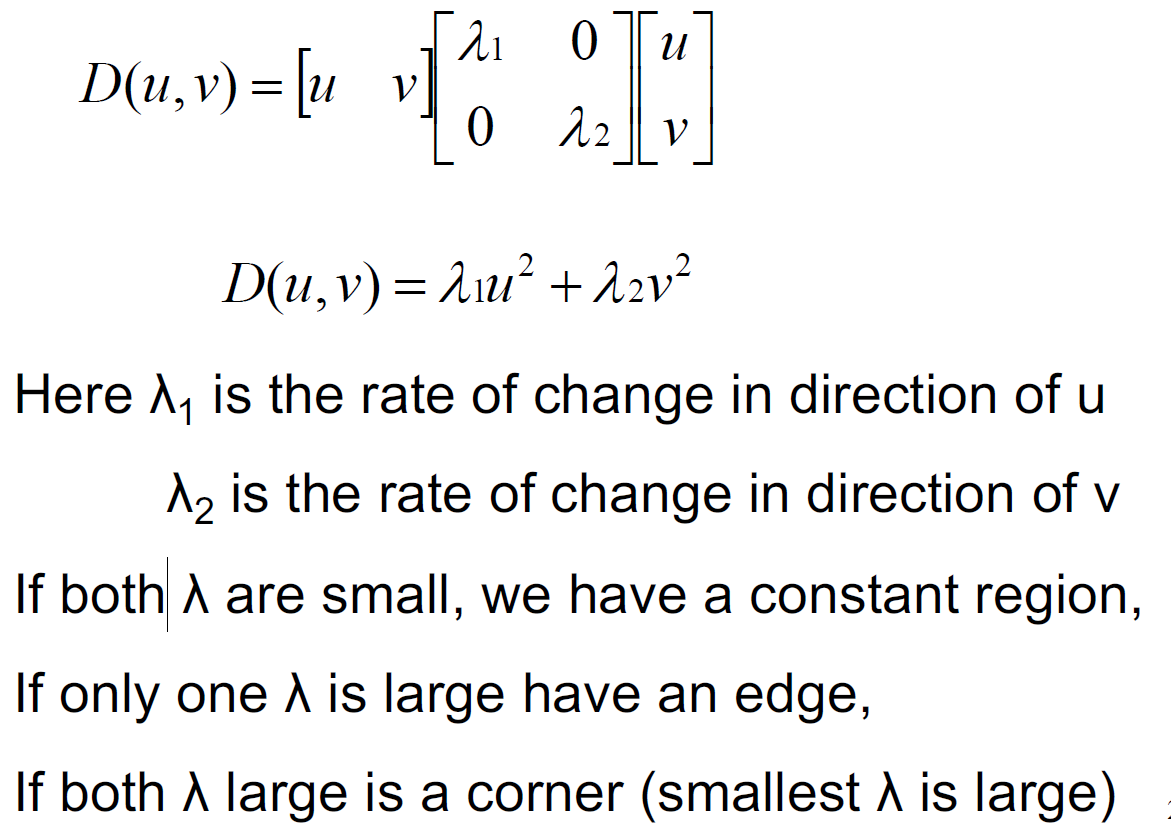Corner / Interest Point:
- can help recognize a kind of object
- can be used in robotics
- can build 2D maps
- can build a panorama

- image alignment
- etc.
How to build parorama:
Purpose: match images
- Detect interest points / corner points in both images
- Find same interest points in both images
- But the detection procedure should be done independently per image
Extract corner descriptors at interest points:
- Take some neighbourhood (small window) around each interest point in both images
- Take pixels in neighbourhood and compute a high dimensional vector
- Find invariance to geometric and photometric differences between the 2 views
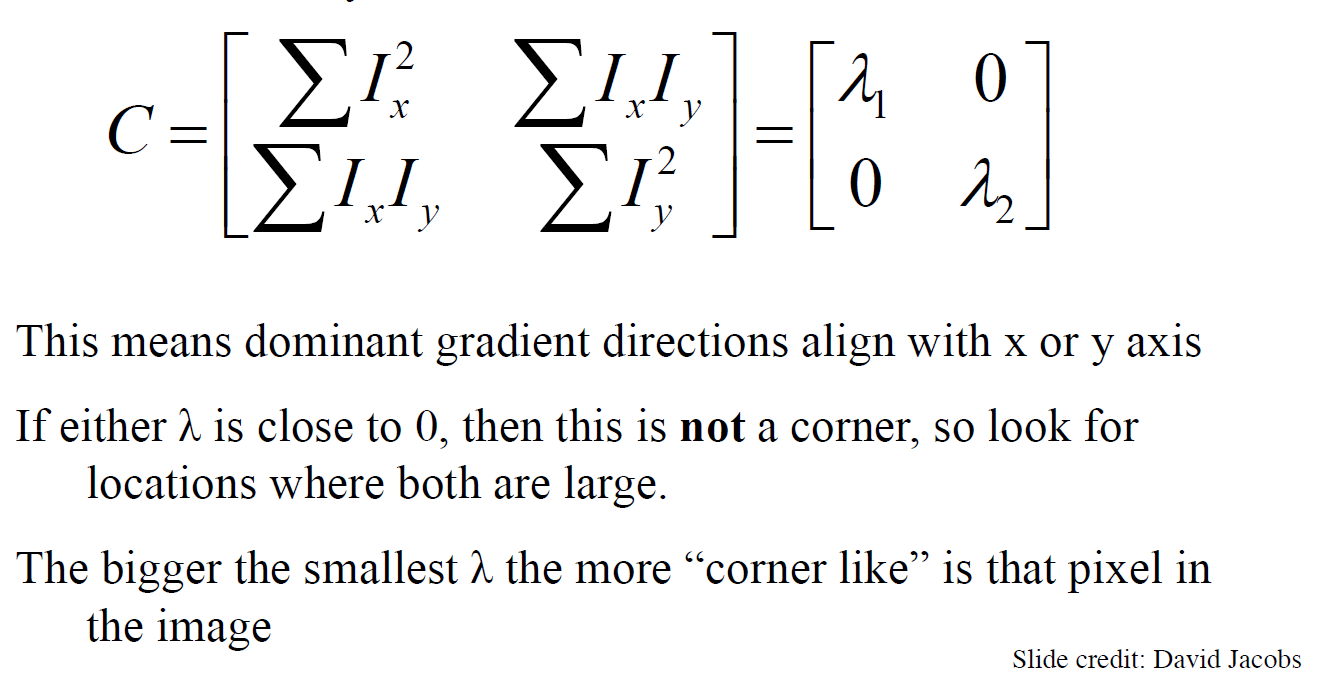
Corner Feature:
Corners are image locations that have large intensity changes in more than one direction.
- The intensity change at a given pixel in the direction (u,v) is measured by sum-of-squared-difference
- (SSD) of all pixels in a nbhd of that window, and the associated pixel shifted by (u,v).
Harris Corner Detection:
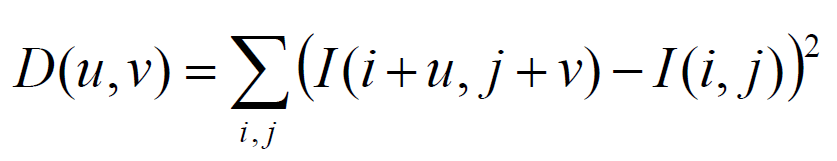

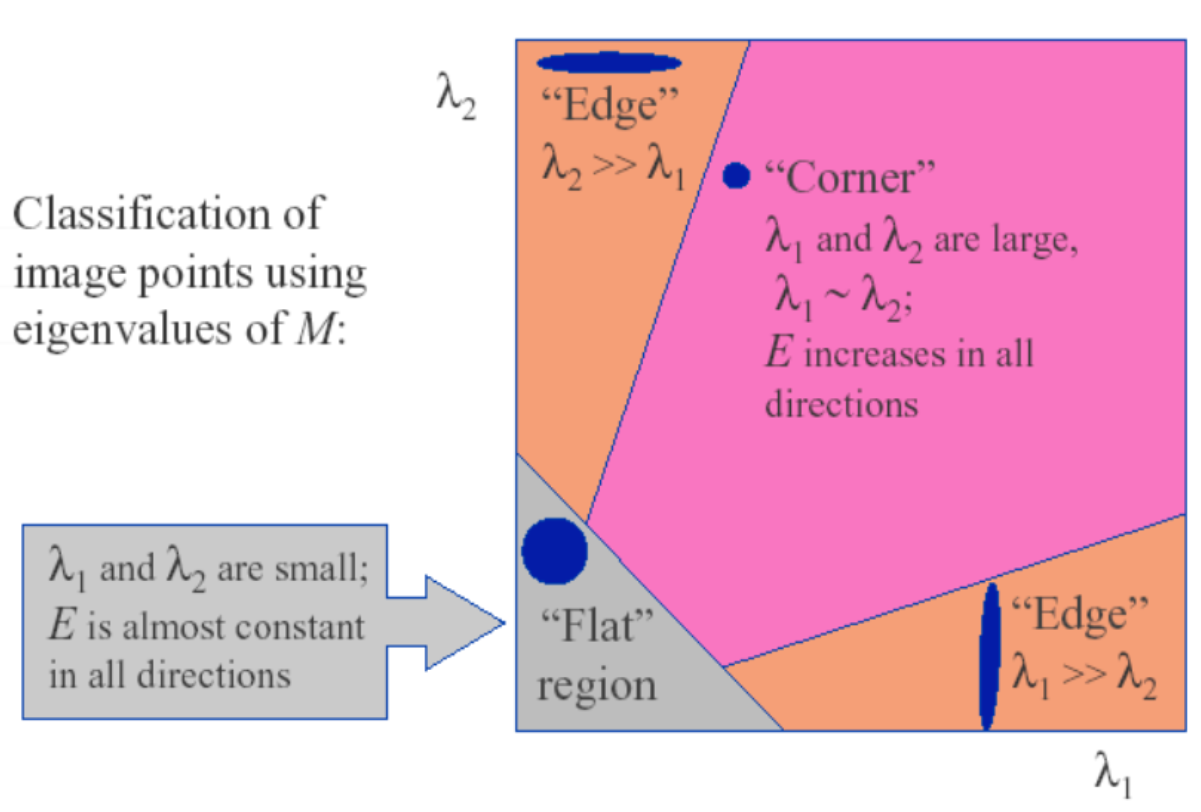
Eigenvalue Analysis:
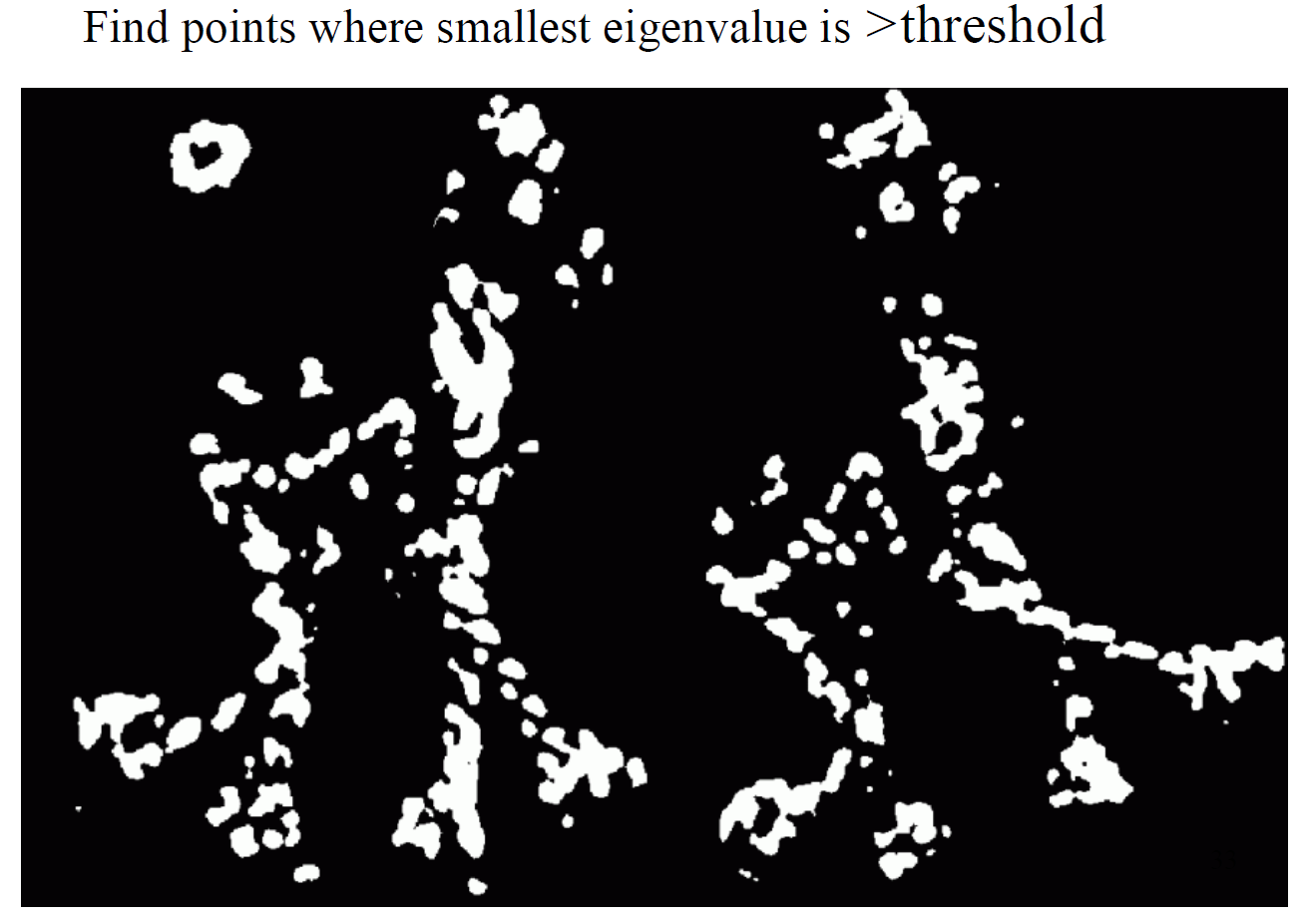
Alternatives to using eigenvalues / Harris Detector:
- use
- M is the matrix C before
- k is a threshold on the value of R
- A pixel with an R > threshold (experimental) is a corner
Invariance:
To decide which 2 pixels from 2 different images are actually the same point
- Translation
- Rotation in image plane
- Scale change
- Rotate out of camera plane (no good solution)
Instead of Harris, there are also other methods like SIFT/SURF matchings to detect invariances.
Differences between 2 methods:
- Harris features work only for some motions (rotation in camera plane, translation)
- SIFT/SURF features work for larger motions, and for different types of motions
- blur, lighting, compression, all motion in the camera plane, and some motions out of the camera plane, etc.
- but SIFT/SURF is slower
Reference:
- wikipedia
- handout of COMP4102: Introduction to Computer Vision from Carleton University School of Computer Science, 2019