一、TXT文件操作
读取全部内容
import numpy as npimport pandas as pd
txt_filename = './files/python_wiki.txt'# 打开文件file_obj = open(txt_filename,'r')# 读取整个文件内容all_content = file_obj.read()# 关闭文件file_obj.close()print (all_content)
Python is a widely used high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language.[24][25] Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability, and its syntax allows programmers to express concepts in fewer lines of code than possible in languages such as C++ or Java.[26][27] The language provides constructs intended to enable writing clear programs on both a small and large scale.[28]Python supports multiple programming paradigms, including object-oriented, imperative and functional programming or procedural styles. It features a dynamic type system and automatic memory management and has a large and comprehensive standard library.[29]Python interpreters are available for many operating systems, allowing Python code to run on a wide variety of systems. CPython, the reference implementation of Python, is open source software[30] and has a community-based development model, as do nearly all of its variant implementations. CPython is managed by the non-profit Python Software Foundation.
逐行读取
txt_filename = './files/python_wiki.txt'# 打开文件file_obj = open(txt_filename, 'r')# 逐行读取line1 = file_obj.readline()print (line1)
Python is a widely used high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language.[24][25] Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability, and its syntax allows programmers to express concepts in fewer lines of code than possible in languages such as C++ or Java.[26][27] The language provides constructs intended to enable writing clear programs on both a small and large scale.[28]
# 继续读下一行【不会全部读完】line2 = file_obj.readline()print (line2)# 关闭文件file_obj.close()
Python supports multiple programming paradigms, including object-oriented, imperative and functional programming or procedural styles. It features a dynamic type system and automatic memory management and has a large and comprehensive standard library.[29]
读取全部内容,返回列表
txt_filename = './files/python_wiki.txt'# 打开文件file_obj = open(txt_filename, 'r')lines = file_obj.readlines()for i, line in enumerate(lines):print ('%i: %s' %(i, line))# 关闭文件file_obj.close()
0: Python is a widely used high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language.[24][25] Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability, and its syntax allows programmers to express concepts in fewer lines of code than possible in languages such as C++ or Java.[26][27] The language provides constructs intended to enable writing clear programs on both a small and large scale.[28]1: Python supports multiple programming paradigms, including object-oriented, imperative and functional programming or procedural styles. It features a dynamic type system and automatic memory management and has a large and comprehensive standard library.[29]2: Python interpreters are available for many operating systems, allowing Python code to run on a wide variety of systems. CPython, the reference implementation of Python, is open source software[30] and has a community-based development model, as do nearly all of its variant implementations. CPython is managed by the non-profit Python Software Foundation.
写操作
txt_filename = './files/test_write.txt'# 打开文件file_obj = open(txt_filename, 'w')# 写入全部内容file_obj.write("《Python数据分析》")file_obj.close()
txt_filename = './files/test_write.txt'# 打开文件file_obj = open(txt_filename, 'w')# 写入字符串列表lines = ['这是第%i行\n' %n for n in range(10)]file_obj.writelines(lines)file_obj.close()
with语句
txt_filename = './files/test_write.txt'with open(txt_filename, 'r') as f_obj:print (f_obj.read())
这是第0行这是第1行这是第2行这是第3行这是第4行这是第5行这是第6行这是第7行这是第8行这是第9行
二、CSV文件操作
pandas读csv文件
根据路径导入数据以及指定的列
import pandas as pdfilename = './files/presidential_polls.csv'df = pd.read_csv(filename, usecols=['cycle', 'type', 'startdate'])#导入指定列print (type(df))print (df.head())
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>cycle type startdate0 2016 polls-plus 10/25/20161 2016 polls-plus 10/27/20162 2016 polls-plus 10/27/20163 2016 polls-plus 10/20/20164 2016 polls-plus 10/20/2016
引用指定的列
cycle_se = df['cycle']print (type(cycle_se))print (cycle_se.head())
<class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>0 20161 20162 20163 20164 2016Name: cycle, dtype: int64
多层索引成dataframe类型
filename = './files/presidential_polls.csv'df1 = pd.read_csv(filename,usecols=['cycle', 'type', 'startdate','state','grade'],index_col = ['state','grade'])print(df1.head())
cycle type startdatestate gradeU.S. B 2016 polls-plus 10/25/2016A+ 2016 polls-plus 10/27/2016Virginia A+ 2016 polls-plus 10/27/2016Florida A 2016 polls-plus 10/20/2016U.S. B+ 2016 polls-plus 10/20/2016
跳过指定的行
filename = './files/presidential_polls.csv'df2 = pd.read_csv(filename,usecols=['cycle', 'type', 'startdate','state','grade'],skiprows=[1, 2, 3])print(df2.head())
cycle type state startdate grade0 2016 polls-plus Florida 10/20/2016 A1 2016 polls-plus U.S. 10/20/2016 B+2 2016 polls-plus U.S. 10/22/2016 A3 2016 polls-plus U.S. 10/26/2016 A-4 2016 polls-plus Pennsylvania 10/25/2016 B-
pandas写csv文件
·to_csv里面的index参数作用?===可能是不要索引的意思。
filename = './files/pandas_output.csv'df.to_csv(filename, index=None)
三、JSON文件操作
json读操作
import jsonfilename = './files/global_temperature.json'with open(filename, 'r') as f_obj:json_data = json.load(f_obj)# 返回值是dict类型print (type(json_data))
<class 'dict'>
print (json_data.keys())
dict_keys(['description', 'data'])
json转CSV
#print json_data['data'].keys()print (json_data['data'].values())
dict_values(['-0.1247', '-0.0707', '-0.0710', '-0.1481', '-0.2099', '-0.2220', '-0.2101', '-0.2559', '-0.1541', '-0.1032', '-0.3233', '-0.2552', '-0.3079', '-0.3221', '-0.2828', '-0.2279', '-0.0971', '-0.1232', '-0.2578', '-0.1172', '-0.0704', '-0.1471', '-0.2535', '-0.3442', '-0.4240', '-0.2967', '-0.2208', '-0.3767', '-0.4441', '-0.4332', '-0.3862', '-0.4367', '-0.3318', '-0.3205', '-0.1444', '-0.0747', '-0.2979', '-0.3193', '-0.2118', '-0.2082', '-0.2152', '-0.1517', '-0.2318', '-0.2161', '-0.2510', '-0.1464', '-0.0618', '-0.1506', '-0.1749', '-0.2982', '-0.1016', '-0.0714', '-0.1214', '-0.2481', '-0.1075', '-0.1445', '-0.1173', '-0.0204', '-0.0318', '-0.0157', '0.0927', '0.1974', '0.1549', '0.1598', '0.2948', '0.1754', '-0.0013', '-0.0455', '-0.0471', '-0.0550', '-0.1579', '-0.0095', '0.0288', '0.0997', '-0.1118', '-0.1305', '-0.1945', '0.0538', '0.1145', '0.0640', '0.0252', '0.0818', '0.0924', '0.1100', '-0.1461', '-0.0752', '-0.0204', '-0.0112', '-0.0282', '0.0937', '0.0383', '-0.0775', '0.0280', '0.1654', '-0.0698', '0.0060', '-0.0769', '0.1996', '0.1139', '0.2288', '0.2651', '0.3024', '0.1836', '0.3429', '0.1510', '0.1357', '0.2308', '0.3710', '0.3770', '0.2982', '0.4350', '0.4079', '0.2583', '0.2857', '0.3420', '0.4593', '0.3225', '0.5185', '0.6335', '0.4427', '0.4255', '0.5455', '0.6018', '0.6145', '0.5806', '0.6583', '0.6139', '0.6113', '0.5415', '0.6354', '0.7008', '0.5759', '0.6219', '0.6687', '0.7402', '0.8990'])
# 转换keyyear_str_lst = json_data['data'].keys()year_lst = [int(year_str) for year_str in year_str_lst]print (year_lst)
[1880, 1881, 1882, 1883, 1884, 1885, 1886, 1887, 1888, 1889, 1890, 1891, 1892, 1893, 1894, 1895, 1896, 1897, 1898, 1899, 1900, 1901, 1902, 1903, 1904, 1905, 1906, 1907, 1908, 1909, 1910, 1911, 1912, 1913, 1914, 1915, 1916, 1917, 1918, 1919, 1920, 1921, 1922, 1923, 1924, 1925, 1926, 1927, 1928, 1929, 1930, 1931, 1932, 1933, 1934, 1935, 1936, 1937, 1938, 1939, 1940, 1941, 1942, 1943, 1944, 1945, 1946, 1947, 1948, 1949, 1950, 1951, 1952, 1953, 1954, 1955, 1956, 1957, 1958, 1959, 1960, 1961, 1962, 1963, 1964, 1965, 1966, 1967, 1968, 1969, 1970, 1971, 1972, 1973, 1974, 1975, 1976, 1977, 1978, 1979, 1980, 1981, 1982, 1983, 1984, 1985, 1986, 1987, 1988, 1989, 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015]
# 转换valuetemp_str_lst = json_data['data'].values()temp_lst = [float(temp_str) for temp_str in temp_str_lst]print (temp_lst)
[-0.1247, -0.0707, -0.071, -0.1481, -0.2099, -0.222, -0.2101, -0.2559, -0.1541, -0.1032, -0.3233, -0.2552, -0.3079, -0.3221, -0.2828, -0.2279, -0.0971, -0.1232, -0.2578, -0.1172, -0.0704, -0.1471, -0.2535, -0.3442, -0.424, -0.2967, -0.2208, -0.3767, -0.4441, -0.4332, -0.3862, -0.4367, -0.3318, -0.3205, -0.1444, -0.0747, -0.2979, -0.3193, -0.2118, -0.2082, -0.2152, -0.1517, -0.2318, -0.2161, -0.251, -0.1464, -0.0618, -0.1506, -0.1749, -0.2982, -0.1016, -0.0714, -0.1214, -0.2481, -0.1075, -0.1445, -0.1173, -0.0204, -0.0318, -0.0157, 0.0927, 0.1974, 0.1549, 0.1598, 0.2948, 0.1754, -0.0013, -0.0455, -0.0471, -0.055, -0.1579, -0.0095, 0.0288, 0.0997, -0.1118, -0.1305, -0.1945, 0.0538, 0.1145, 0.064, 0.0252, 0.0818, 0.0924, 0.11, -0.1461, -0.0752, -0.0204, -0.0112, -0.0282, 0.0937, 0.0383, -0.0775, 0.028, 0.1654, -0.0698, 0.006, -0.0769, 0.1996, 0.1139, 0.2288, 0.2651, 0.3024, 0.1836, 0.3429, 0.151, 0.1357, 0.2308, 0.371, 0.377, 0.2982, 0.435, 0.4079, 0.2583, 0.2857, 0.342, 0.4593, 0.3225, 0.5185, 0.6335, 0.4427, 0.4255, 0.5455, 0.6018, 0.6145, 0.5806, 0.6583, 0.6139, 0.6113, 0.5415, 0.6354, 0.7008, 0.5759, 0.6219, 0.6687, 0.7402, 0.899]
import pandas as pd# 构建 dataframeyear_se = pd.Series(year_lst, name = 'year')temp_se = pd.Series(temp_lst, name = 'temperature')result_df = pd.concat([year_se, temp_se], axis = 1)print (result_df.head())# 保存csvresult_df.to_csv('./files/json_to_csv.csv', index = None)
year temperature0 1880 -0.12471 1881 -0.07072 1882 -0.07103 1883 -0.14814 1884 -0.2099
写json操作
book_dict = [{'书名':'无声告白', '作者':'伍绮诗'}, {'书名':'我不是潘金莲', '作者':'刘震云'}, {'书名':'沉默的大多数 (王小波集)', '作者':'王小波'}]filename = './files/json_output.json'with open(filename, 'w') as f_obj:f_obj.write(json.dumps(book_dict, ensure_ascii=False))# 不需要加, encoding='utf-8'参数
四、SQLite基本操作
连接数据库
import sqlite3db_path = './files/test.sqlite'conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path)cur = conn.cursor()conn.text_factory = str # 处理中文
获取基本信息
cur.execute('SELECT SQLITE_VERSION()')print ('SQLite版本:%s' %str(cur.fetchone()[0]))
SQLite版本:3.30.0
逐条插入数据
cur.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS book")cur.execute("CREATE TABLE book(id INT, name TEXT, price DOUBLE)")cur.execute("INSERT INTO book VALUES(1,'肖秀荣考研书系列:肖秀荣(2017)考研政治命题人终极预测4套卷',14.40)")cur.execute("INSERT INTO book VALUES(2,'法医秦明作品集:幸存者+清道夫+尸语者+无声的证词+第十一根手指(套装共5册) (两种封面随机发货)',100.00)")cur.execute("INSERT INTO book VALUES(3,'活着本来单纯:丰子恺散文漫画精品集(收藏本)',30.90)")cur.execute("INSERT INTO book VALUES(4,'自在独行:贾平凹的独行世界',26.80)")cur.execute("INSERT INTO book VALUES(5,'当你的才华还撑不起你的梦想时',23.00)")cur.execute("INSERT INTO book VALUES(6,'巨人的陨落(套装共3册)',84.90)")cur.execute("INSERT INTO book VALUES(7,'孤独深处(收录雨果奖获奖作品《北京折叠》)',21.90)")cur.execute("INSERT INTO book VALUES(8,'世界知名企业员工指定培训教材:所谓情商高,就是会说话',22.00)")
<sqlite3.Cursor at 0x2d2d64e7c00>
批量插入数据
books = ((9, '人间草木', 30.00),(10,'你的善良必须有点锋芒', 20.50),(11, '这么慢,那么美', 24.80),(12, '考拉小巫的英语学习日记:写给为梦想而奋斗的人(全新修订版)', 23.90))cur.executemany("INSERT INTO book VALUES(?, ?, ?)", books)
<sqlite3.Cursor at 0x2d2d64e7c00>
conn.commit()
查找数据
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM book')rows = cur.fetchall()# 通过索引号访问for row in rows:print ('序号: %i, 书名: %s, 价格: %.2f' %(row[0], row[1], row[2]))
序号: 1, 书名: 肖秀荣考研书系列:肖秀荣(2017)考研政治命题人终极预测4套卷, 价格: 14.40序号: 2, 书名: 法医秦明作品集:幸存者+清道夫+尸语者+无声的证词+第十一根手指(套装共5册) (两种封面随机发货), 价格: 100.00序号: 3, 书名: 活着本来单纯:丰子恺散文漫画精品集(收藏本), 价格: 30.90序号: 4, 书名: 自在独行:贾平凹的独行世界, 价格: 26.80序号: 5, 书名: 当你的才华还撑不起你的梦想时, 价格: 23.00序号: 6, 书名: 巨人的陨落(套装共3册), 价格: 84.90序号: 7, 书名: 孤独深处(收录雨果奖获奖作品《北京折叠》), 价格: 21.90序号: 8, 书名: 世界知名企业员工指定培训教材:所谓情商高,就是会说话, 价格: 22.00序号: 9, 书名: 人间草木, 价格: 30.00序号: 10, 书名: 你的善良必须有点锋芒, 价格: 20.50序号: 11, 书名: 这么慢,那么美, 价格: 24.80序号: 12, 书名: 考拉小巫的英语学习日记:写给为梦想而奋斗的人(全新修订版), 价格: 23.90
conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Rowcur = conn.cursor()cur.execute('SELECT * FROM book')rows = cur.fetchall()# 通过列名访问for row in rows:print ('序号: %i, 书名: %s, 价格: %.2f' %(row['id'], row['name'], row['price']))
序号: 1, 书名: 肖秀荣考研书系列:肖秀荣(2017)考研政治命题人终极预测4套卷, 价格: 14.40序号: 2, 书名: 法医秦明作品集:幸存者+清道夫+尸语者+无声的证词+第十一根手指(套装共5册) (两种封面随机发货), 价格: 100.00序号: 3, 书名: 活着本来单纯:丰子恺散文漫画精品集(收藏本), 价格: 30.90序号: 4, 书名: 自在独行:贾平凹的独行世界, 价格: 26.80序号: 5, 书名: 当你的才华还撑不起你的梦想时, 价格: 23.00序号: 6, 书名: 巨人的陨落(套装共3册), 价格: 84.90序号: 7, 书名: 孤独深处(收录雨果奖获奖作品《北京折叠》), 价格: 21.90序号: 8, 书名: 世界知名企业员工指定培训教材:所谓情商高,就是会说话, 价格: 22.00序号: 9, 书名: 人间草木, 价格: 30.00序号: 10, 书名: 你的善良必须有点锋芒, 价格: 20.50序号: 11, 书名: 这么慢,那么美, 价格: 24.80序号: 12, 书名: 考拉小巫的英语学习日记:写给为梦想而奋斗的人(全新修订版), 价格: 23.90
conn.close()
五、SQLite_json操作
import sqlite3db_path = './files/test_join.sqlite'conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path)cur = conn.cursor()
# 建 depaetment 表,并插入数据cur.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS department")cur.execute("CREATE TABLE department(\id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, \dept CHAR(50) NOT NULL, \emp_id INT NOT NULL)")depts = ((1, 'IT Builing', 1),(2, 'Engineerin', 2),(3, 'Finance', 7))cur.executemany("INSERT INTO department VALUES(?, ?, ?)", depts)
<sqlite3.Cursor at 0x2d2d64f70a0>
conn.commit()
CROSS JOIN 交叉连接
cur.execute("SELECT emp_id, name, dept FROM company CROSS JOIN department;")rows = cur.fetchall()for row in rows:print (row)
# 建 company 表,并插入数据cur.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS company")cur.execute("CREATE TABLE company(\id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, \name CHAR(50) NOT NULL, \age INT NOT NULL, \address CHAR(50) NOT NULL,\salary DOUBLE NOT NULL)")companies = ((1, 'Paul', 32, 'California', 20000.0),(2, 'Allen', 25, 'Texas', 15000.0),(3, 'Teddy', 23, 'Norway', 20000.0),(4, 'Mark', 25, 'Rich-Mond', 65000.0),(5, 'David', 27, 'Texas', 85000.0),(6, 'Kim', 22, 'South-Hall', 45000.0),(7, 'James', 24, 'Houston', 10000.0))cur.executemany("INSERT INTO company VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)", companies)
<sqlite3.Cursor at 0x2d2d64f70a0>
INNER JOIN 内连接
cur.execute("SELECT emp_id, name, dept FROM company INNER JOIN department \ON company.id = department.emp_id;")rows = cur.fetchall()for row in rows:print (row)
(1, 'Paul', 'IT Builing')(2, 'Allen', 'Engineerin')(7, 'James', 'Finance')
OUTER JOIN 外连接
# 左连接cur.execute("SELECT emp_id, name, dept FROM company LEFT OUTER JOIN department \ON company.id = department.emp_id;")rows = cur.fetchall()for row in rows:print (row)
(1, 'Paul', 'IT Builing')(2, 'Allen', 'Engineerin')(None, 'Teddy', None)(None, 'Mark', None)(None, 'David', None)(None, 'Kim', None)(7, 'James', 'Finance')
# 右连接 (目前不支持)cur.execute("SELECT emp_id, name, dept FROM company RIGHT OUTER JOIN department \ON company.id = department.emp_id;")rows = cur.fetchall()for row in rows:print (row)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------OperationalError Traceback (most recent call last)<ipython-input-41-ce0fc573748b> in <module>1 # 右连接 (目前不支持)2 cur.execute("SELECT emp_id, name, dept FROM company RIGHT OUTER JOIN department \----> 3 ON company.id = department.emp_id;")4 rows = cur.fetchall()5 for row in rows:OperationalError: RIGHT and FULL OUTER JOINs are not currently supported
# 右连接,交换两张表cur.execute("SELECT emp_id, name, dept FROM department LEFT OUTER JOIN company \ON company.id = department.emp_id;")rows = cur.fetchall()for row in rows:print (row)
(1, 'Paul', 'IT Builing')(2, 'Allen', 'Engineerin')(7, 'James', 'Finance')
sqlite> SELECT EMP_ID, NAME, DEPT FROM COMPANY LEFT OUTER JOIN DEPARTMENTON COMPANY.ID = DEPARTMENT.EMP_ID;
File "<ipython-input-43-a0833b733075>", line 1sqlite> SELECT EMP_ID, NAME, DEPT FROM COMPANY LEFT OUTER JOIN DEPARTMENT^SyntaxError: invalid syntax
六、Excel文件操作
pandas.read_excel(io, sheet_name=0, header=0, names=None, index_col=None, usecols=None, squeeze=False, dtype=None, engine=None, converters=None, true_values=None, false_values=None, skiprows=None, nrows=None, na_values=None, keep_default_na=True, verbose=False, parse_dates=False, date_parser=None, thousands=None, comment=None, skipfooter=0, convert_float=True, mangle_dupe_cols=True, **kwds)
df_fujian = pd.read_excel(“./datafiles/fujian.xlsx”,sheet_name=’日数据’)
Jupyter Notebook的安装
一般有两种方法,第一种是下载Anaconda,自带python环境以及Jupyter Notebook环境,但这一般都是刚学机器学习那会的集成安装方式,最主要的劝退原因是所占体积较大,所以这里介绍原生的安装方式,在纯Python环境下,使用自带的pip包管理工具下载,类似地像Pandas、Numpy等包也可以以此种方式安装。
打脸YYDS,收回上面画斜线的文字,因为自己以前的笔记里面,有许多其他库,一个一个安装太繁杂了,所以还是下载Anaconda集成环境吧。
具体下载配置参考之前的文章:Pycharm,Anaconda,JetBrains系列app相关总结 | 尼采般地抒情
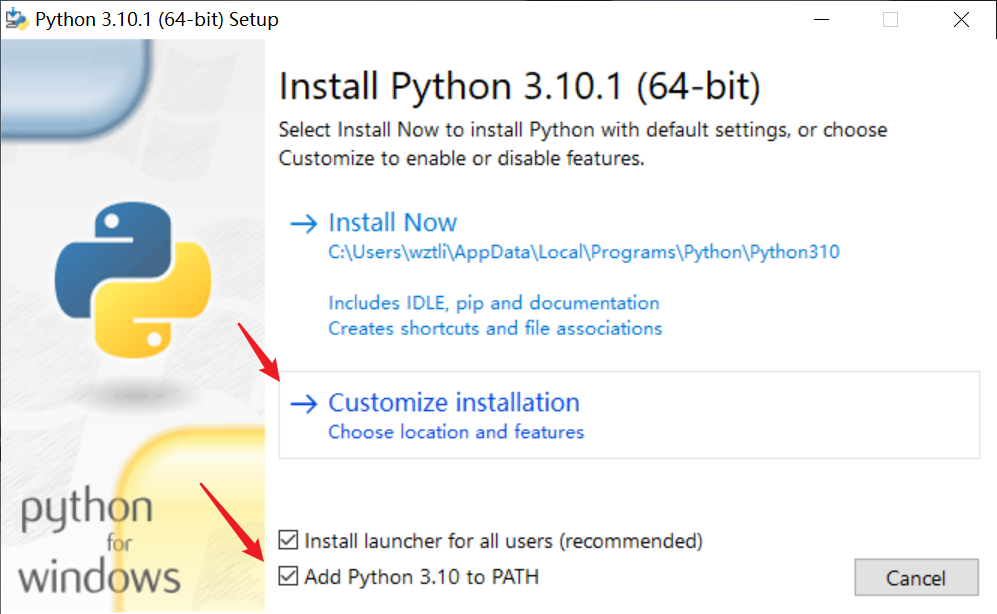
安装python
地址:https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/
安装完之后进入cmd查看
安装jupyter
pip install jupyter
安装成功之后,在项目文件夹下,打开powershell终端输入:jupyter notebook
报错
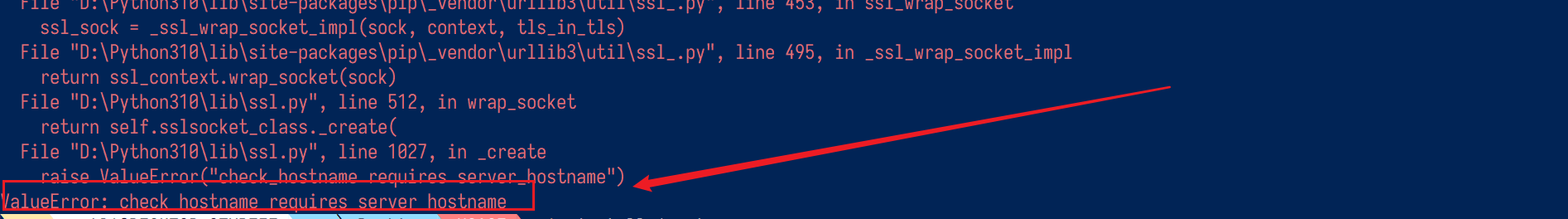
ValueError: check_hostname requires server_hostname
ReadTimeoutError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host=’files.pythonhosted.org’, port=443): Read timed out.

按照报错信息,更新pip
数据分析
本地数据的读取