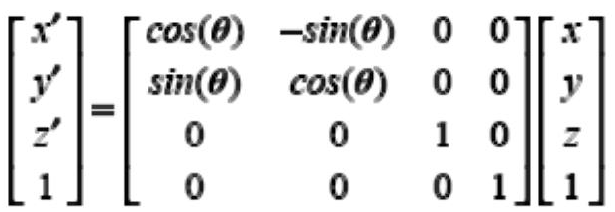Perspective Projection:
Perspective Projection Equations:
Coordinate Rotation and Translation:
2D coordinate rotation and transformation: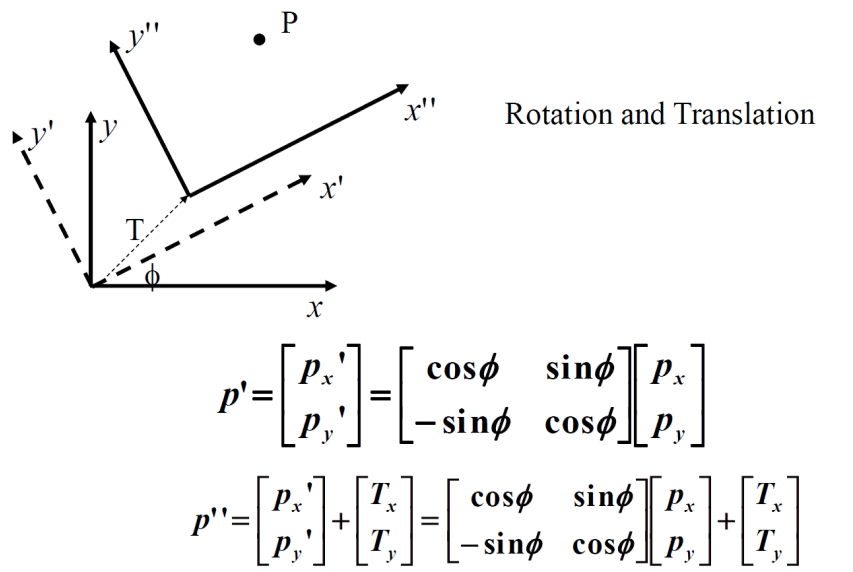
2D coordinate transformation using Homogeneous Coordinates: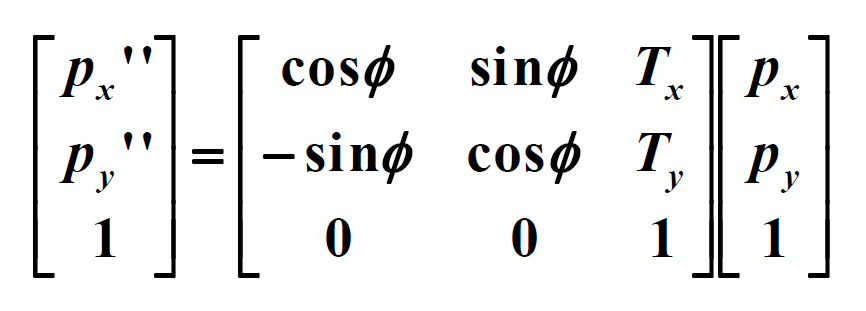
**
Homogeneous Coordinates:
translations with HC:
scalings with HC:
rotation with HC:
w:
3D Rotation:
3D Rotation in homogeneous coordinates:
X-axis:
Y-axis:
Z-axis:
combine the 3 rotations:
inversions of 3D rotation matrix:
so that
Also,
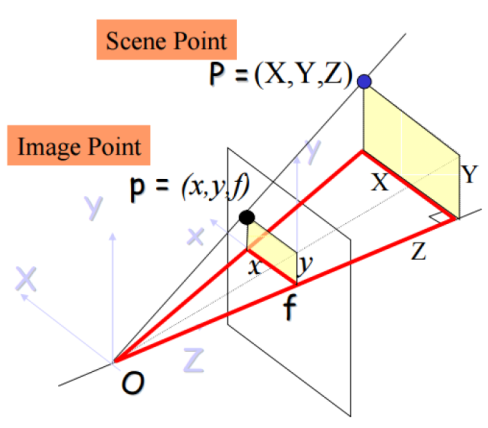
Perspective Projection:
2 methods:
- Transformation
- N dim to N dim
- Projection
- N dim to M dim
and we seek a transformation matrix in:
using homogenous coordinate, we have a linear relation:
so that
Perspective Projection Matrix:
(using homogeneous coordinates)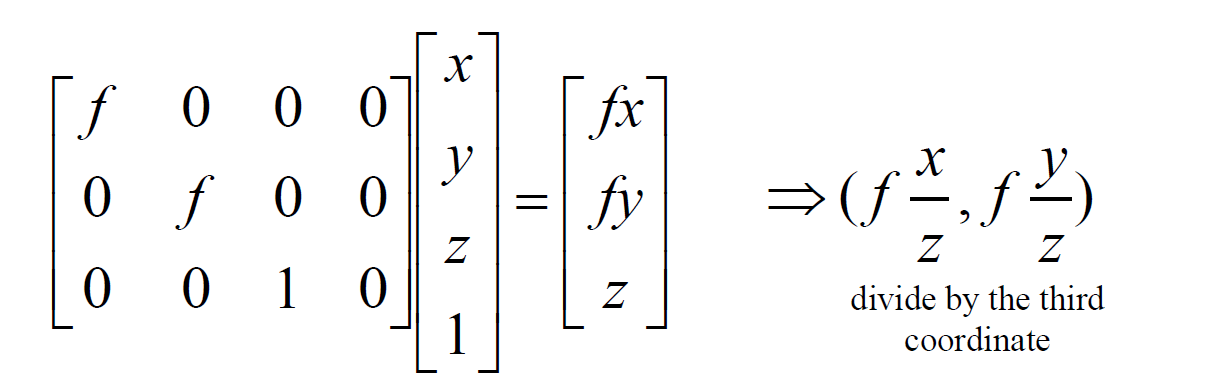
World to camera transformation:
Transform coordinations, R is based on from Pw to Pc.
(w = world, c = camera)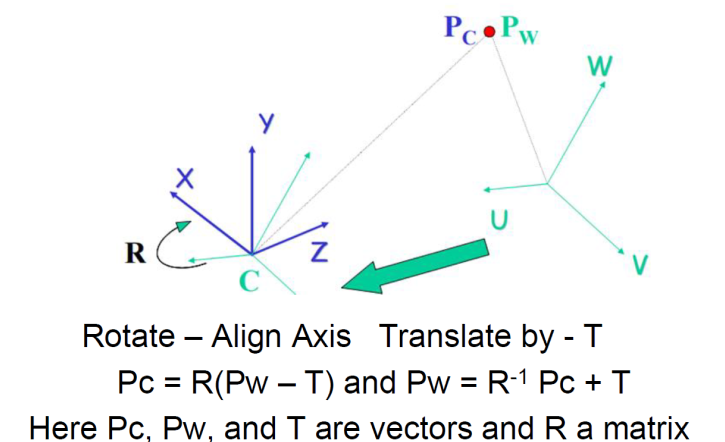
(Pc and Pw are from the same point)
World to Camera Coordinate Transformation Matrix:
R is 3D rotation matrix,
C is a vector of camera position in world frame
for example, this matrix looks like:
Then the corresponding transformation from world coordinates to camera coordinates is: 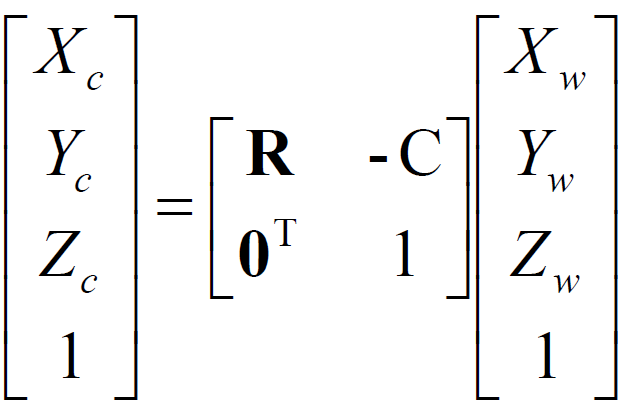
Camera Coordinates to Image Coordinates Matrix:
: pixel sizes in mm per pixel

and the camera calibration matrix is:
- x, y are in pixels, so
are in millimeters/pixel
- f is in millimeters
are in pixels

- Image co-ordinates are in pixels
- Camera co-ordinates are in millimetres
In/Extrinsic Parameters:
- Extrinsic parameters define the location and orientation of the world reference frame with respect to the camera reference frame
- Intrinsic parameters link pixel co-ordinates in the image with the corresponding co-ordinates in the camera reference frame
Parameters in K are intrinsic camera parameters.
[R -C] has extrinsic camera parameters.
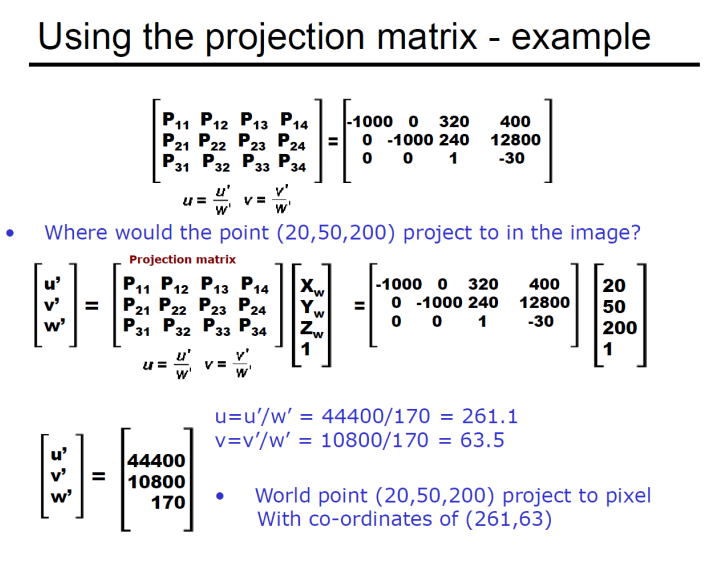
Projection matrix:
It maps 3d points to the appropriate image coordinates in pixels
example: 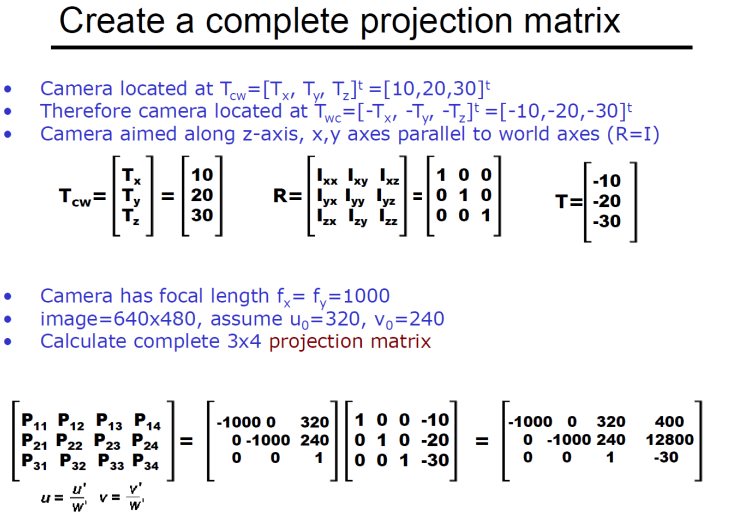
Weak Perspective Model / Orthography:
If the distance between any 2 points in an object is much smaller (1/20 at most) at most than the average distance of the object ()
The camera projection can be approximated as:
(simply is to approximate the coordinate with a approximate average Z value)
This method can simplify some mathematics.
Image distortion due to optics:
Radial Distortion:
depends on radius r, there is radial distortion from center of image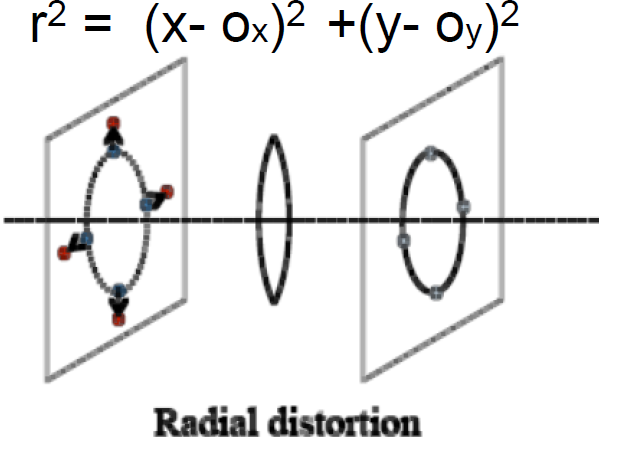
Error is proportional to distance of pixel from the camera center (the radius of the point)
Tangential Distortion:
(Ox, Oy) – center of projection is not the center of image
Reference:
- wikipedia
- https://www.tomdalling.com/blog/modern-opengl/explaining-homogenous-coordinates-and-projective-geometry/
- handout of COMP4102: Introduction to Computer Vision from Carleton University School of Computer Science, 2019