Polar representation:
- a line in the plane maps to a point in the
space

- all lines passing through a point map to a sinusoidal curve in the
space

= distance
= angle
Hough Idea:
- Each straight line in this image can be described by an equation
- Each white point if considered in isolation could lie on an infinite number of straight lines
- In the Hough transform each point votes for every line it could be on
- The lines with the most votes win
Hough Processing:

- find the edges in the image (Canny operator common)
- use each edge point to vote in the accumulator space
- accumulator space also called the Hough Space
- find the peak(s) in the accumulator space
- example
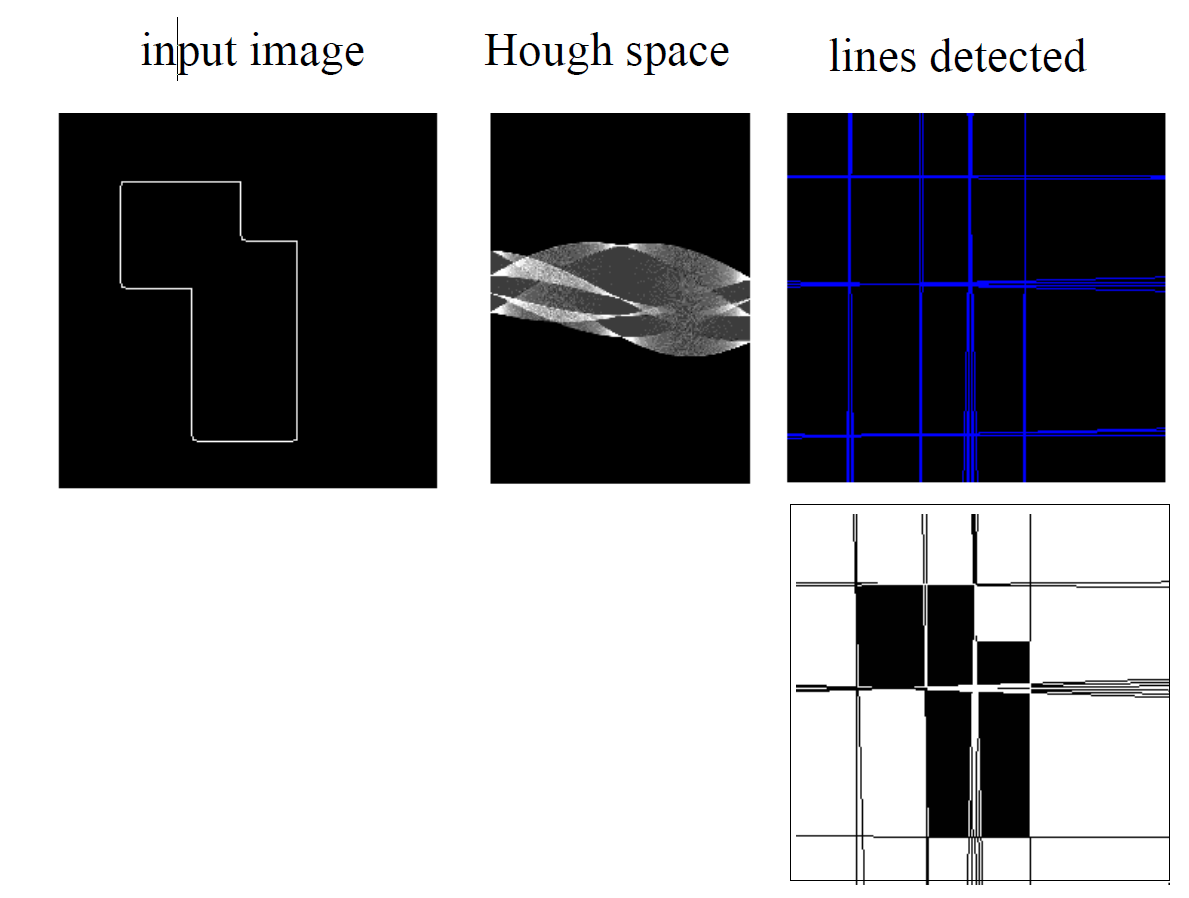
- Hough Processing also can find circles
Reference:
- wikipedia
- http://sites.science.oregonstate.edu/math/home/programs/undergrad/CalculusQuestStudyGuides/vcalc/coord/coord.html
- handout of COMP4102: Introduction to Computer Vision from Carleton University School of Computer Science, 2019

