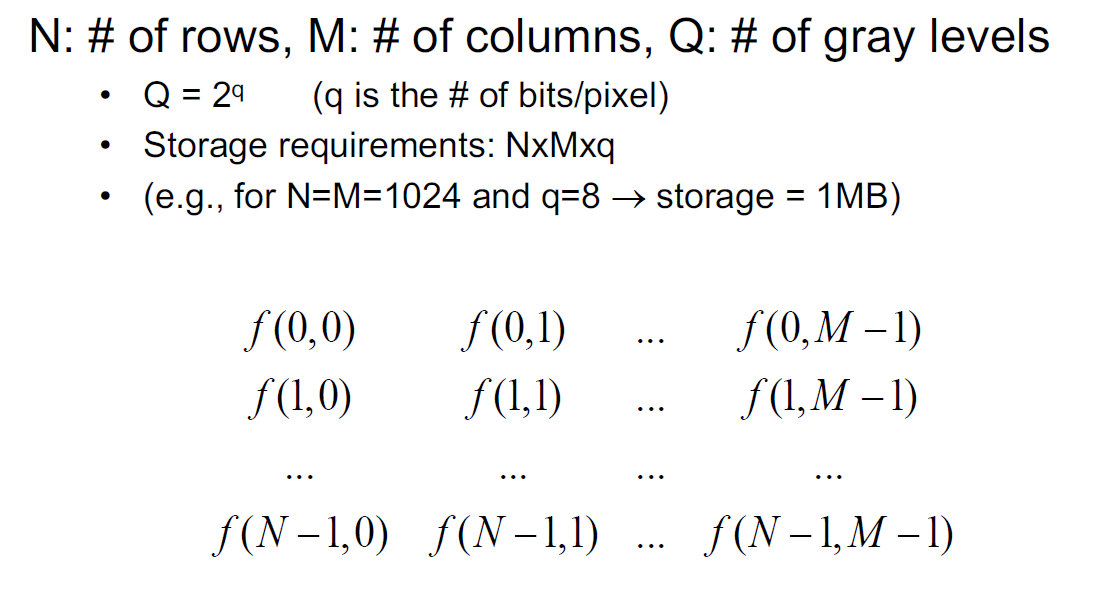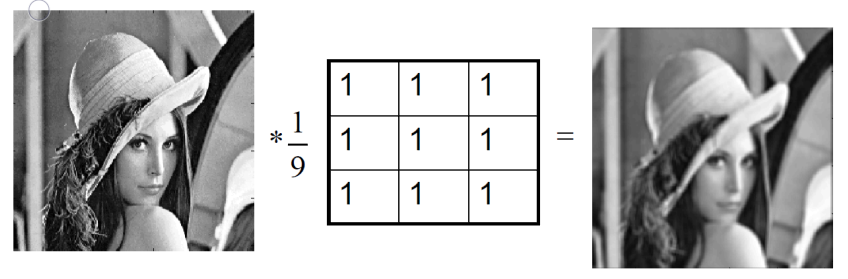Digital Images:
- An image is a rectangular double array of integers
- Each integer is the brightness of the image at that point
Read and display an image in OpenCV:
The programming language below is C++
Image noises:
- due to reasons like numerical inaccuracies, we may have some entities that made images unclear.

Representative noises that usually appear are
- Gaussian Noise
- uniformly distributed

- Impulsive Noise
- sudden noises
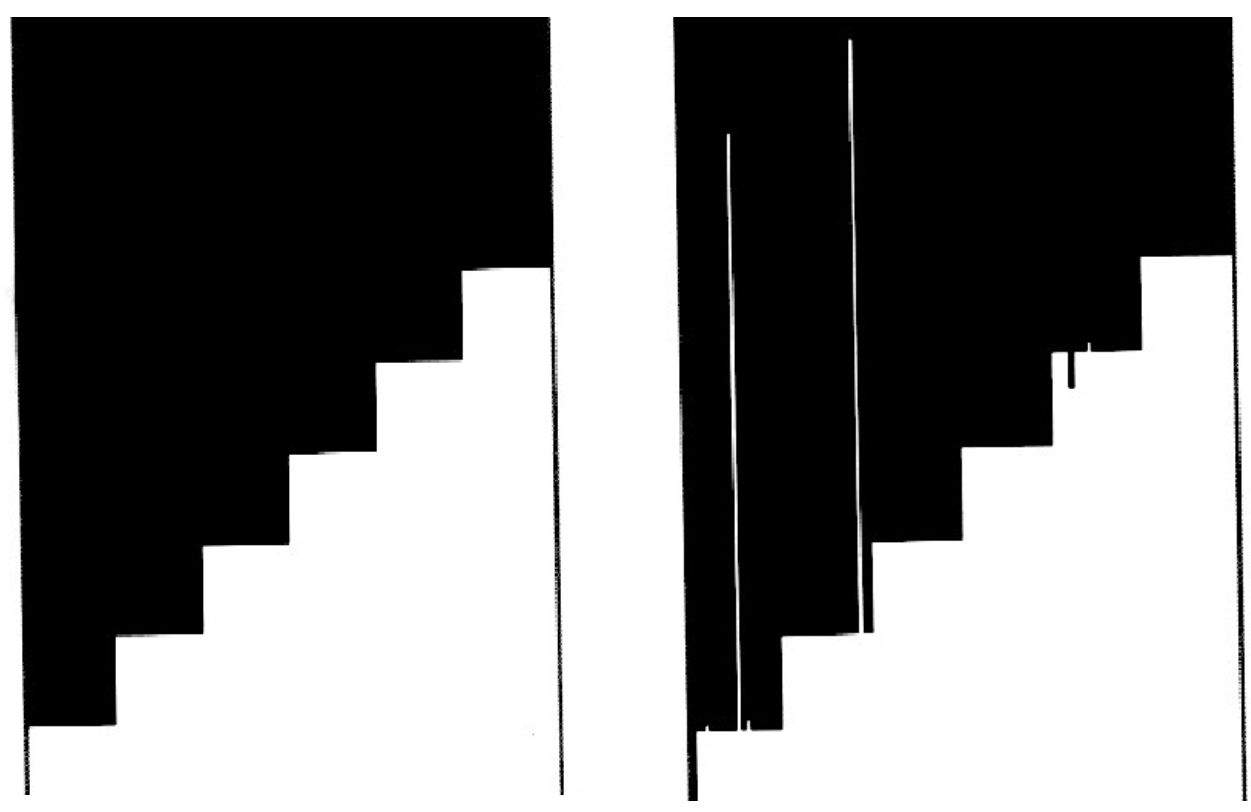

Image Processing:
Definition: The input is an image, the output is an image that has been processed
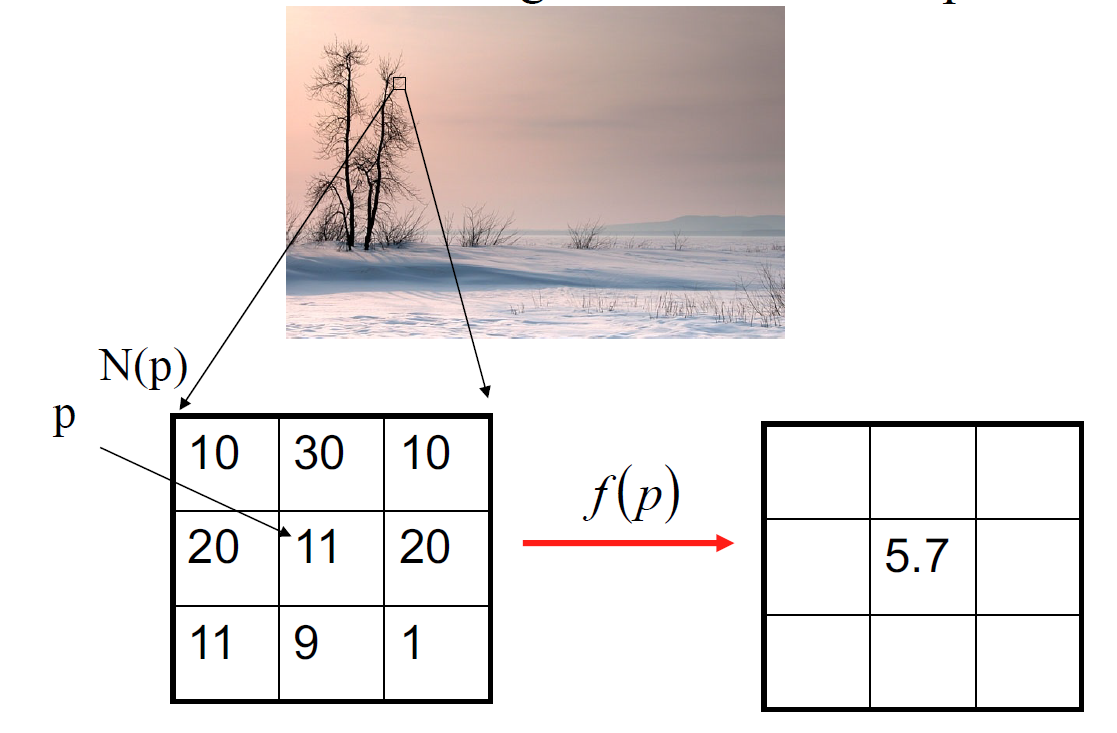
Filtering:
a type of Image Processing
- it modifies the pixels in an image based on some function of the local neighbourhood of the pixels
Image Filter:
- use a function to take neighbour pixels of each pixel
balance a new pixel value to replace the old one based on an algorithm
Linear Filter / Concolution:
if the function in the image filter is a linear combination of these original pixels
- we need a kernel to process image.
kernel is a matrix of size m by m
 is for convolution,
is for convolution,  is for cross correslation
is for cross correslation
- results of cross correlation and convolution are the same iff kernel is both horizontally and vertically symmetric.
- convolution is also used in neural network: http://cs231n.stanford.edu
If meet border pixels, we can
smoothing images by averaging
Gaussian Filter:
- Discreate Gaussian Kernel:

- filter with Gaussian distribution
Noise Filtering:
- Goal is to remove noise and still preserve image structure (edges)
- Gaussian smoothing preserves edges better than average filter
- Gaussian filter best at removing Gaussian noise



- Neither Gaussian nor average filter removes salt and pepper noise (Impulsive Noise)
Nonlinear Filtering:
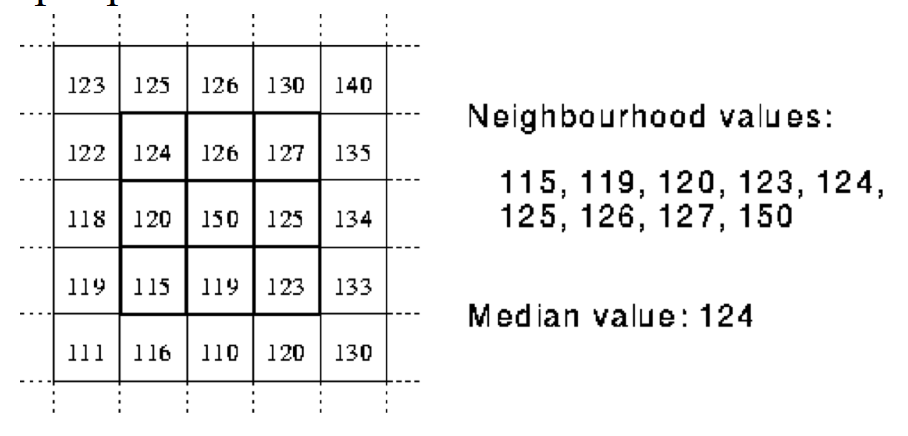
Median Filter:
- Replace each pixel value I(i, j) with the median of the values found in a local neighbourhood of (i, j).
Noise Filtering:
- Median filter can fix salt-and-pepper noise

Reference:
- wikipedia
- handout of COMP4102: Introduction to Computer Vision from Carleton University School of Computer Science, 2019