- May. 13 - Start a video uploading and saving app
- May. 14 - Middlewares 101: Authorization, Logging and Debugging
- May. 15 - Data Binding and Validation
- May. 16-17 - HTML, Templates and Multi-Route Grouping
- May. 18-19 - Deployment on AWS with Elastic Beanstalk (bonus: IAM setup)
- !/usr/bin/env bash
- install packages and dependencies
- build command
Homepage of gin: https://gin-gonic.com/
Github page of gin: https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin
The code in this articel is based on and modified from Go Gin Framework Crash Course of Pragmatic Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qR0WnWL2o1Q&list=PL3eAkoh7fypr8zrkiygiY1e9osoqjoV9w
May. 13 - Start a video uploading and saving app
initialize the project:
For golang, we initialize a project by making a directory and move into that directory:
[root@localhost src]# mkdir gin[root@localhost src]# cd gin/
create go.mod and go.sum:
[root@localhost gin]# go mod init gin[root@localhost gin]# go get -u github.com/gin-gonic/gin
create a main server program ‘server.go’ in the same folder to initialize a server using the gin library: ```go package main
import “github.com/gin-gonic/gin”
func main() { server := gin.Default()
//create an endpointserver.GET("/test", func(ctx *gin.Context) {//http code 200 means 'OK'ctx.JSON(200, gin.H{"message": "OK!!",})})server.Run(":9090")
}
to test, use the terminal:```bash[root@localhost gin]# go run server.go[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Creating an Engine instance with the Logger and Recovery middleware already attached.[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production.- using env: export GIN_MODE=release- using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)[GIN-debug] GET /test --> main.main.func1 (3 handlers)[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :9090
use the browser to access “localhost:9090/test”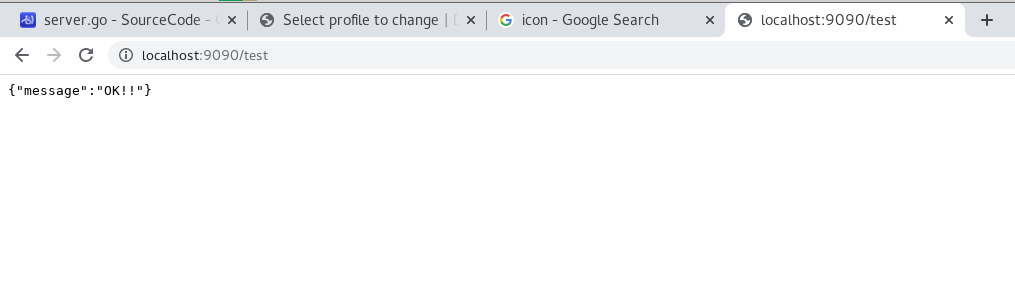
Then we have some response on the terminal as server:
[GIN] 2020/05/13 - 16:49:56 | 200 | 165.343µs | ::1 | GET "/test"
other packages:
- Entity:
- create an “entity” folder
- in “entity”, create “video.go”: ```go package entity
type Video struct {
//json:"XXX" after variable type define the name of the variable shown in JSON
Title string json:"title"
Description string json:"description"
URL string json:"url"
}
- Service:- create a "service" folder- in "service", create "video-service.go":```gopackage servicetype VideoService interface {Save(entity.Video) entity.Video // save the videoFindAll() []entity.Video // return a slice of video}//define "videos" as the list of all videostype videoService struct {videos []entity.Video}//new instancefunc New() VideoService {return &videoService{}}//save a new video in the video listfunc (service *videoService) Save(video entity.Video) entity.Video {service.videos = append(service.videos, video)return video}//find all videos in the listfunc (service *videoService) FindAll() []entity.Video {return service.videos}
- Controller:
- create a “controller” folder
- in “controller”, create “video-controller.go”: ```go package controller
import ( “github.com/gin-gonic/gin” “gin/entity” )
type VideoController interface { FindAll() []entity.Video Save(ctx *gin.Context) entity.Video }
type controller struct { service service.VideoService }
func New(service service.VideoService) VideoController { return &controller{ service: service, } }
//refer to service package func (c *controller) FindAll() []entity.Video { return c.service.FindAll() }
func (c controller) Save(ctx gin.Context) entity.Video { var video entity.Video ctx.BindJSON(&video) c.service.Save(video) return video }
<a name="irH7l"></a>#### change server.go to handle GET and POST:```gopackage mainimport ("github.com/gin-gonic/gin""gin/controller""gin/service")var (videoService service.VideoService = service.New()videoController controller.VideoController = controller.New(videoService))func main() {server := gin.Default()server.GET("/videos", func(ctx *gin.Context) {ctx.JSON(200, videoController.FindAll())})server.POST("/videos", func(ctx *gin.Context) {ctx.JSON(200, videoController.Save(ctx))})server.Run(":9090")}
to test, we use “Postman” (upper square is data, lower square is output)
we send 2 POST requests:

and a GET request: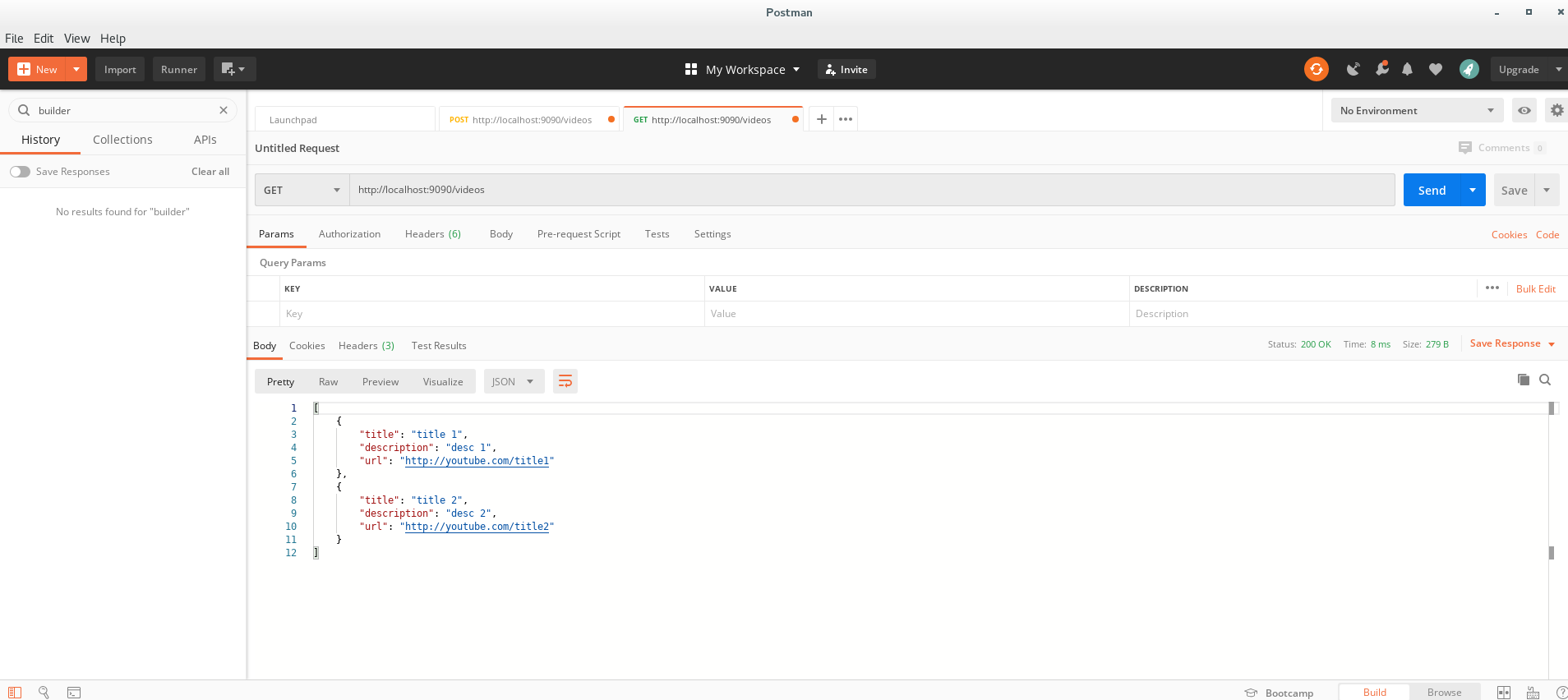
now we see 2 video data information are sent and could be pulled out by POST and GET.
May. 14 - Middlewares 101: Authorization, Logging and Debugging
Customize the server by not using gin.Default():
- we used gin.Default() for server, but we need to customize our server for more methods:
- create a folder (for package) called /middlewares, and in /middlewares, create a “logger.go” to let server print the information about a specific request: ```go // /middlewares/logger.go
package middlewares
import ( “fmt” “time”
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func Logger() gin.HandlerFunc { return gin.LoggerWithFormatter(func(param gin.LogFormatterParams) string { return fmt.Sprintf(“%s - [%s] %s %s %d %s \n”, param.ClientIP, param.TimeStamp.Format(time.RFC822), param.Method, param.Path, param.StatusCode, param.Latency, ) }) }
- apply middlewares package and logger on server.go:```gopackage mainimport ("github.com/gin-gonic/gin""gin/controller""gin/middlewares" //new"gin/service")var (videoService service.VideoService = service.New()videoController controller.VideoController = controller.New(videoService))func main() {//server := gin.Default()server := gin.New() //newserver.Use(gin.Recovery(), middlewares.Logger()) //newserver.GET("/videos", func(ctx *gin.Context) {ctx.JSON(200, videoController.FindAll())})server.POST("/videos", func(ctx *gin.Context) {ctx.JSON(200, videoController.Save(ctx))})server.Run(":9090")}
to test, use the terminal as the server:
[root@localhost gin]# go run server.go[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production.- using env: export GIN_MODE=release- using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)[GIN-debug] GET /videos --> main.main.func1 (3 handlers)[GIN-debug] POST /videos --> main.main.func2 (3 handlers)[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :9090
and send a GET request to http://localhost:9090/videos by using Postman, then server prints the information:
::1 - [14 May 20 13:18 EDT] GET /videos 200 167.528µs::1 - [14 May 20 13:23 EDT] POST /videos 200 115.442µs
- For the first request:
- client ip: 1
- time sent/received: 14 May 20 13:18 EDT
- a GET request
- path is /videos
- status code 200
- latency is 167.528µs
For the first request:
for server.go: ```go package main
import ( “gin/controller” “gin/middlewares” “gin/service” “os” // new “io” // new
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func setupLogOutput() { f, _ := os.Create(“gin.log”) gin.DefaultWriter = io.MultiWriter(f, os.Stdout) }
func main() { setupLogOutput() /… }
we can add those codes to create a gin.log, and put server terminal outputs to this file, until next time the server restarts:<br /><a name="4icdr"></a>#### Authoization:- in /middlewares, add a "basic-auth.go":```gopackage middlewaresimport "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"func BasicAuth() gin.HandlerFunc {return gin.BasicAuth(gin.Accounts{"pragmatic": "reviews",})}
and apply BasicAuth() on server.go:
//...//server.Use(gin.Recovery(), middlewares.Logger())server.Use(gin.Recovery(), middlewares.Logger(), middlewares.BasicAuth())//...
if send requests by Postman as before, we will see that the status code is 401 (unauthorized):
::1 - [14 May 20 15:10 EDT] GET /videos 401 53.656µs::1 - [14 May 20 15:35 EDT] POST /videos 401 4.729µs
to get 200 instead of 401, we will apply the username & password pair before to send the request as an authorized user (“pragmatic”: “reviews”):
::1 - [14 May 20 15:45 EDT] GET /videos 401 4.38µs
- here we extract the code and make it into tester.go: ```go package main
import ( “fmt” “net/http” “io/ioutil” )
func main() {
url := “http://localhost:9090/videos“ method := “GET”
client := &http.Client { } req, err := http.NewRequest(method, url, nil)
if err != nil { fmt.Println(err) } req.Header.Add(“Authorization”, “Basic cHJhZ21hdGljOnJldmlld3M=”) //cHJhZ21hdGljOnJldmlld3M= can be encoded from base 64 format //then we get pragmatic:reviews - the pair of username and password for auth above
res, err := client.Do(req) defer res.Body.Close() body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
fmt.Println(string(body)) }
we can run this tester.go when the server is online, and the result is same as we send request by Postman.<a name="37xUQ"></a>#### gindump:- simply, it's just a package that let server shows more detail about the request:- server.go:```goimport ("gin/controller""gin/middlewares""gin/service""io""os"gindump "github.com/tpkeeper/gin-dump" // new"github.com/gin-gonic/gin")func main() {//...server.Use(gin.Recovery(), middlewares.Logger(), middlewares.BasicAuth(), gindump.Dump())//...}
to test, send a request as before, and the server terminal:
Request-Header:{"Accept": ["*/*"],"Accept-Encoding": ["gzip, deflate, br"],"Authorization": ["Basic cHJhZ21hdGljOnJldmlld3M="],"Connection": ["keep-alive"],"Postman-Token": ["3b60ec66-1f54-441c-99e9-44c9b44fe97c"],"User-Agent": ["PostmanRuntime/7.24.1"]}Response-Header:{"Content-Type": ["application/json; charset=utf-8"]}Response-Body:null::1 - [16 May 20 15:57 EDT] GET /videos 200 387.07µs
May. 15 - Data Binding and Validation
BindJSON to ShouldBindJSON:
a slient change on video-controller.go in controller package:
//...type VideoController interface {FindAll() []entity.VideoSave(ctx *gin.Context) error}//...func (c *controller) Save(ctx *gin.Context) error { //entity.Videovar video entity.Video//ctx.BindJSON(&video)err := ctx.ShouldBindJSON(&video) //will only return error, not return status code 400if err != nil {return err}c.service.Save(video)return nil}
Entity binding:
a video should have an author
- we add a Person struct in entity package, video.go and assign it to Video struct: ```go package entity
type Person struct {
FirstName string json:"firstname"
LastName string json:"lastname"
Age uint8 json:"age"
Email string json:"email"
}
type Video struct {
Title string json:"title"
Description string json:"description"
URL string json:"url"
Author Person json:"author"
}
- also, we can apply **binding** for variables inside those structs if necessary:```go// /entity/video.gopackage entitytype Person struct {FirstName string `json:"firstname" binding:"required"` // must haveLastName string `json:"lastname" binding:"required"` // must haveAge uint8 `json:"age" binding:"gte=0,lte=130"` // age >= 0, <= 130Email string `json:"email" binding:"required,email"` // must have, and format should be email}type Video struct {Title string `json:"title" binding:"min=2,max=10"` // 2-10 charactersDescription string `json:"description" binding:"max=20"` // at most 20 charactersURL string `json:"url" binding:"required,url"` // must have, and format should be urlAuthor Person `json:"author" binding:"required"` // must have}
- modify server.go to return different JSON message: ```go package main
import ( “gin/controller” “gin/middlewares” “gin/service” “io” “net/http” //new “os”
gindump "github.com/tpkeeper/gin-dump""github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
//…
func main() {
//...server.POST("/videos", func(ctx *gin.Context) {err := videoController.Save(ctx)if err != nil {ctx.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})} else {ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "Video Input is valid"})}})server.Run(":9090")
}
to test, send POST request (or course, from an authorized user):```json{"title" : "title","description" : "desc","url" : "http://youtube.com/title2","author" : {"firstname" : "K","lastname" : "R","age" : 22,"email" : "KR@gmail.com"}}
# server terminalResponse-Body:{"message": "Video Input is valid"}::1 - [15 May 20 08:57 EDT] POST /videos 200 219.004µs
and we send some other invalid requests:
{"title" : "title","description" : "desc","url" : "http://youtube.com/title2","author" : {"firstname" : "K","lastname" : "R","age" : 200,"email" : "KR@gmail.com"}}{"title" : "title","description" : "desc","url" : "http://youtube.com/title2","author" : {"firstname" : "K","lastname" : "R","age" : 22,"email" : "KRgmail.com"}}{"title" : "22222222222222222222222222222222","description" : "desc","url" : "http://youtube.com/title2","author" : {"firstname" : "K","lastname" : "R","age" : 22,"email" : "KRgmail.com"}}
# server terminalResponse-Body:{"error": "Key: 'Video.Author.Age' Error:Field validation for 'Age' failed on the 'lte' tag"}::1 - [15 May 20 09:04 EDT] POST /videos 400 332.862µsResponse-Body:{"error": "Key: 'Video.Author.Email' Error:Field validation for 'Email' failed on the 'email' tag"}::1 - [15 May 20 09:05 EDT] POST /videos 400 398.871µsResponse-Body:{"error": "Key: 'Video.Title' Error:Field validation for 'Title' failed on the 'max' tag\nKey: 'Video.Author.Email' Error:Field validation for 'Email' failed on the 'email' tag"}::1 - [15 May 20 09:07 EDT] POST /videos 400 763.254µs
Entity validation:
- for this section, we need a /validators package and a validators.go: ```go package validators
import ( “strings”
"gopkg.in/go-playground/validator.v9"
)
// ValidateCoolTitle - return true if the field value contains the word “cool”. func ValidateCoolTitle(fl validator.FieldLevel) bool { return strings.Contains(fl.Field().String(), “Cool”) }
- apply it in video-controller:```gopackage controllerimport ("gin/entity""gin/service""gin/validators" //new"github.com/gin-gonic/gin""gopkg.in/go-playground/validator.v9" //new)//...var validate *validator.Validate //newfunc New(service service.VideoService) VideoController {validate = validator.New() //newvalidate.RegisterValidation("is-cool", validators.ValidateCoolTitle) //newreturn &controller{service: service,}}//...func (c *controller) Save(ctx *gin.Context) error {var video entity.Videoerr := ctx.ShouldBindJSON(&video)if err != nil {return err}//newerr = validate.Struct(video)if err != nil {return err}c.service.Save(video)return nil}//...
- and add is-cool validate after title in /entity/video.go: ```go package entity
type Person struct {
FirstName string json:"firstname" binding:"required" // must have
LastName string json:"lastname" binding:"required" // must have
Age uint8 json:"age" binding:"gte=0,lte=130" // age >= 0, <= 130
Email string json:"email" binding:"required,email" // must have, and format should be email
}
type Video struct {
Title string json:"title" binding:"min=2,max=10" validate:"is-cool" // 2-10 characters, includes the word “Cool”
Description string json:"description" binding:"max=20" // at most 20 characters
URL string json:"url" binding:"required,url" // must have, and format should be url
Author Person json:"author" binding:"required" // must have
}
to test, again send different POST requests:<br />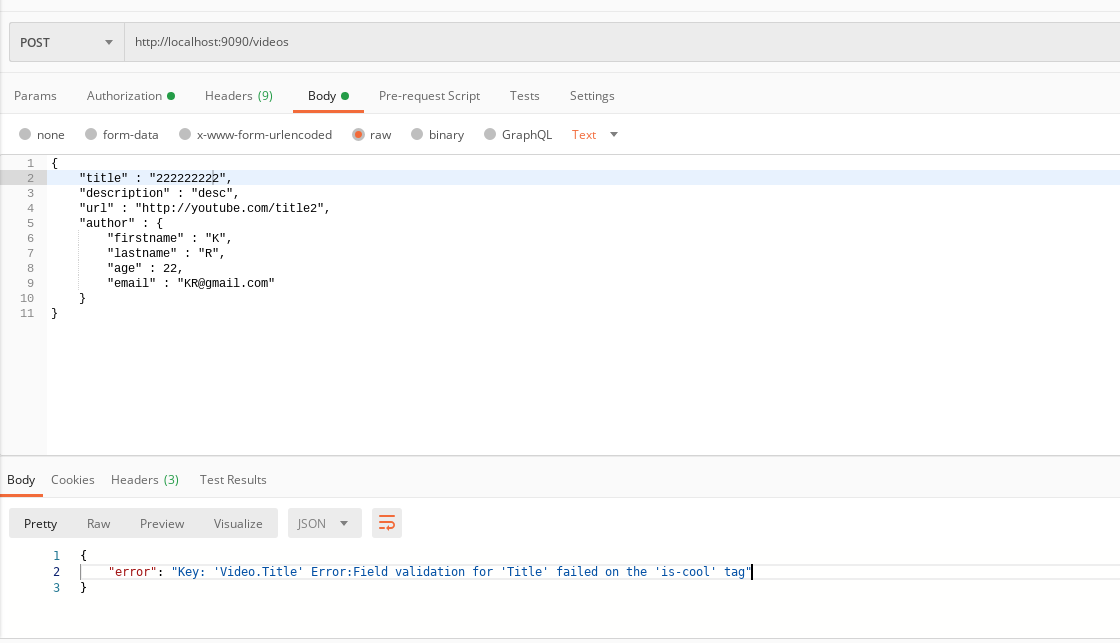```json{"title" : "222222222","description" : "desc","url" : "http://youtube.com/title2","author" : {"firstname" : "K","lastname" : "R","age" : 22,"email" : "KR@gmail.com"}}{"title" : "2222Cool","description" : "desc","url" : "http://youtube.com/title2","author" : {"firstname" : "K","lastname" : "R","age" : 22,"email" : "KR@gmail.com"}}
get:
# server terminalResponse-Body:{"error": "Key: 'Video.Title' Error:Field validation for 'Title' failed on the 'is-cool' tag"}::1 - [15 May 20 14:32 EDT] POST /videos 400 292.831µsResponse-Body:{"message": "Video Input is valid"}::1 - [15 May 20 14:33 EDT] POST /videos 200 231.704µs
May. 16-17 - HTML, Templates and Multi-Route Grouping
- First, we need a folder for templates package, so create /templates
- then create 3 separate parts:
- header.html
- footer.html
- index.html ```html
<!DOCTYPE html>
html
```html<!--index.html-->{{ template "header.html" .}}{{ template "footer.html" .}}
and in /templates, create /css/index.css for formats later.
Separate apiRoutes and fieldRoutes:
- add a ShowAll() function in /controller/video-controller.go: ```go package controller
import ( “gin/entity” “gin/service” “gin/validators” “net/http” // new
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin""gopkg.in/go-playground/validator.v9"
)
type VideoController interface { FindAll() []entity.Video Save(ctx gin.Context) error ShowAll(ctx gin.Context) // new } /… func (c controller) ShowAll(ctx gin.Context) { // new videos := c.service.FindAll() data := gin.H{ “title”: “Video Page”, “videos”: videos, } ctx.HTML(http.StatusOK, “index.html”, data) }
- apply ShowAll(), css file and add apiRoutes/fieldRoutes in server.go:```gopackage mainimport ("gin/controller""gin/middlewares""gin/service""io""net/http" //new"os"gindump "github.com/tpkeeper/gin-dump""github.com/gin-gonic/gin")//...func main() {setupLogOutput()server := gin.New()server.Static("/css", "./templates/css")server.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*.html")apiRoutes := server.Group("/api"){server.Use(gin.Recovery(), middlewares.Logger(), middlewares.BasicAuth(), gindump.Dump())//server.GET("/videos", func(ctx *gin.Context) {apiRoutes.GET("/videos", func(ctx *gin.Context) {ctx.JSON(200, videoController.FindAll())})//server.POST("/videos", func(ctx *gin.Context) {apiRoutes.POST("/videos", func(ctx *gin.Context) {err := videoController.Save(ctx)if err != nil {ctx.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})} else {ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "Video Input is valid"})}})}viewRoutes := server.Group("/view"){viewRoutes.GET("/videos", videoController.ShowAll)}server.Run(":9090")}
loop in index.html:
- create a loop to show all contents of the video list (use range) ```html {{ template “header.html” .}}
{{range .videos }}
{{.Title}}
{{.Description}}
{{end}}
{{ template “footer.html” .}}
- before testing, make the title and description can include more letters (/entity/video.go):```go//...type Video struct {//Title string `json:"title" binding:"min=2,max=10" validate:"is-cool"`Title string `json:"title" binding:"min=2,max=200" validate:"is-cool"`//Description string `json:"description" binding:"max=20"`Description string `json:"description" binding:"max=200"`//...}//...
to test, use Postman to send GET/POST requests,
this time use the url localhost:9090/api/videos: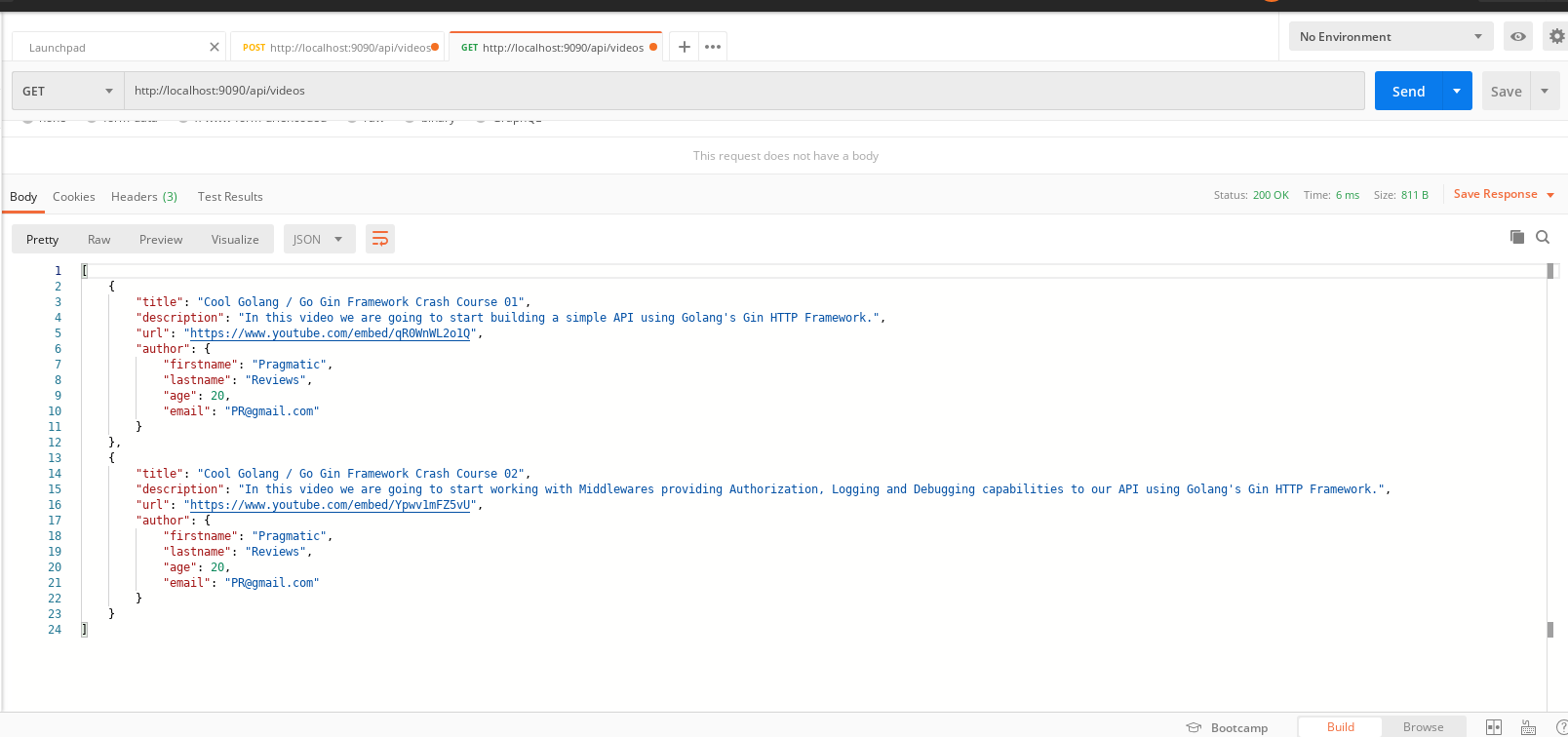
and we use localhost:9090/view/videos in a browser: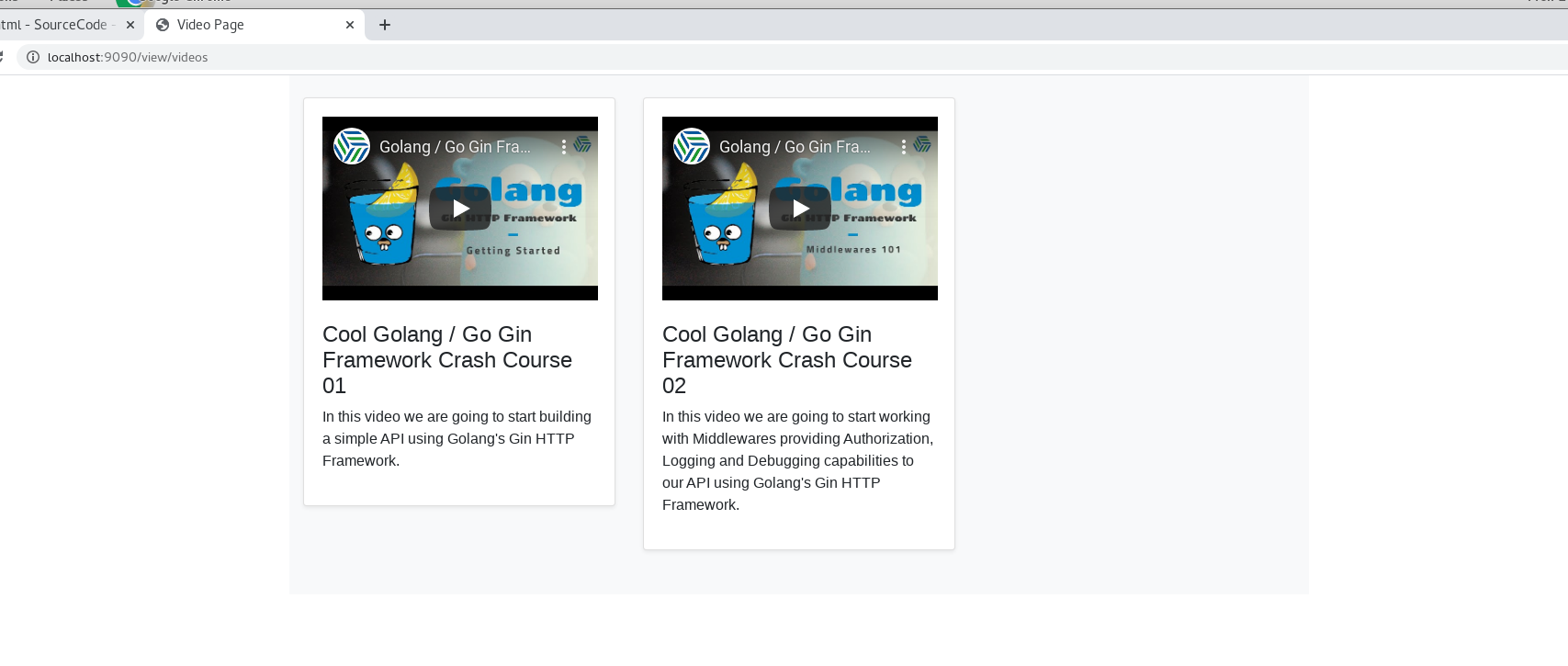
now we have a video collection browser, it even can play the video.
About embedded youtube videos:
Hint: to upload youtube video as an embedded version, the upload format is:
https://www.youtube.com/embed/[video_id]
**
May. 18-19 - Deployment on AWS with Elastic Beanstalk (bonus: IAM setup)
AWS Preparation:
About AWS Elastic Beanstalk:
- a developer-friendly platform to platform to deploy and scale web applications
- support golang, node.js, python, etc.
About IAM:
“AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a web service that helps you securely control access to AWS resources.”
To use AWS, we first need to create an AWS account.
- After that, sign into AWS Management Console:

Choose “IAM”: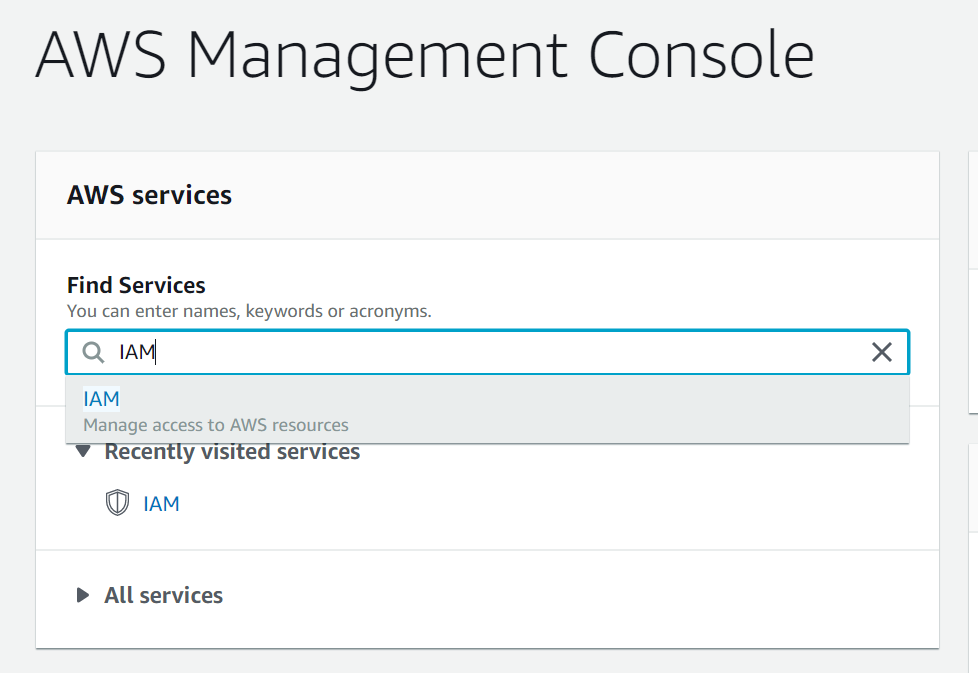
Choose “Policies” and find “AWSElasticBeanstalkFullAccess”:
and we can find a JSON file:
{"Version": "2012-10-17","Statement": [{"Effect": "Allow","Action": ["elasticbeanstalk:*","ec2:*","ecs:*","ecr:*","elasticloadbalancing:*","autoscaling:*","cloudwatch:*","s3:*","sns:*","cloudformation:*","dynamodb:*","rds:*","sqs:*","logs:*","iam:GetPolicyVersion","iam:GetRole","iam:PassRole","iam:ListRolePolicies","iam:ListAttachedRolePolicies","iam:ListInstanceProfiles","iam:ListRoles","iam:ListServerCertificates","acm:DescribeCertificate","acm:ListCertificates","codebuild:CreateProject","codebuild:DeleteProject","codebuild:BatchGetBuilds","codebuild:StartBuild"],"Resource": "*"},{"Effect": "Allow","Action": ["iam:AddRoleToInstanceProfile","iam:CreateInstanceProfile","iam:CreateRole"],"Resource": ["arn:aws:iam::*:role/aws-elasticbeanstalk*","arn:aws:iam::*:instance-profile/aws-elasticbeanstalk*"]},{"Effect": "Allow","Action": ["iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole"],"Resource": ["arn:aws:iam::*:role/aws-service-role/autoscaling.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForAutoScaling*"],"Condition": {"StringLike": {"iam:AWSServiceName": "autoscaling.amazonaws.com"}}},{"Effect": "Allow","Action": ["iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole"],"Resource": ["arn:aws:iam::*:role/aws-service-role/elasticbeanstalk.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForElasticBeanstalk*"],"Condition": {"StringLike": {"iam:AWSServiceName": "elasticbeanstalk.amazonaws.com"}}},{"Effect": "Allow","Action": ["iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole"],"Resource": ["arn:aws:iam::*:role/aws-service-role/elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForElasticLoadBalancing*"],"Condition": {"StringLike": {"iam:AWSServiceName": "elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com"}}},{"Effect": "Allow","Action": ["iam:AttachRolePolicy"],"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::*:role/aws-elasticbeanstalk*","Condition": {"StringLike": {"iam:PolicyArn": ["arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AWSElasticBeanstalk*","arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSElasticBeanstalk*"]}}}]}
back to the previous page, click “Create Policy”: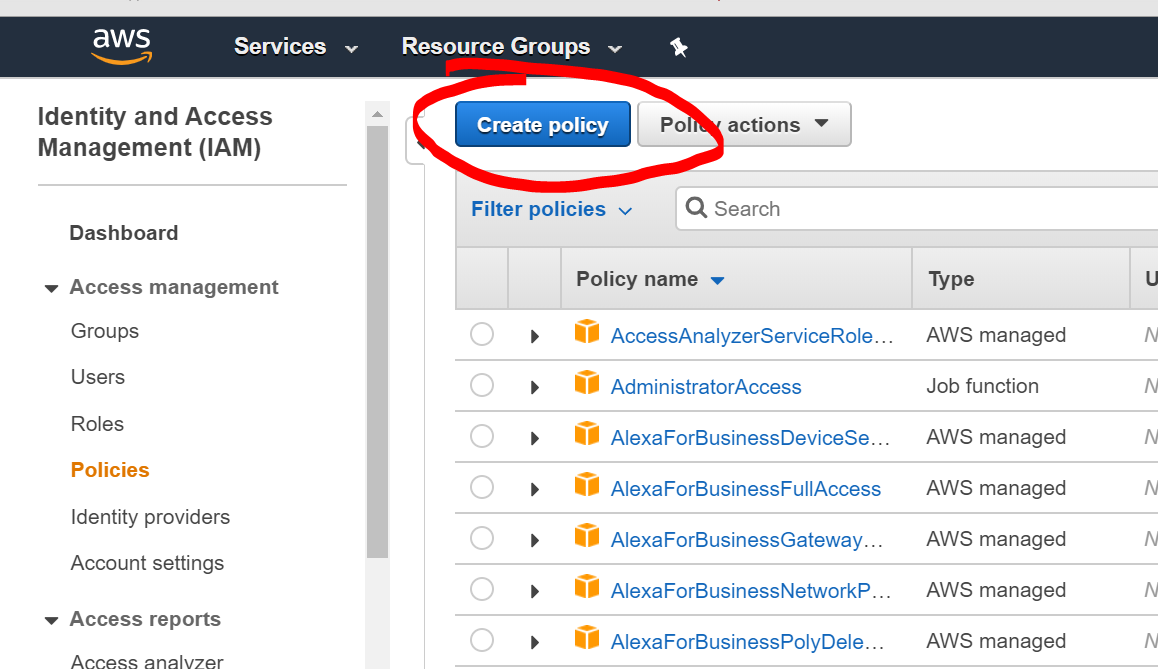
we copy the previous JSON file into it but remove “dynamodb:“, “rds:“, “sqs:*”,
set the name as “eb-deploy”
- Click “Create New Group” called eb-deploy and include that eb-deploy policy before:
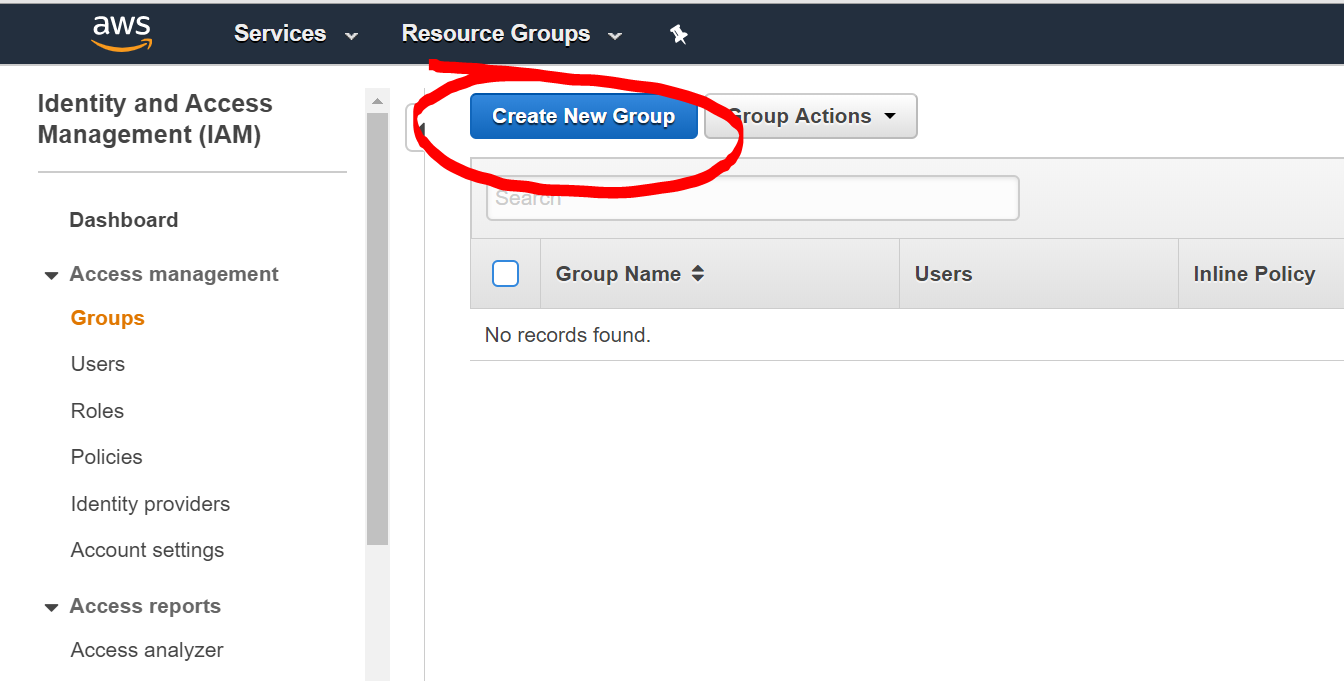
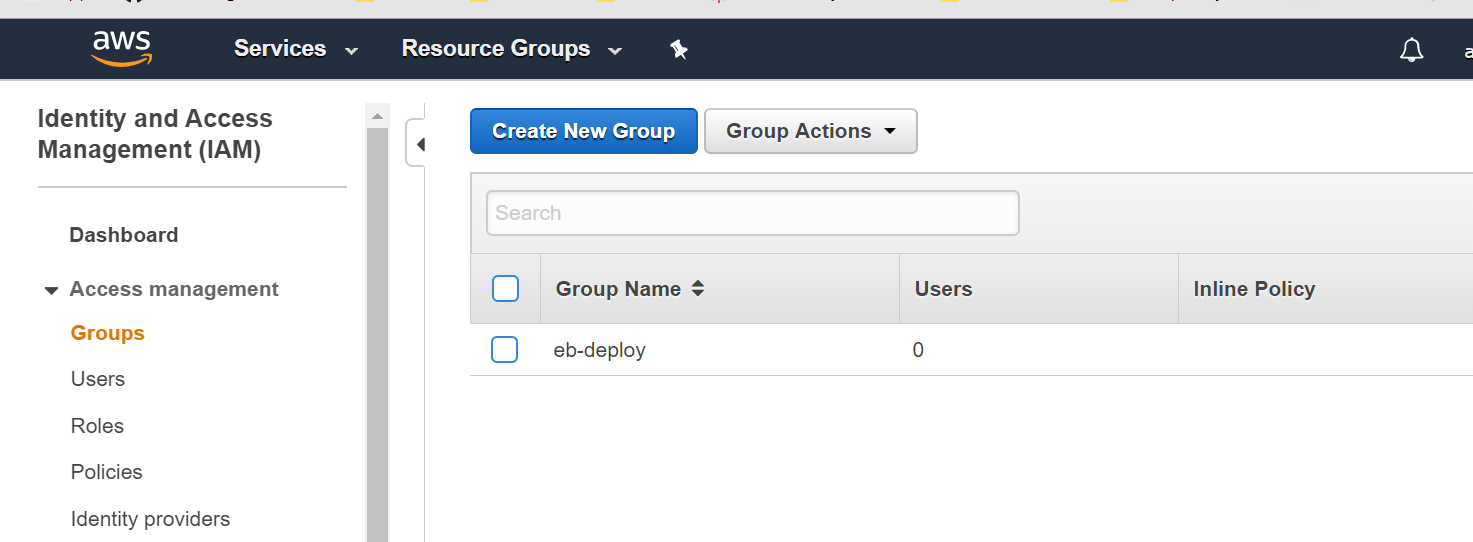
- Create a new user and include that user into the group before:
Default port:
For later requests might not add a port number, so we need to modify server.go for a default port:
//...func main() {//...port := os.Getenv("PORT")if port == "" {port = "9090"}//server.Run(":9090")server.Run(":" + port)}
Deploy golang app without using Docker:
Create a “build.sh” shell file in /gin: ```bash
!/usr/bin/env bash
set -xe
install packages and dependencies
go get github.com/gin-gonic/gin
go get gopkg.in/go-playground/validator.v9
build command
go build -o bin/application server.go
- Also we need a "Buildfile" in /gin to apply build.sh:
make: ./build.sh
- Finally, a "Procfile" in /gin to run web application:
web: bin/application
<a name="3zc8B"></a>### May. 20<a name="AaqA5"></a>#### install aws-elastic-beanstalk-cli:- aws-elastic-beanstalk-cli (a.k.a. "eb")- how to install it varies depends on your operating systems- [https://github.com/aws/aws-elastic-beanstalk-cli-setup](https://github.com/aws/aws-elastic-beanstalk-cli-setup) includes the process, I applied:```bashgit clone https://github.com/aws/aws-elastic-beanstalk-cli-setup.git# install dependenciesyum group install "Development Tools"yum install \zlib-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel libffi-devel \sqlite-devel.x86_64 readline-devel.x86_64 bzip2-devel.x86_64./aws-elastic-beanstalk-cli-setup/scripts/bundled_installer# ensure `eb` is in PATHecho 'export PATH="/root/.ebcli-virtual-env/executables:$PATH"' >> ~/.bash_profile && source ~/.bash_profile# ensure `python` is in PATHecho 'export PATH=/root/.pyenv/versions/3.7.2/bin:$PATH' >> /root/.bash_profile && source /root/.bash_profile
Apply policies:
in users/security credenitals, “Create Access Key” and download the corresponding csv file for keypairs we need.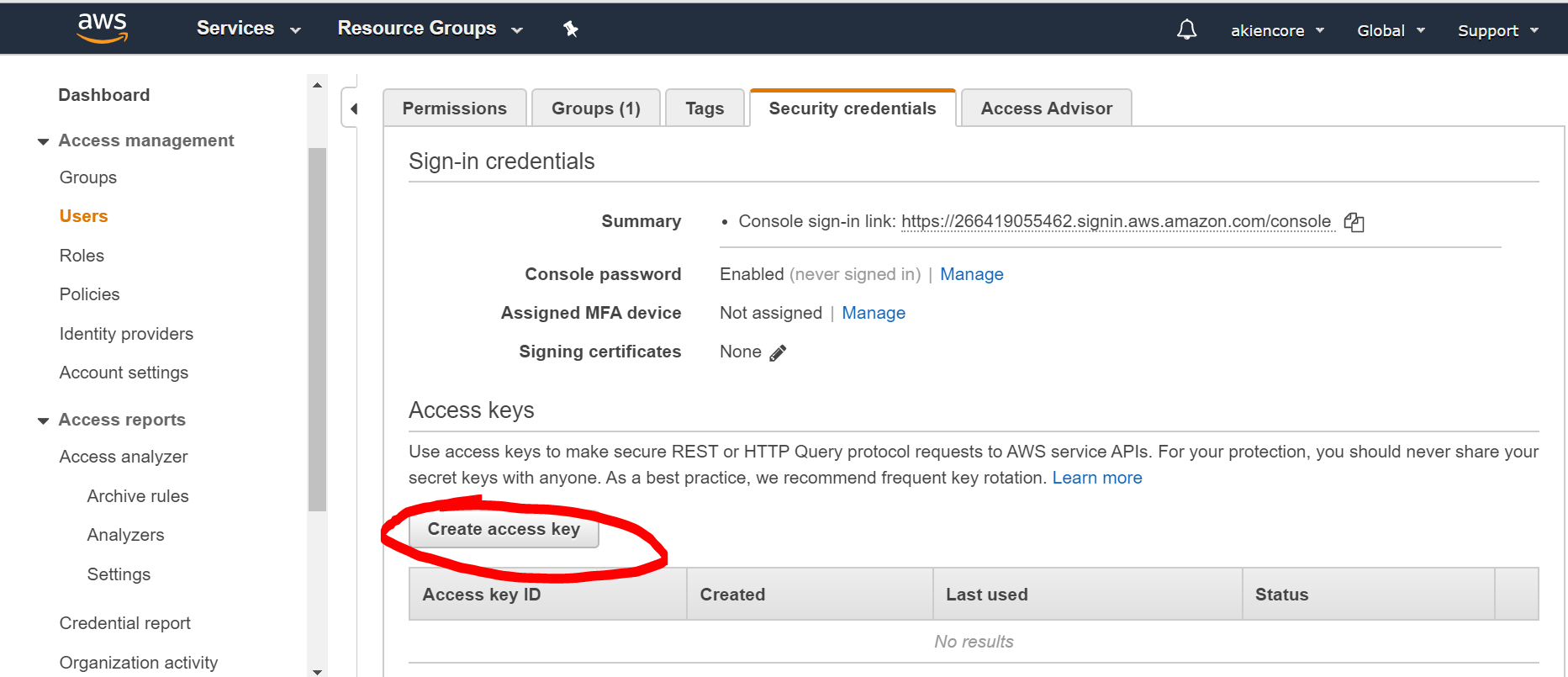

The .csv file looks like:
Access key ID,Secret access key[Access key ID string],[Secret access key string]
- in the terminal, use: ```bash [root@localhost Downloads]# eb init
Select a default region 1) us-east-1 : US East (N. Virginia) 2) us-west-1 : US West (N. California) 3) us-west-2 : US West (Oregon) 4) eu-west-1 : EU (Ireland) 5) eu-central-1 : EU (Frankfurt) 6) ap-south-1 : Asia Pacific (Mumbai) 7) ap-southeast-1 : Asia Pacific (Singapore) 8) ap-southeast-2 : Asia Pacific (Sydney) 9) ap-northeast-1 : Asia Pacific (Tokyo) 10) ap-northeast-2 : Asia Pacific (Seoul) 11) sa-east-1 : South America (Sao Paulo) 12) cn-north-1 : China (Beijing) 13) cn-northwest-1 : China (Ningxia) 14) us-east-2 : US East (Ohio) 15) ca-central-1 : Canada (Central) 16) eu-west-2 : EU (London) 17) eu-west-3 : EU (Paris) 18) eu-north-1 : EU (Stockholm) 19) eu-south-1 : EU (Milano) 20) ap-east-1 : Asia Pacific (Hong Kong) 21) me-south-1 : Middle East (Bahrain) 22) af-south-1 : Africa (Cape Town) (default is 3): 1
The most suitable region can be found by using ping resultsChoose the one address with the least latency here: [https://www.cloudping.info/](https://www.cloudping.info/)Then, the terminal will ask for the keypair before:```bashYou have not yet set up your credentials or your credentials are incorrectYou must provide your credentials.(aws-access-id): [Access key ID string](aws-secret-key): [Secret access key string]
Then, language and other settings:
Select an application to use1) golang-api2) [ Create new Application ](default is 2): 1Select a platform.1) .NET on Windows Server2) Docker3) GlassFish4) Go5) Java6) Node.js7) PHP8) Packer9) Python10) Ruby11) Tomcat(make a selection): 4Select a platform branch.1) Go 1 running on 64bit Amazon Linux 22) Go 1 running on 64bit Amazon Linux3) Preconfigured Docker - Go 1.4 running on 64bit Debian (Deprecated)4) Preconfigured Docker - Go 1.3 running on 64bit Debian (Deprecated)(default is 1): 1Cannot setup CodeCommit because there is no Source Control setup, continuing with initializationDo you want to set up SSH for your instances?(Y/n): n
now we have a .elasticbeanstalk/config.yml:
branch-defaults:default:environment: nullglobal:application_name: golang-apibranch: nulldefault_ec2_keyname: nulldefault_platform: Go 1 running on 64bit Amazon Linux 2default_region: us-east-1include_git_submodules: trueinstance_profile: nullplatform_name: nullplatform_version: nullprofile: eb-clirepository: nullsc: nullworkspace_type: Application
- and create the app with that setting
create in Linux met unexpected error, so I was trying to use browser:eb create --single

unsuccessful, there is a hidden problem
—————————————————————————————————————————————————


