Basic:
We have 2 types of images:
- Intensity
- light intensity
- Range (depth)
- shape and distance
Elements of a real imaging device:
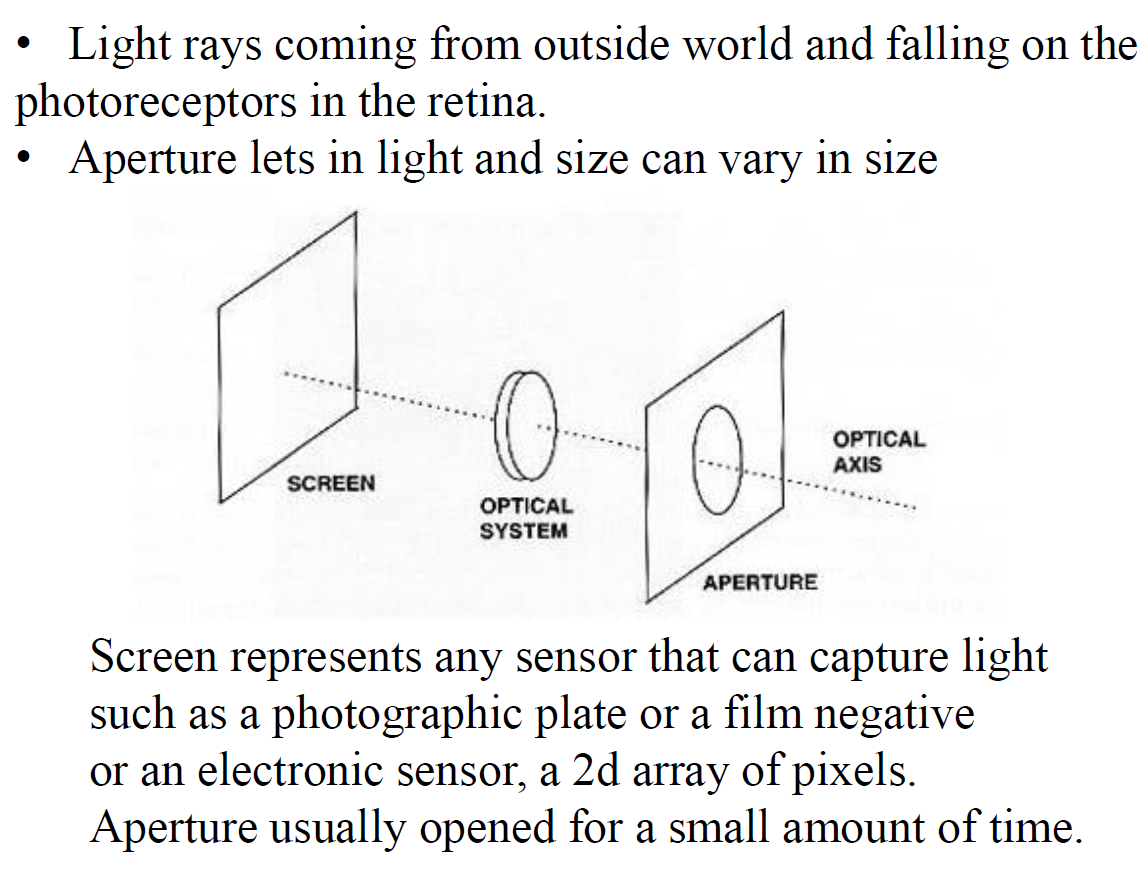
Why Lenses?


Adding a lens:
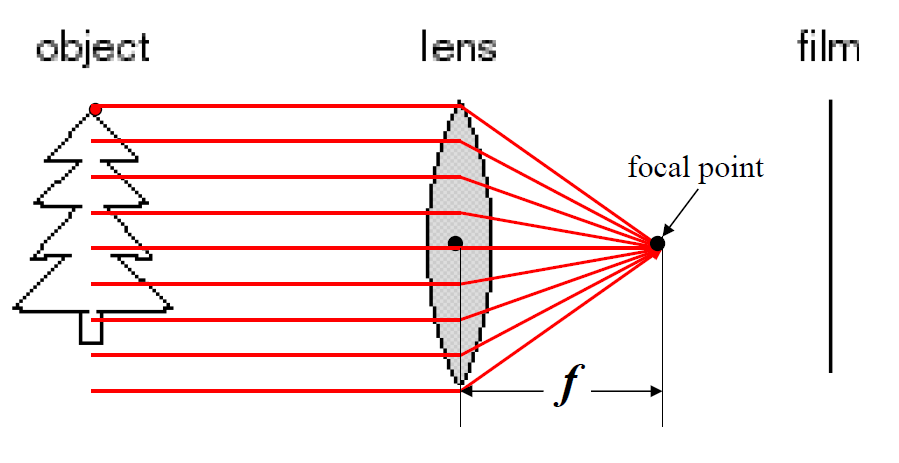
- all parallel rays converge to one point on a plane located at the focal length f.

- points “in focus” (red line) are projected to one point on the film
- others are projected to a “circle of confuion” (blurring) in the image
- Changing the shape of the lens changes this distance
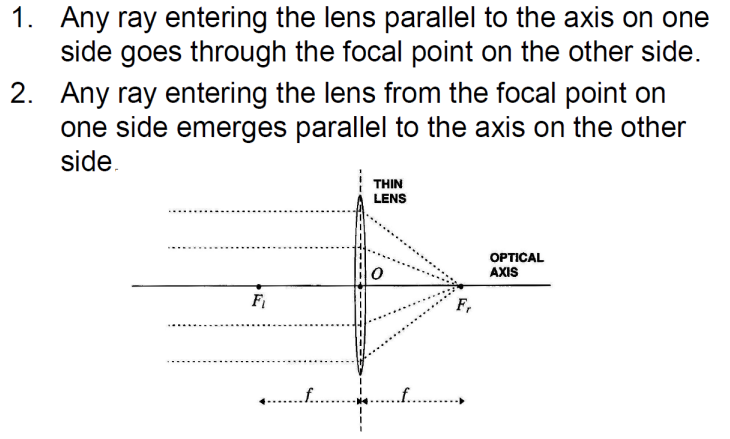
Thin Lens Model:
Thin Lenses Equation:
is the distance of the object from lens
is the distance of the in focus image plane
- f is the focal length of the lens
- if
increases,
decreases, and vice versa
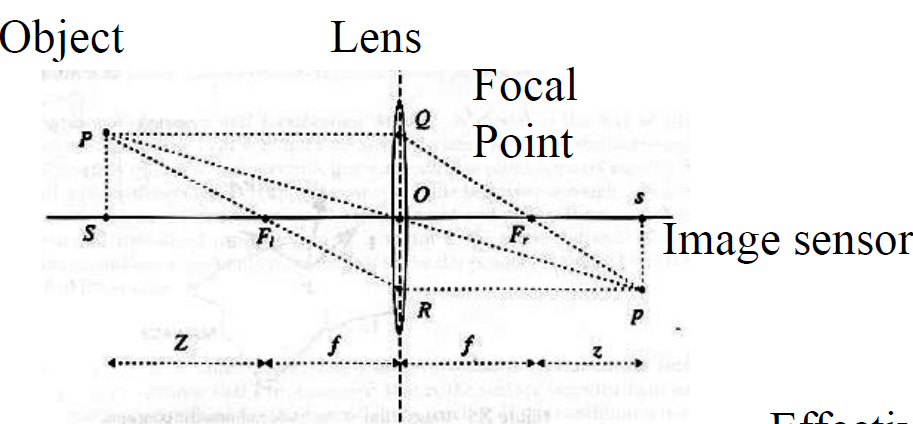
Depth of Field:
- The range of Z that is in focus is called the depth of field.
- Changes with lens focal length f and image plane distance
In this picture, object is on the right: 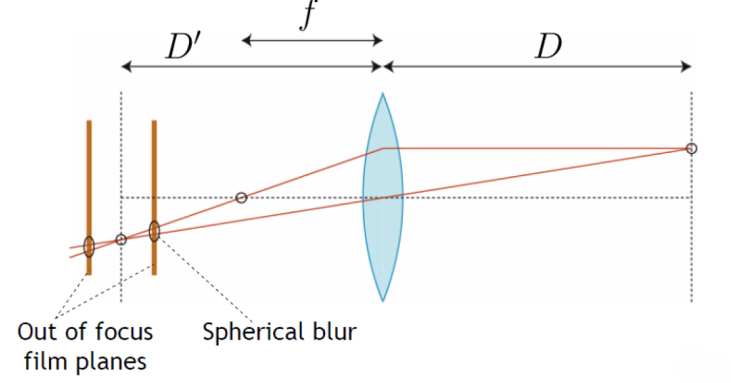
- pin hole camera has infinite DoF
- Thin lens implies there is always a finite DoF
- Change change DoF by changing lens or aperture size
- Larger aperture means smaller DoF, more light

The distance between 2 lines before and after the tree is DoF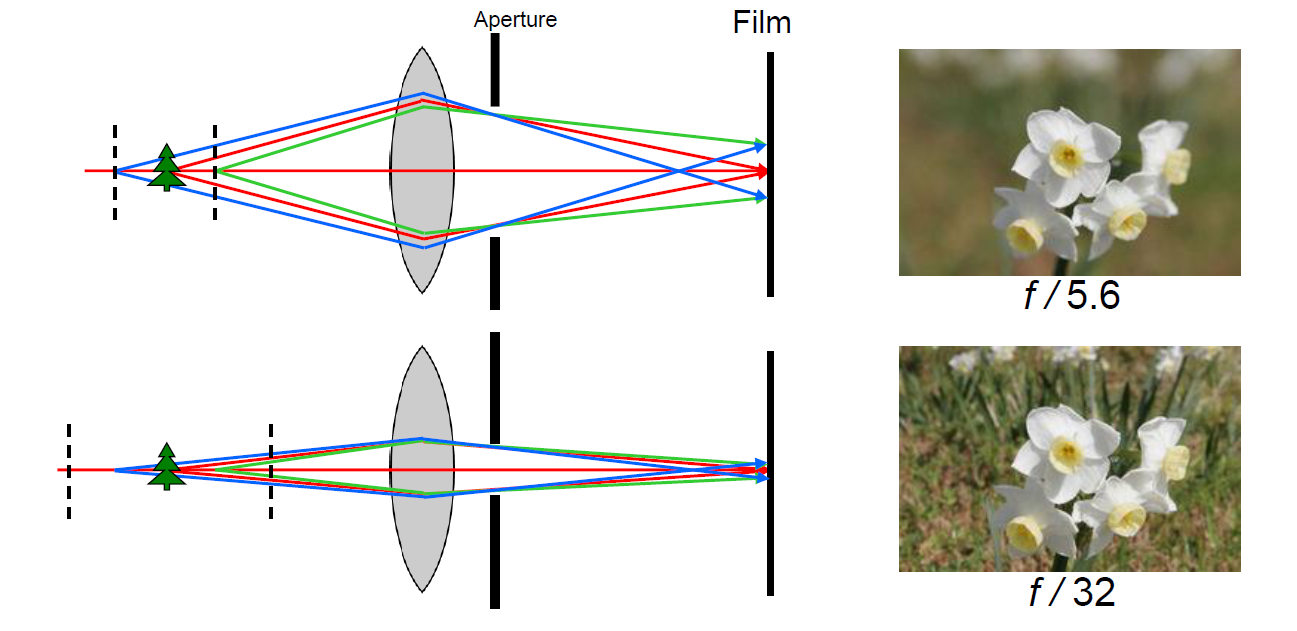
f-stop number:
- f-stop number = f / D
- f is focal length
- D is diameter of the pin hole
- if f-stop number ↑
- the image is darker
- DoF is greater
- if f-stop number ↓
- the image is brighter
- DoF is smaller
Field of View:
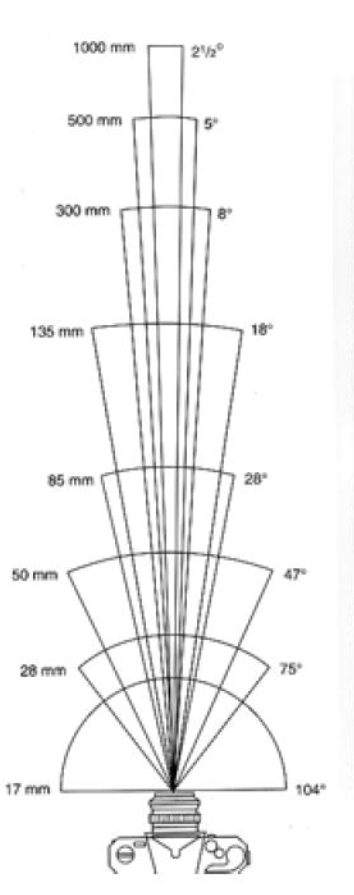
- FOV depends on Focal Length (f)
Effect of change in focal length:
strong perspective and weak perspective:
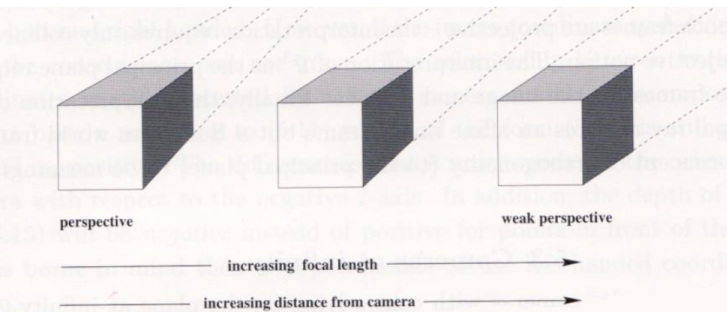
small f = strong perspective = parallel lines seem not parallel
large f = weak perspective = not parallel lines might seem parallel
Specularity:
- The changes in appearance of a surface point defines the specularity
- Plain sheet of paper is non-specular (no change)
- Desktop is semi-specular (some change)
- Mirror is very specular (a great deal of change)
Image Digitization:
- Sampling – measuring the value of an image at a finite number of points.
- Quantization – representing the measured value at the sampled point, by an integer.
- Pixel – picture element, usually in the range [0,255]
Grayscale Image:

A digital image is represented by an integer array E of m-by-n. E(i,j), a pixel, is an integer in the range [0, 255].
Color Image:

3 channels of a color image - blue, green, and red.
Those 3 colors can be mixed into other colors.
Geometric Model of Camera:


- 3D -> 2D
- P is the point of object, p is the corresponding image point
Reference:
- wikipedia
- handout of COMP4102: Introduction to Computer Vision from Carleton University School of Computer Science, 2019