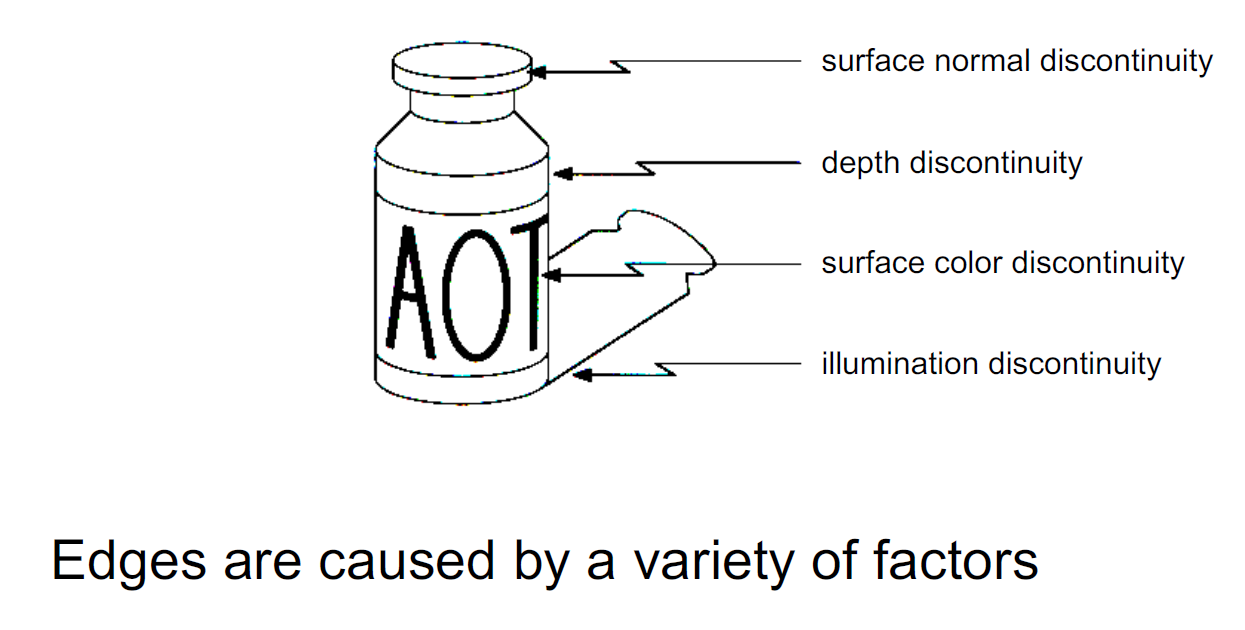
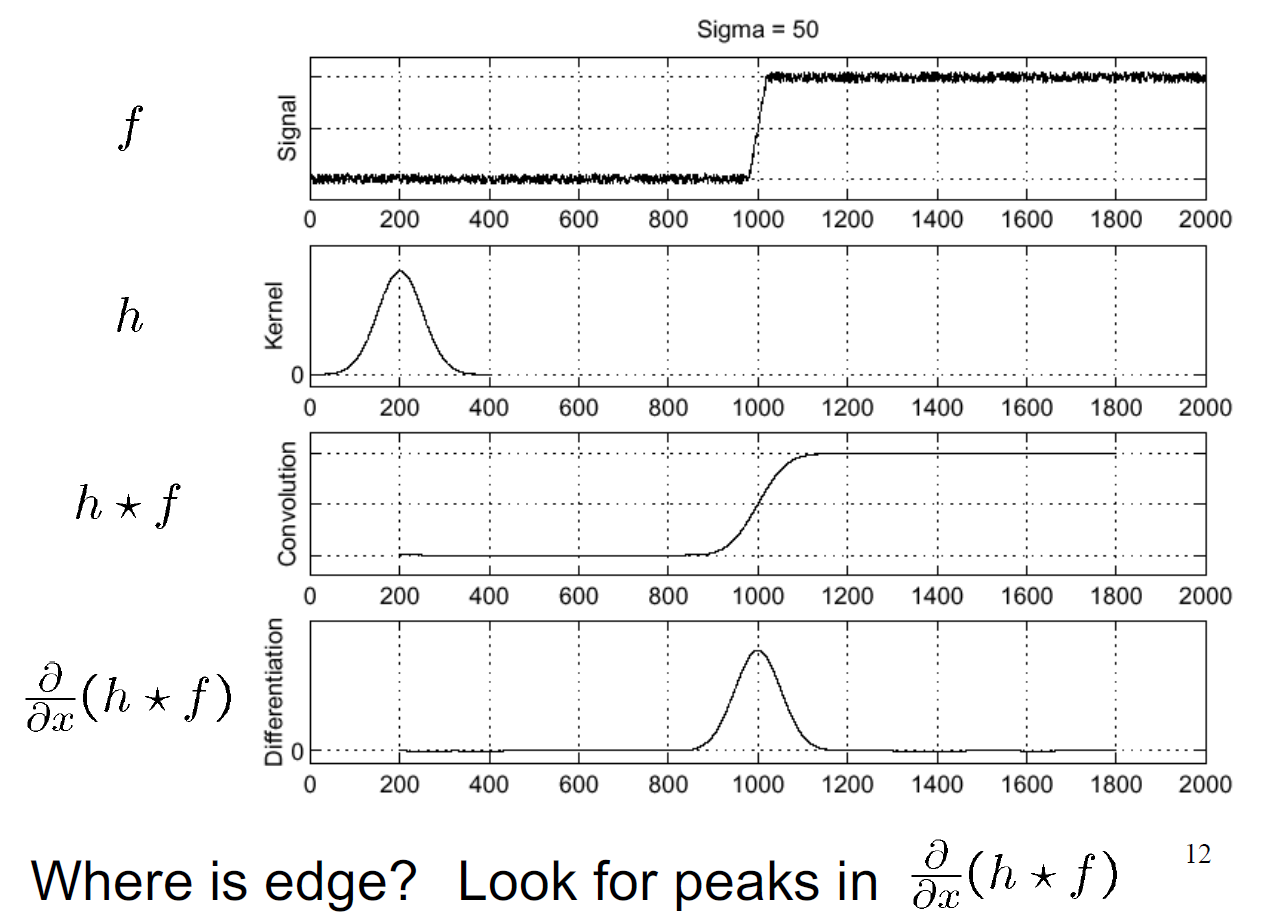
Edges:
- a image feature
- shouble be invariant to changes in the image
- local, meaningful, detectable part
- Definition: significant local changes of intensity in an image
- typically occur on the boundary between 2 different regions in an image
Invariant features:
- the features that have only little changes after changes of particular conditions
- possible cases:
- Change scale, move camera closer or farther
- Change viewpoint, a number of possibilities
- Rotate the object being viewed in the camera plane
- Rotate the object being viewed out of the camera plane
- Translate the object being viewed
- Change the lighting (darker, lighter, shadows, etc.)
- If we can use this feature to distinguish or classify objects, then it must be discriminatory
- all speed limit signs have the same shape and color
Edge Detection:
3 steps:
- Noise smoothing to make the noise does not affect the true edges
- Edge enhancement to filter edges
- Edge localization to decide which local maxima in the filters output are edges
use derivatives to do edge detection:
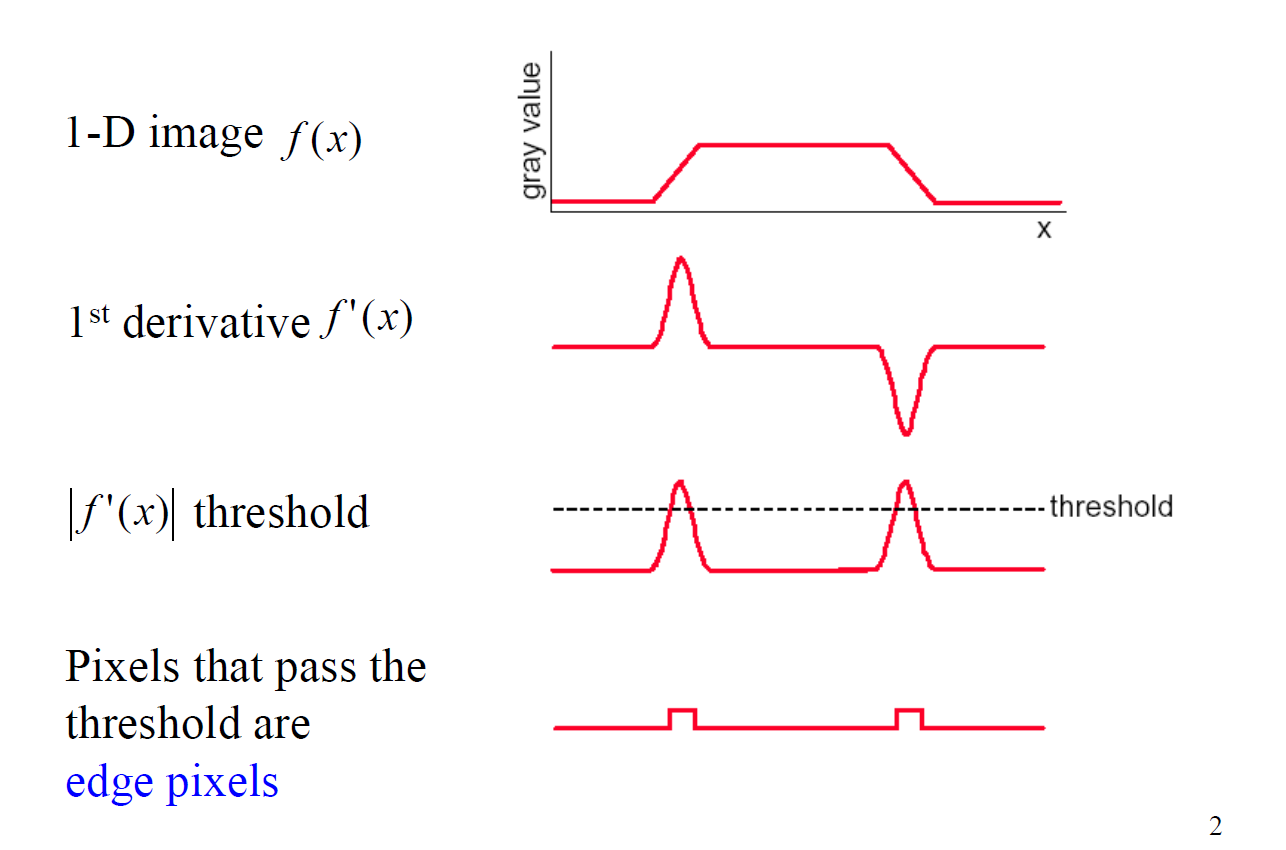
Image Gradient:
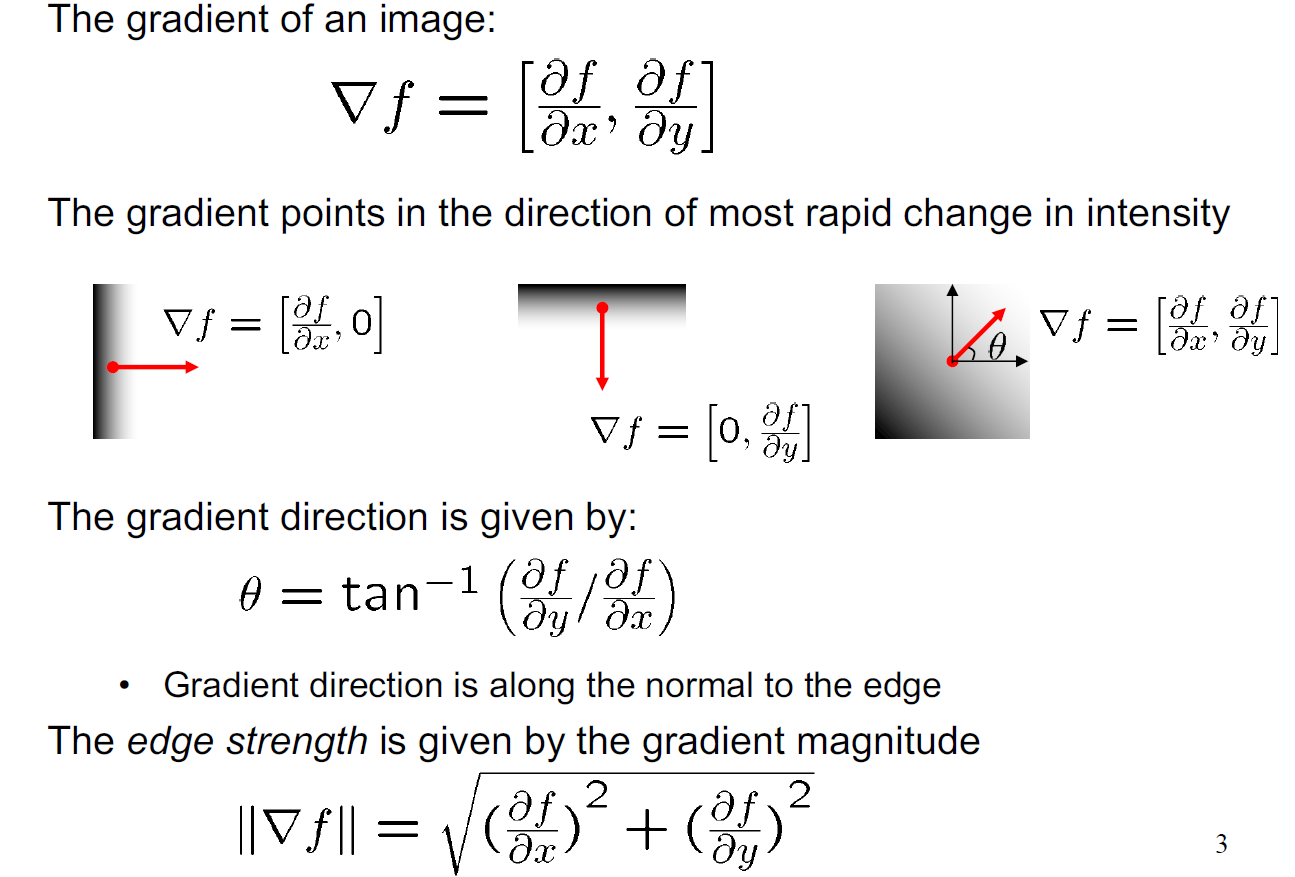
- The magnitude of gradient provides information about the strength of the edge
- edge strength is gradient magnitude
- The direction of gradient is always perpendicular to the direction of the edge
- edge orientation is gradient orientation
Edge Detection Algorithm:
Noise affects edge detection:
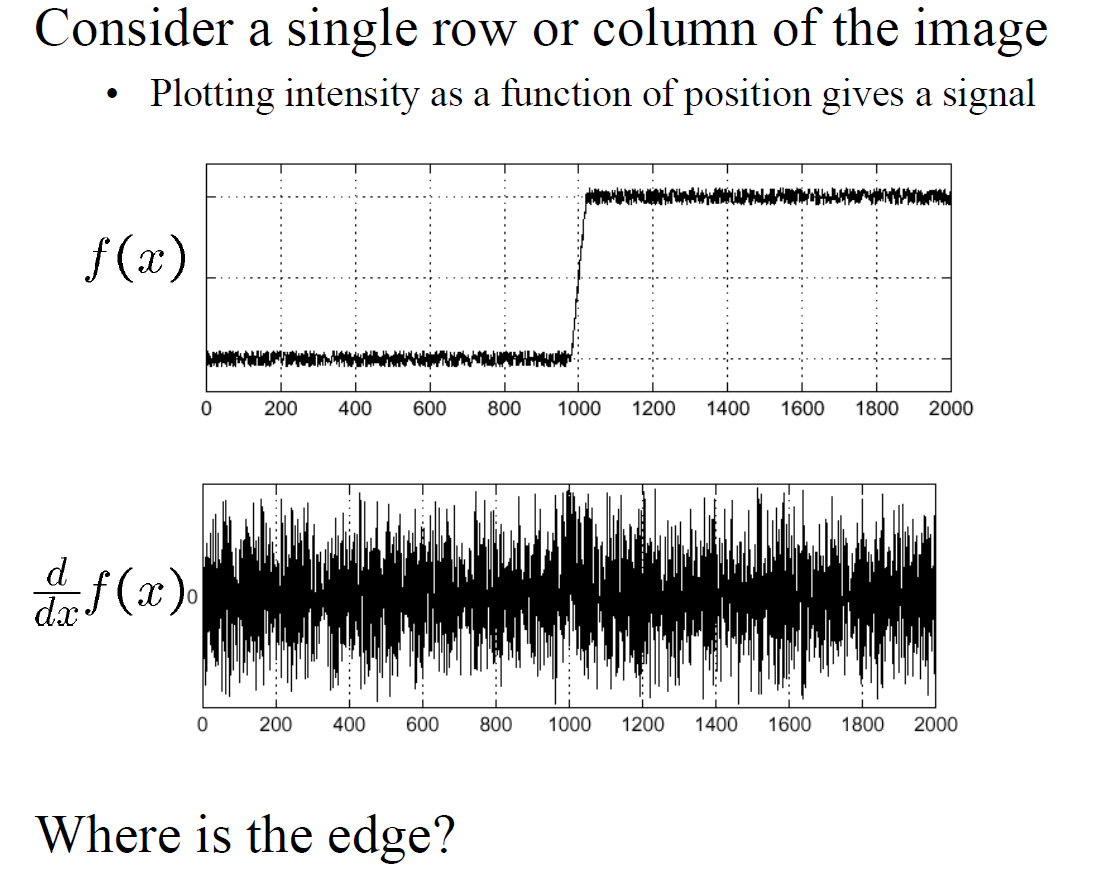
- so before edge detection, we need to smooth first
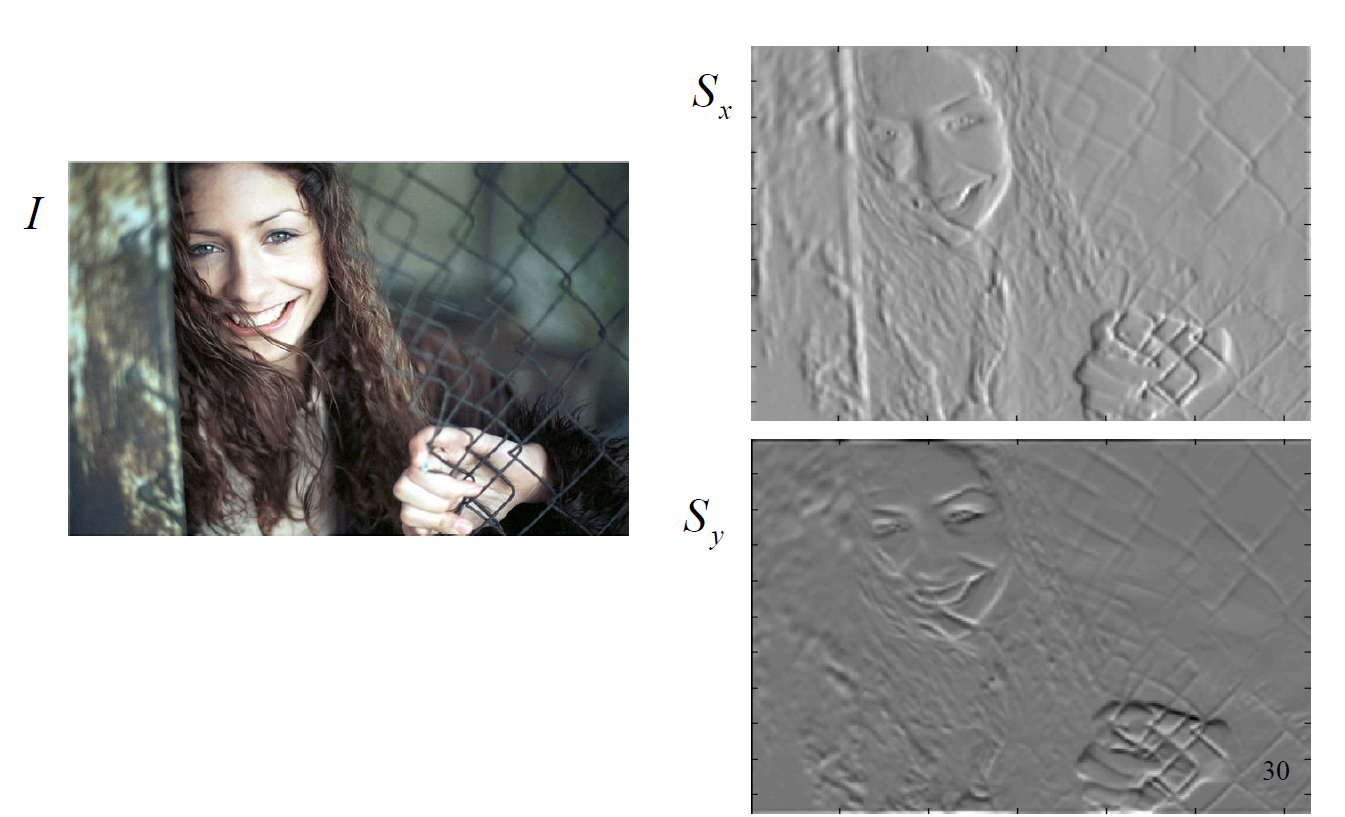
Sobel Edge Detector:
- an example of smoothing first
non-maxima suppression:
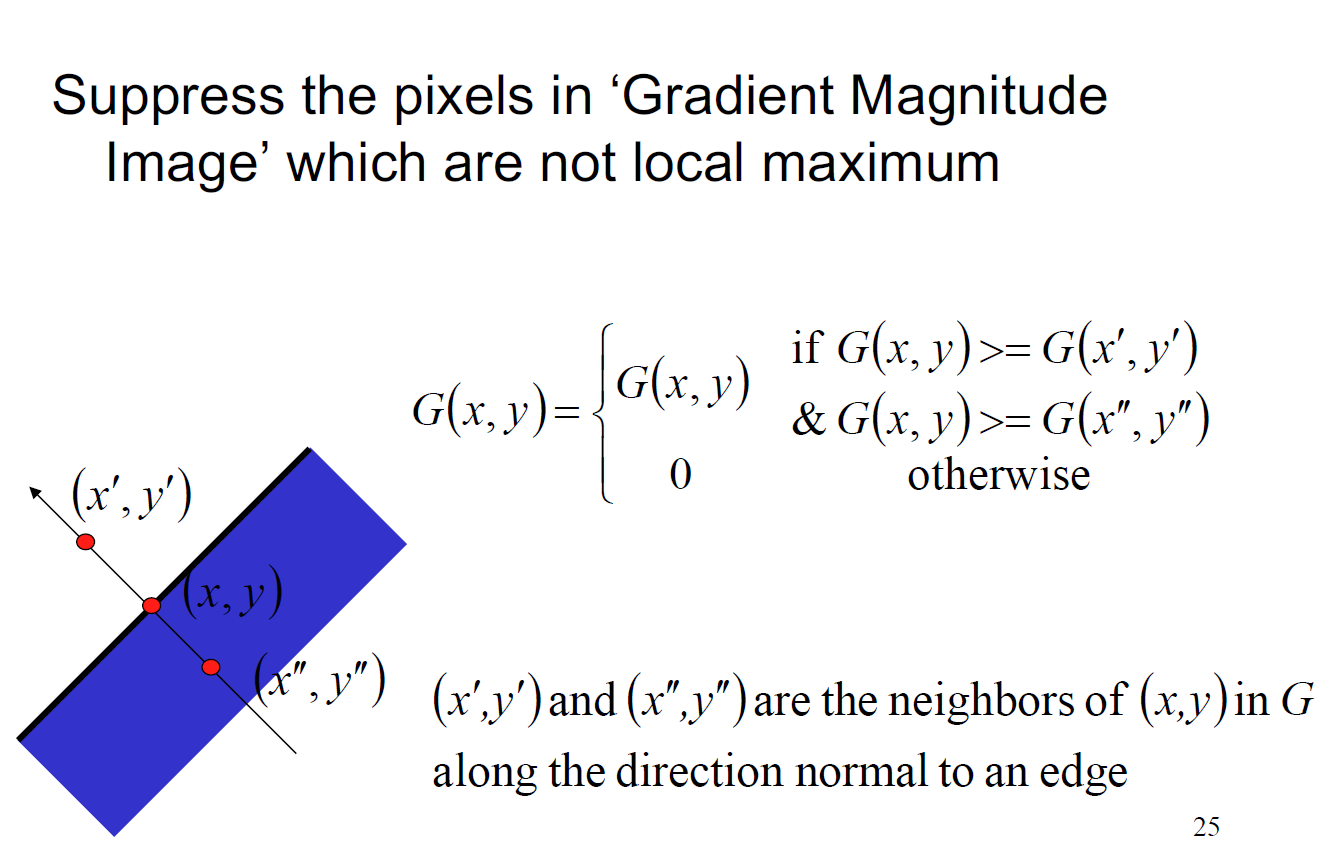


Canny Edge Detection:
similar to simple edge detection but
- localizes by thinning edges to 1 pixel by non-maxima suppression
- uses hysteresis thresholding instead of simple thr esholding
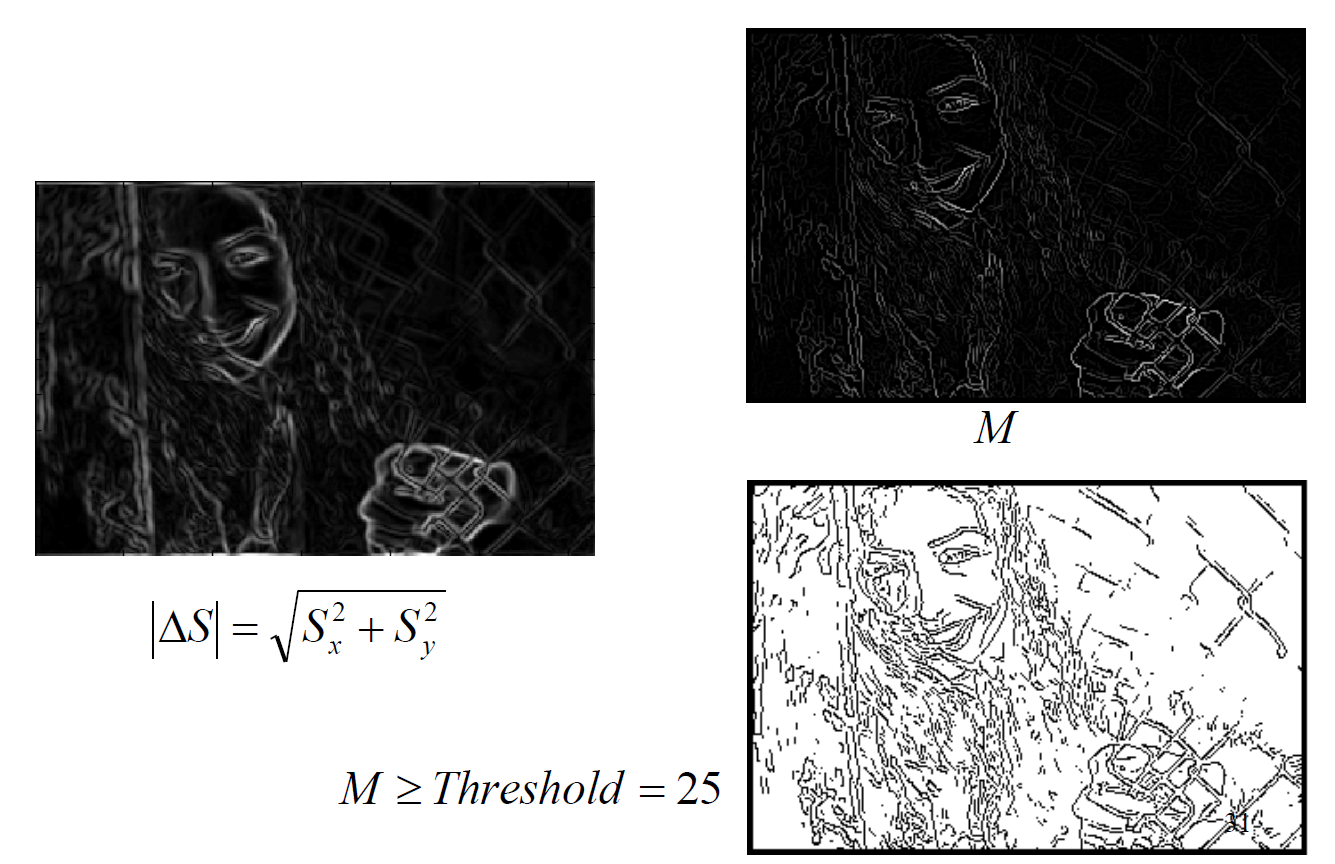

,
are gradient components,
is edge strength.
**
Hysteresis Thresholding:
- Define a low and a high thresholds.
- If the gradient at a pixel is above “high” declare it an “edge pixel”
- If the gradient at a pixel is below “low”, declare it a “non-edge-pixel”
- If the gradient at a pixel is between “low” and “high” then declare it an “edge pixel”, iff it is connected to
an “edge pixel” directly or via pixels between “low” and “high”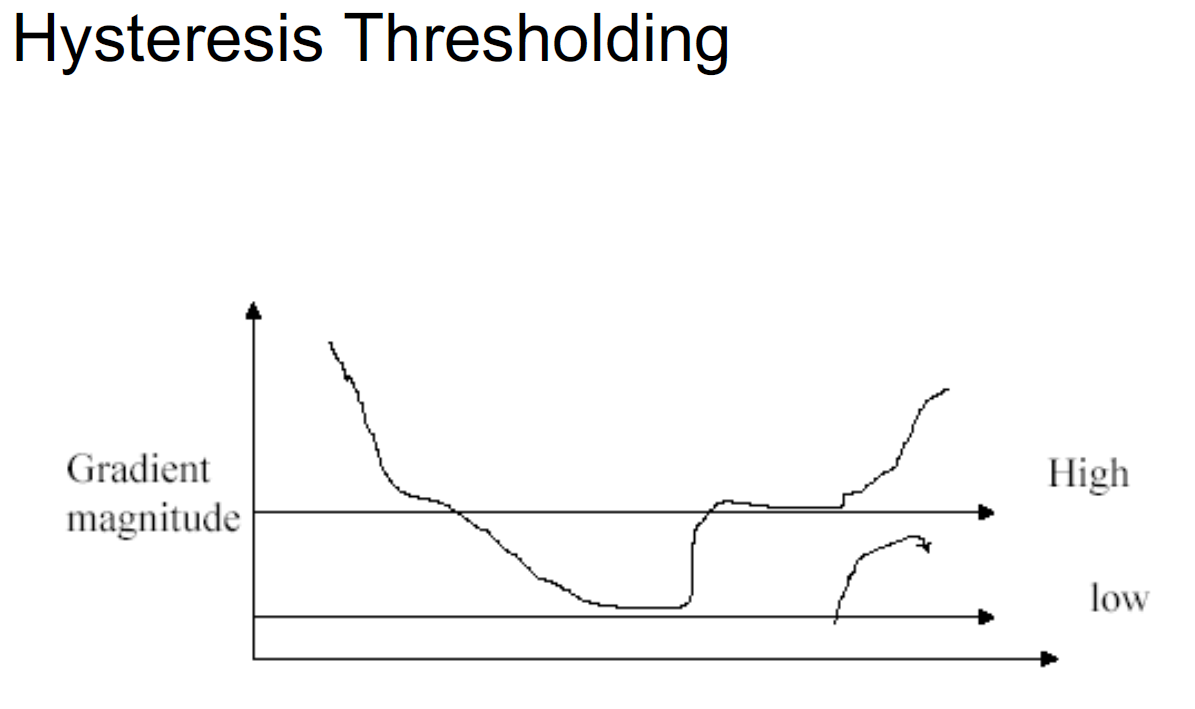
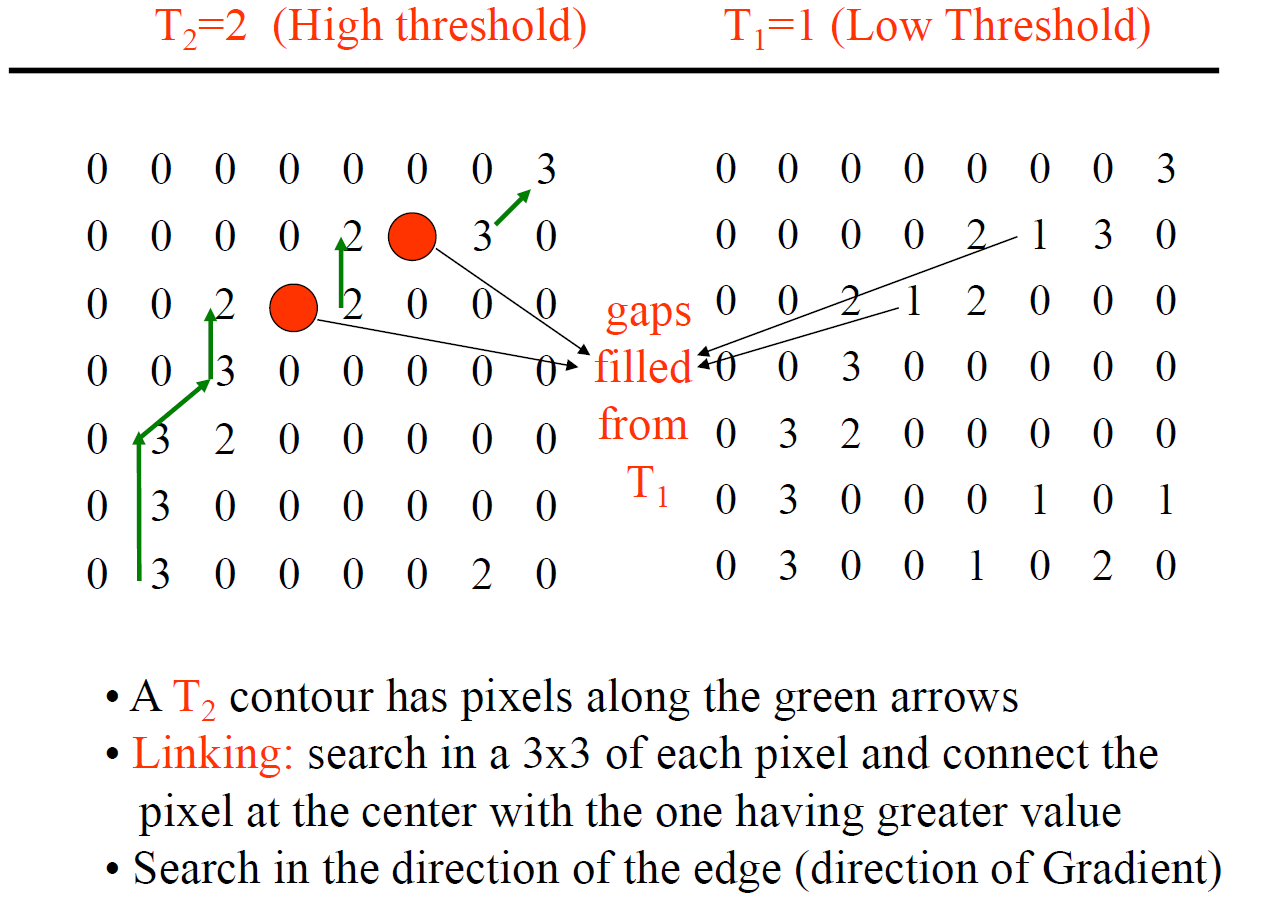
example: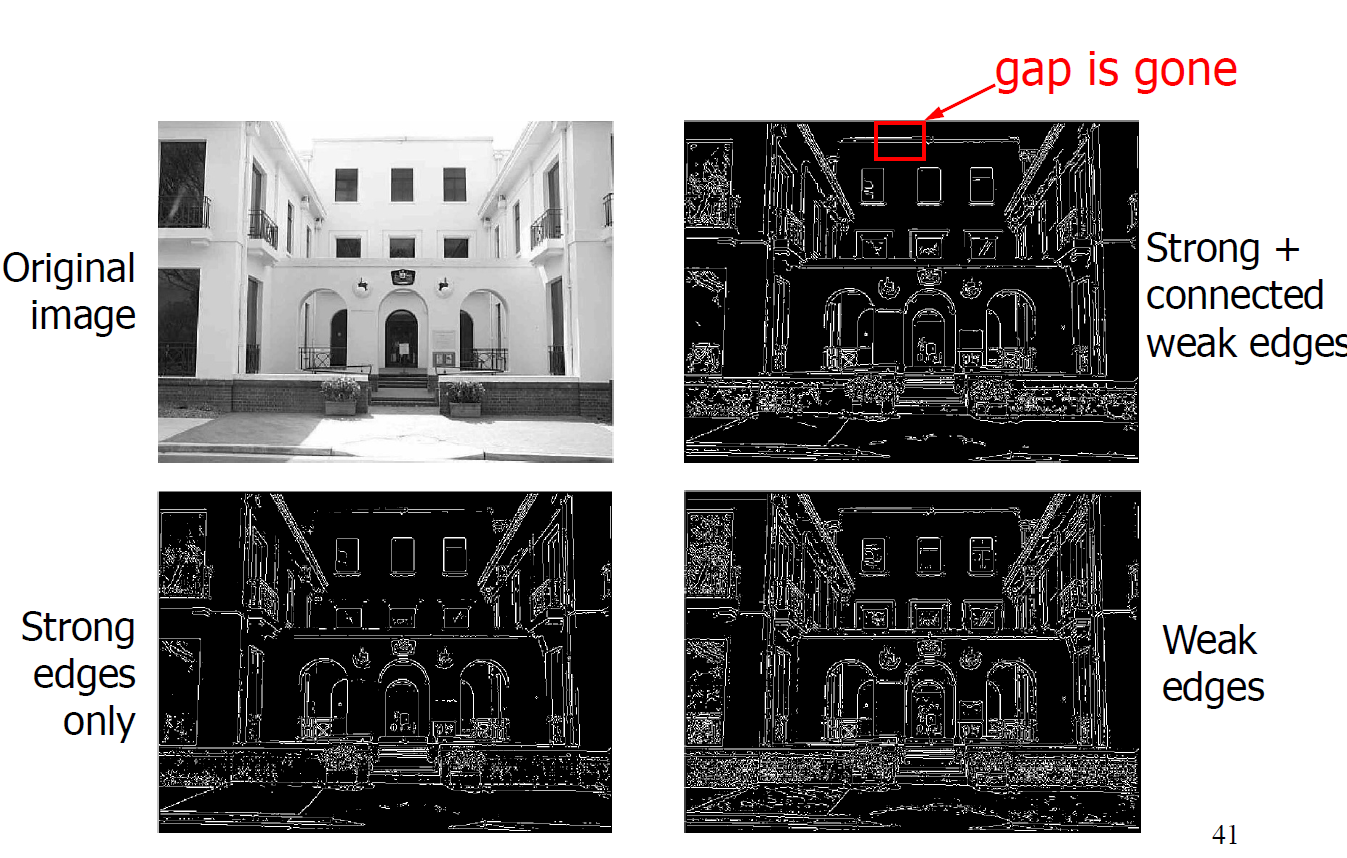 
tradeoff between detection and localization:
- detection: find all important edges
- localization: find images accurately
- we can not simultaneously improve detection and localization in edge detection
Reference:
- wikipedia
- handout of COMP4102: Introduction to Computer Vision from Carleton University School of Computer Science, 2019