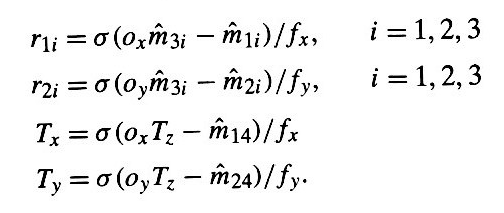EXIF:
Full name is Exchangeable Image File Format
- .JPG
- .TIF
- .WAV
EXIF tag include information of the camera and photo
- Date and time information
- Camera settings
- A thumbnail (picture as icon)
- Descriptions
- Copyright information
Find intrinsic camera parameters:
- EXIF has focal length f (in millimeters)
- camera manual has pixel size
Camera calibration:
Purpose:
to determine geometric parameters of the image formation process
Explicit camera calibration:
Use a calibration object with a known geometry
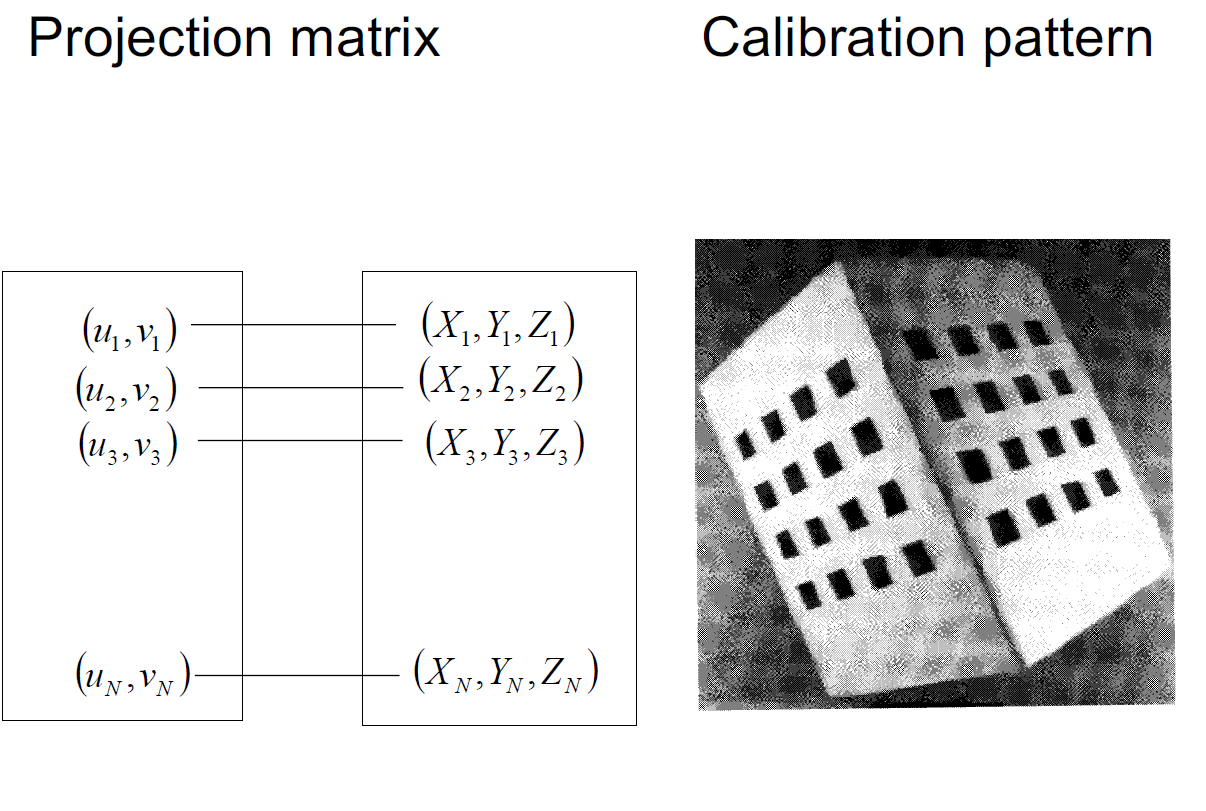
- Write equations linking co-ordinates of the projected points,
and the camera parameters
- From images of the calibration target
- Intrinsic camera parameters
- (depend only on camera characteristics)
- Extrinsic camera parameters
- (depend only on position camera)
- In OpenCV, the calibration process finds fx, fy, ox, oy, along with the distortion parameters
- Intrinsic camera parameters
Methods:
- Direct Approach (Tsai method)
- Write projection equations in terms of all the parameters
- That is all the unknown intrinsic and extrinsic parameters
- Solve for these parameters using non-linear equations
- Projection Matrix Approach
- Compute the projection matrix (the 3x4 matrix M)
- Compute camera parameters as closed-form functions of M
both approaches work with same data, but the direct approach requires an extra step
All calibration methods:
- Use patterns with know geometry or shape
- Take multiple views of theses patterns
- Match the information across the different views
Camera Parameters:
Intrinsic parameters (K matrix):
- Focal length f
- Pixel size in x and y directions: sx & sy
-
Extrinsic parameters ([R | T] matrix):
Rotation matrix R
-
Projection matrix:
P = K [R | T]
(3 by 4 matrix)
and the relationship between a image pixel and it’s corresponding world pixel is:
estimating the projection matrix:
solve Ax = 0 system with SVD
Decompose project matrix:


- Find scale
by using unit vector
- Divide computed M by
to get a new M matrix
- Then,
(i = 1, 2, 3)
with
Taking the dot products of q3 with q1 and q2 we find
Then fx and fy can be recovered:
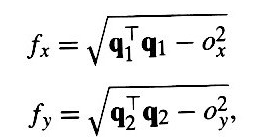
- and the rest of extrinsic parameters:
Reference:
- wikipedia
- handout of COMP4102: Introduction to Computer Vision from Carleton University School of Computer Science, 2019