ResNet在一定程度上解决了过深模型(比如几百甚至上千层)梯度发散导致无法训练的问题,其关键之处在于层间的快速连接。受此启发,能否进一步增加连接,充分利用所有层的特征呢?DenseNet就是这样的模型。
DenseNet结构
DenseNet模块中的核心模块Dense Block如下图所示,相比ResNet的残差模块,DenseNet具有更多的跨层快捷连接,从输入层开始,每层都作为后面各层的输入。
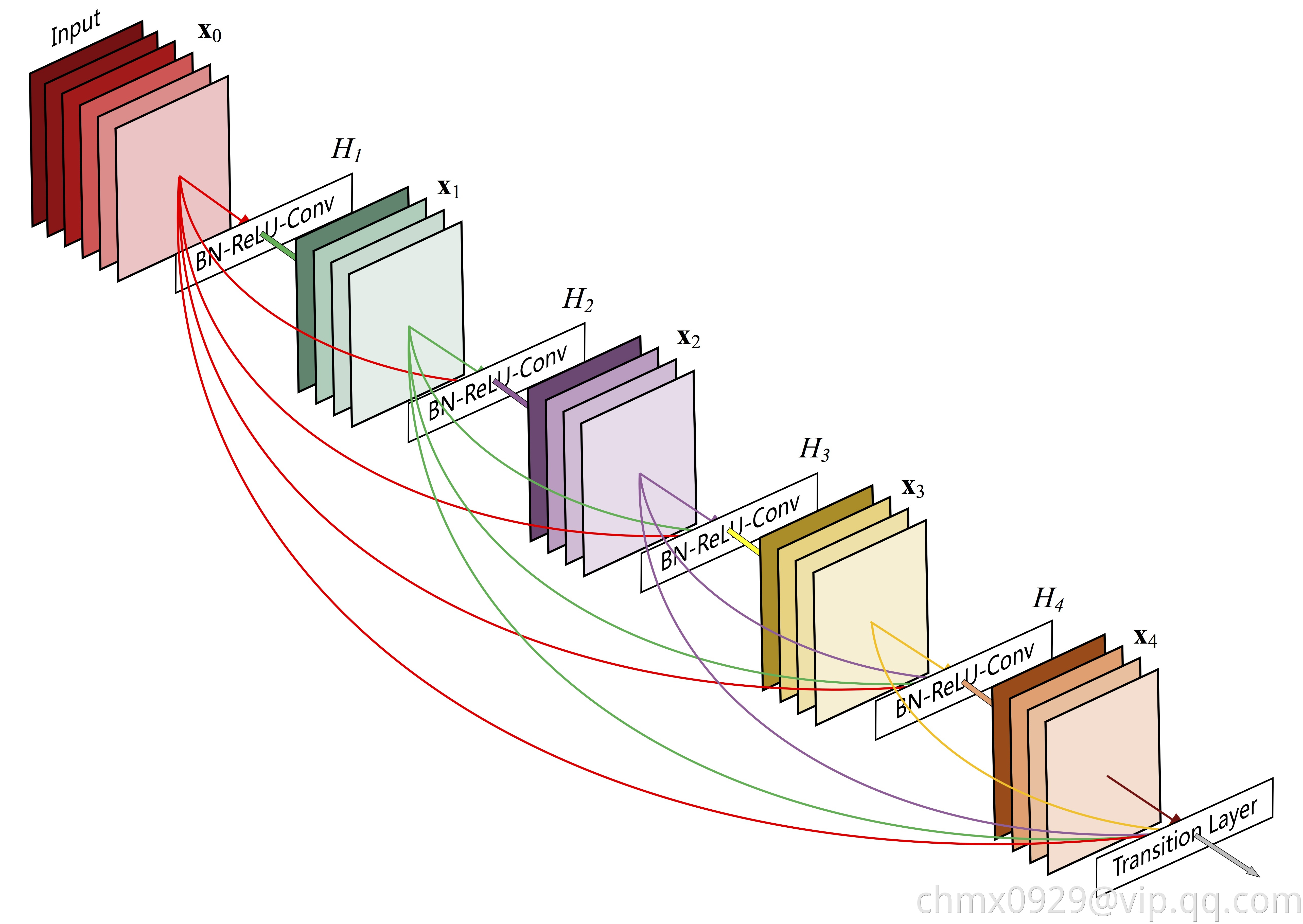
在具体实现上,在ResNet中,第层的输入
经过层的转换函数
后得到对应的输出
,该输出与输入
的线性组合就成了下一层的输入
。即:
而在Dense Block中,第层的新增输入
与之前的所有输入
按照通道拼接在一起组成真正的输入,即
,该输入经过一个Batch Normalization层、ReLU和卷积层得到对应的隐层输出
,该隐层输出就是下一层的新增输入
,即:
再与之前的所有输入拼接为
作为下一层的输入。一般来说,每层新增输入
的通道数量
都很小,在上图中为4,原论文中的模型一般取
。这个新增通道数量
有一个专门的名字叫增长率(Growth Rate)。由于采用这种拼接方式,同时每个隐层特别瘦(即增长率
较小),使得DenseNet看起来连接很密集,但实际参数数量及对应运算量反而较少。DenseNet相比ResNet在性能上有一定的优势,在ImageNet分类数据集上达到同样的准确率,DenseNet的参数数量及运算量可能只需要ResNet的一半左右。
最终的DenseNet由Dense Block以及转换层(Transition Layer)组成,转换层一般由一个Batch Normalization层、卷积核大小为11的卷积层和池化层组成,其中11的卷积主要用于瘦身,即降低通道数量。如下图所示,是包含三个Dense Block的DenseNet模型。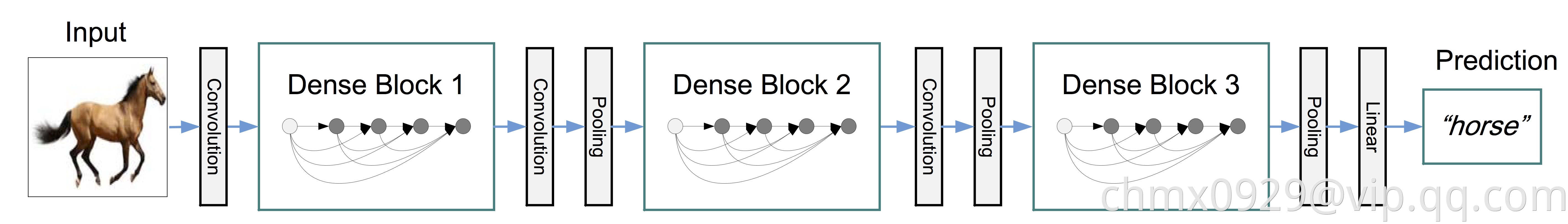
用于ImageNet的DenseNet架构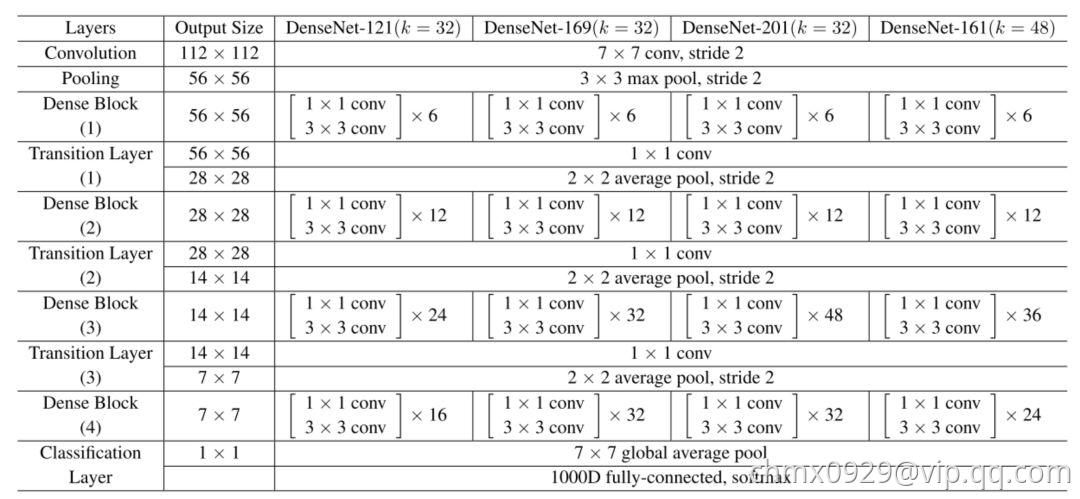
Code实现
def DenseNet121(nb_dense_block=4, growth_rate=32, nb_filter=64, reduction=0.0, dropout_rate=0.0, weight_decay=1e-4, classes=1000, weights_path=None):'''Instantiate the DenseNet 121 architecture,# Argumentsnb_dense_block: number of dense blocks to add to endgrowth_rate: number of filters to add per dense blocknb_filter: initial number of filtersreduction: reduction factor of transition blocks.dropout_rate: dropout rateweight_decay: weight decay factorclasses: optional number of classes to classify imagesweights_path: path to pre-trained weights# ReturnsA Keras model instance.'''eps = 1.1e-5# compute compression factorcompression = 1.0 - reduction# Handle Dimension Ordering for different backendsglobal concat_axisif K.image_dim_ordering() == 'tf':concat_axis = 3img_input = Input(shape=(224, 224, 3), name='data')else:concat_axis = 1img_input = Input(shape=(3, 224, 224), name='data')# From architecture for ImageNet (Table 1 in the paper)nb_filter = 64nb_layers = [6,12,24,16] # For DenseNet-121# Initial convolutionx = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3), name='conv1_zeropadding')(img_input)x = Convolution2D(nb_filter, 7, 7, subsample=(2, 2), name='conv1', bias=False)(x)x = BatchNormalization(epsilon=eps, axis=concat_axis, name='conv1_bn')(x)x = Scale(axis=concat_axis, name='conv1_scale')(x)x = Activation('relu', name='relu1')(x)x = ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), name='pool1_zeropadding')(x)x = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2), name='pool1')(x)# Add dense blocksfor block_idx in range(nb_dense_block - 1):stage = block_idx+2x, nb_filter = dense_block(x, stage, nb_layers[block_idx], nb_filter, growth_rate, dropout_rate=dropout_rate, weight_decay=weight_decay)# Add transition_blockx = transition_block(x, stage, nb_filter, compression=compression, dropout_rate=dropout_rate, weight_decay=weight_decay)nb_filter = int(nb_filter * compression)final_stage = stage + 1x, nb_filter = dense_block(x, final_stage, nb_layers[-1], nb_filter, growth_rate, dropout_rate=dropout_rate, weight_decay=weight_decay)x = BatchNormalization(epsilon=eps, axis=concat_axis, name='conv'+str(final_stage)+'_blk_bn')(x)x = Scale(axis=concat_axis, name='conv'+str(final_stage)+'_blk_scale')(x)x = Activation('relu', name='relu'+str(final_stage)+'_blk')(x)x = GlobalAveragePooling2D(name='pool'+str(final_stage))(x)x = Dense(classes, name='fc6')(x)x = Activation('softmax', name='prob')(x)model = Model(img_input, x, name='densenet')if weights_path is not None:model.load_weights(weights_path)return modeldef conv_block(x, stage, branch, nb_filter, dropout_rate=None, weight_decay=1e-4):'''Apply BatchNorm, Relu, bottleneck 1x1 Conv2D, 3x3 Conv2D, and option dropout# Argumentsx: input tensorstage: index for dense blockbranch: layer index within each dense blocknb_filter: number of filtersdropout_rate: dropout rateweight_decay: weight decay factor'''eps = 1.1e-5conv_name_base = 'conv' + str(stage) + '_' + str(branch)relu_name_base = 'relu' + str(stage) + '_' + str(branch)# 1x1 Convolution (Bottleneck layer)inter_channel = nb_filter * 4x = BatchNormalization(epsilon=eps, axis=concat_axis, name=conv_name_base+'_x1_bn')(x)x = Scale(axis=concat_axis, name=conv_name_base+'_x1_scale')(x)x = Activation('relu', name=relu_name_base+'_x1')(x)x = Convolution2D(inter_channel, 1, 1, name=conv_name_base+'_x1', bias=False)(x)if dropout_rate:x = Dropout(dropout_rate)(x)# 3x3 Convolutionx = BatchNormalization(epsilon=eps, axis=concat_axis, name=conv_name_base+'_x2_bn')(x)x = Scale(axis=concat_axis, name=conv_name_base+'_x2_scale')(x)x = Activation('relu', name=relu_name_base+'_x2')(x)x = ZeroPadding2D((1, 1), name=conv_name_base+'_x2_zeropadding')(x)x = Convolution2D(nb_filter, 3, 3, name=conv_name_base+'_x2', bias=False)(x)if dropout_rate:x = Dropout(dropout_rate)(x)return xdef transition_block(x, stage, nb_filter, compression=1.0, dropout_rate=None, weight_decay=1E-4):''' Apply BatchNorm, 1x1 Convolution, averagePooling, optional compression, dropout# Argumentsx: input tensorstage: index for dense blocknb_filter: number of filterscompression: calculated as 1 - reduction. Reduces the number of feature maps in the transition block.dropout_rate: dropout rateweight_decay: weight decay factor'''eps = 1.1e-5conv_name_base = 'conv' + str(stage) + '_blk'relu_name_base = 'relu' + str(stage) + '_blk'pool_name_base = 'pool' + str(stage)x = BatchNormalization(epsilon=eps, axis=concat_axis, name=conv_name_base+'_bn')(x)x = Scale(axis=concat_axis, name=conv_name_base+'_scale')(x)x = Activation('relu', name=relu_name_base)(x)x = Convolution2D(int(nb_filter * compression), 1, 1, name=conv_name_base, bias=False)(x)if dropout_rate:x = Dropout(dropout_rate)(x)x = AveragePooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name=pool_name_base)(x)return xdef dense_block(x, stage, nb_layers, nb_filter, growth_rate, dropout_rate=None, weight_decay=1e-4, grow_nb_filters=True):''' Build a dense_block where the output of each conv_block is fed to subsequent ones# Argumentsx: input tensorstage: index for dense blocknb_layers: the number of layers of conv_block to append to the model.nb_filter: number of filtersgrowth_rate: growth ratedropout_rate: dropout rateweight_decay: weight decay factorgrow_nb_filters: flag to decide to allow number of filters to grow'''eps = 1.1e-5concat_feat = xfor i in range(nb_layers):branch = i+1x = conv_block(concat_feat, stage, branch, growth_rate, dropout_rate, weight_decay)concat_feat = merge([concat_feat, x], mode='concat', concat_axis=concat_axis, name='concat_'+str(stage)+'_'+str(branch))if grow_nb_filters:nb_filter += growth_ratereturn concat_feat, nb_filter
Source
https://github.com/liuzhuang13/DenseNet
https://www.jiqizhixin.com/articles/042201?from=synced&keyword=resnet
https://www.cnblogs.com/skyfsm/p/8451834.html

