatchers(PathRequest.toStaticResources().atCommonLocations()).permitAll().antMatchers("/").permitAll().antMatchers("/**").authenticated().and().httpBasic();}}
application.properties的相关配置如下:
# Spring Security Default user name and passwordspring.security.user.name=actuatorspring.security.user.password=actuatorspring.security.user.roles=ACTUATOR_ADMIN