Retweeting Logic:
Or “Comment logic”
- add “parent” variable in /tweets/models,py
at first, the parent of a tweet is itself, and it’s optional
class Tweet(models.Model):parent = models.ForeignKey("self", null=True, on_delete=models.SET_NULL) # refer to self, when deleted->set into NULL# ...
make migrations and migrate
[root@localhost Twittme]# python3 ./manage.py makemigrations[root@localhost Twittme]# python3 ./manage.py migrate
redirect “retweet” button in /tweets/views.py
@api_view(['POST'])@permission_classes([IsAuthenticated])def tweet_action_view(request, *args, **kwargs):# ...elif action == "retweet":new_tweet = Tweet.objects.create(user=request.user,parent=obj,content=content)serializer = TweetSerializer(new_tweet)return Response(serializer.data, status=200)return Response({}, status=200)
add ‘content’ into /tweets/serializers.py
class TweetActionSerializer(serializers.Serializer):id = serializers.IntegerField()action = serializers.CharField()content = serializers.CharField(allow_blank=True, required=False) # new# ...
and into /tweets/views.py
@api_view(['POST'])@permission_classes([IsAuthenticated])def tweet_action_view(request, *args, **kwargs):# id is required# action: like, unlike, retweetserializer = TweetActionSerializer(data=request.data)if serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True):data = serializer.validated_datatweet_id = data.get("id")action = data.get("action")content = data.get("content") # new# ...return Response({}, status=200)
to test, runserver and click “retweet”

so it only create a new tweet without any content for now.
possible question about migration and solution:
- when makemigrations and migrate, sometimes the server cannot get the tweet list
- and shows “no such column: tweets_tweet.parent_id”
possible solution:
declare parent as a constant
class Tweet(models.Model):# parent = models.ForeignKey("self", null=True, on_delete=models.SET_NULL) # refer to self, when deleted->set into NULLparent = 0# ...
make migrations and migrate
[root@localhost Twittme]# python3 ./manage.py makemigrations[root@localhost Twittme]# python3 ./manage.py migrate
again declare parent as a foreign key instead
class Tweet(models.Model):parent = models.ForeignKey("self", null=True, on_delete=models.SET_NULL) # refer to self, when deleted->set into NULL# parent = 0# ...
make migrations and migrate to substitute
[root@localhost Twittme]# python3 ./manage.py makemigrations[root@localhost Twittme]# python3 ./manage.py migrate
Two Types of Serializers:
In this step, we will separate serializer into 2 categories
- update our todo.md to clarify our purpose first ```
- Tweets
-> User Permissions
``` so we need a read only serializer and a create only serializer.-> Creating-> Text-> Image -> Media Storage Server-> Delete-> Retweeting-> Read only serializer-> Create only serializer-> Liking
in /tweets/serializers.py
- modify TweetSerializer
add TweetCreateSerializer to separate create tweet step ```python class TweetCreateSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): # new likes = serializers.SerializerMethodField(read_only=True)
class Meta: model = Tweet fields = [‘id’, ‘content’, ‘likes’] def get_likes(self, obj): return obj.likes.count()
def validate_content(self, value): if len(value) > MAX_TWEET_LENGTH:
raise serializers.ValidationError("This tweet is too long")
return value
class TweetSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): likes = serializers.SerializerMethodField(read_only=True) content = serializers.SerializerMethodField(read_only=True) # new class Meta: model = Tweet fields = [‘id’, ‘content’, ‘likes’]
def get_likes(self, obj):return obj.likes.count()def get_content(self, obj): # newreturn obj.content#def validate_content(self, value):# if len(value) > MAX_TWEET_LENGTH:# raise serializers.ValidationError("This tweet is too long")# return value
- in /tweets/views.py- import TweetCreateSerializer- TweetSerializer -> TweetCreateSerializer for tweet_create_view()```python# ...from .serializers import (TweetSerializer,TweetActionSerializer,TweetCreateSerializer # new)# ...@api_view(['POST']) # http method the client === POST@authentication_classes([SessionAuthentication])@permission_classes([IsAuthenticated])def tweet_create_view(request, *args, **kwargs):# serializer = TweetSerializer(data=request.POST)serializer = TweetCreateSerializer(data=request.POST)# ...return Response({}, status=400)
to test, runserver and send something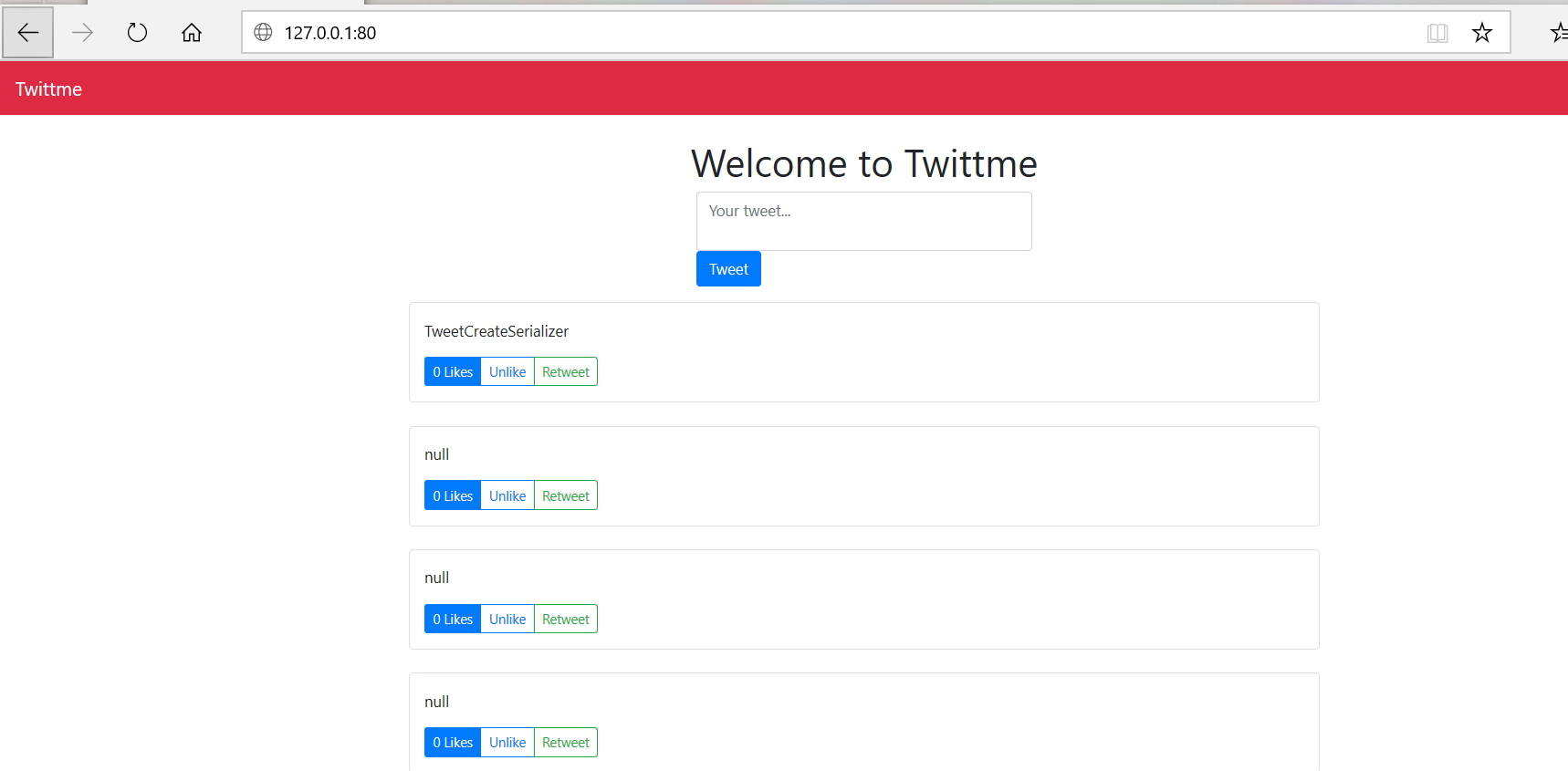
so the create tweet function still works after the separation.
add a boolean to check it the tweet a retweet in /tweets/models.py
class Tweet(models.Model):# ...@propertydef is_retweet(self): # newreturn self.parent != None
add a new field and let the content of retweet become contents of their parents
class TweetSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):class Meta:model = Tweet# fields = ['id', 'content', 'likes']fields = ['id', 'content', 'likes', 'is_retweet']# ...def get_content(self, obj):# return obj.contentcontent = obj.contentif obj.is_retweet: # is this tweet a retweetcontent = obj.parent.contentreturn content
to test, runserver and click retweet


this time the new tweet has content of their parent content instead of just “null”.However, here we should actually pass the parent relationship into the serializer:
modify TweetSerializer in /tweets/serializers.py
class TweetSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):likes = serializers.SerializerMethodField(read_only=True)#content = serializers.SerializerMethodField(read_only=True)parent = TweetCreateSerializer(read_only=True)class Meta:model = Tweet# fields = ['id', 'content', 'likes', 'is_retweet']fields = ['id', 'content', 'likes', 'is_retweet', 'parent']def get_likes(self, obj):return obj.likes.count()#def get_content(self, obj):# content = obj.content# if obj.is_retweet:# content = obj.parent.content# return content
to test, runserver and see /tweets
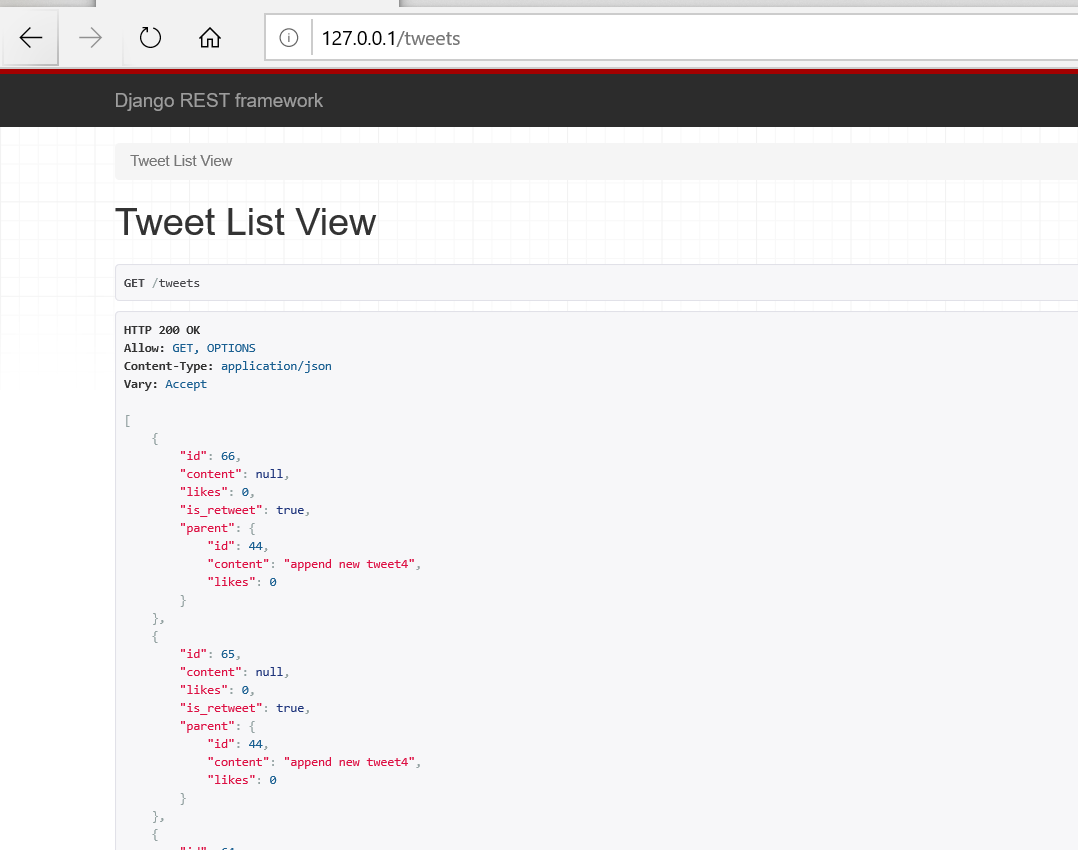

so we have serialized “is_retweet” and “parent” for each tweet.
Internal App Urls:
In this part, we gonna try to make urls into a rest api package.
- create urls.py in /tweets
- it’s similar to /Twittme/urls.py with some changes ```python from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, re_path
from django.urls import path
from tweets.views import (
from .views import ( home_view, tweet_detail_view, tweet_list_view, tweet_create_view, tweet_delete_view, tweet_action_view, )
urlpatterns = [
# path('admin/', admin.site.urls),# path('', home_view),# path('tweets', tweet_list_view),path('', tweet_list_view),# path('api/tweets/action', tweet_action_view),path('action/', tweet_action_view),# path('create-tweet', tweet_create_view),path('create/', tweet_create_view),# path('tweets/<int:tweet_id>', tweet_detail_view),path('<int:tweet_id>/', tweet_detail_view),# path('api/tweets/<int:tweet_id>/delete', tweet_delete_view),path('<int:tweet_id>/delete/', tweet_delete_view),
]
- and add this package into /Twittme/urls.py- then simplify path logic```python# ...# from django.urls import path, re_pathfrom django.urls import path, re_path, include# ...urlpatterns = [path('admin/', admin.site.urls),path('', home_view),path('tweets', tweet_list_view),path('create-tweet', tweet_create_view),path('tweets/<int:tweet_id>', tweet_detail_view),# path('api/tweets/<int:tweet_id>/delete', tweet_delete_view),# path('api/tweets/action', tweet_action_view),path('api/tweets/', include('tweets.urls')), # new]
and those paths about api/tweets/ are still available



Setting up Tests in Django:
In this part, setup some tests in django and run them automatically.
run tests by terminal command:
python3 ./manage.py test
- to test app “tweets”, modify /tweets/tests.py ```python from django.contrib.auth import get_user_model from django.test import TestCase
from rest_framework.test import APIClient
from .models import Tweet
Create your tests here.
User = get_user_model()
class TweetTestCase(TestCase): def setUp(self): # setup 2 users and 3 tweets self.user = User.objects.create_user(username=’cfe’, password=’somepassword’) self.userb = User.objects.create_user(username=’cfe-2’, password=’somepassword2’) Tweet.objects.create(content=”my first tweet”, user=self.user) Tweet.objects.create(content=”my first tweet”, user=self.user) Tweet.objects.create(content=”my first tweet”, user=self.userb) self.currentCount = Tweet.objects.all().count()
def test_tweet_created(self): # is the tweet correctly createdtweet_obj = Tweet.objects.create(content="my second tweet",user=self.user)self.assertEqual(tweet_obj.id, 4)self.assertEqual(tweet_obj.user, self.user)def get_client(self): # could it get the right clientclient = APIClient()client.login(username=self.user.username, password='somepassword')return clientdef test_tweet_list(self): # could it get the right tweet list (for "user")client = self.get_client()response = client.get("/api/tweets/")self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)self.assertEqual(len(response.json()), 3)def test_action_like(self): # is the like action done successfullyclient = self.get_client()response = client.post("/api/tweets/action/",{"id": 1, "action": "like"})self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)like_count = response.json().get("likes")self.assertEqual(like_count, 1)def test_action_unlike(self): # is the unlike action done successfullyclient = self.get_client()response = client.post("/api/tweets/action/",{"id": 2, "action": "like"})self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)response = client.post("/api/tweets/action/",{"id": 2, "action": "unlike"})self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)like_count = response.json().get("likes")self.assertEqual(like_count, 0)def test_action_retweet(self): # is the retweet action done successfullyclient = self.get_client()response = client.post("/api/tweets/action/",{"id": 2, "action": "retweet"})self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 201)data = response.json()new_tweet_id = data.get("id")self.assertNotEqual(2, new_tweet_id)self.assertEqual(self.currentCount + 1, new_tweet_id)def test_tweet_create_api_view(self): # could get the create api view?request_data = {"content": "This is my test tweet"}client = self.get_client()response = client.post("/api/tweets/create/", request_data)self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 201)response_data = response.json()new_tweet_id = response_data.get("id")self.assertEqual(self.currentCount + 1, new_tweet_id)def test_tweet_detail_api_view(self): # could get the detail api view?client = self.get_client()response = client.get("/api/tweets/1/")self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)data = response.json()_id = data.get("id")self.assertEqual(_id, 1)def test_tweet_delete_api_view(self): # could get the delete api view?client = self.get_client()response = client.delete("/api/tweets/1/delete/")self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)client = self.get_client()response = client.delete("/api/tweets/1/delete/")self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 404)response_incorrect_owner = client.delete("/api/tweets/3/delete/")self.assertEqual(response_incorrect_owner.status_code, 401)
- to make sure the test can get enough response, add some details in /tweets/views.py```python@api_view(['POST'])@permission_classes([IsAuthenticated])def tweet_action_view(request, *args, **kwargs):serializer = TweetActionSerializer(data=request.data)if serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True):# ...if action == "like":# ...elif action == "unlike":obj.likes.remove(request.user)serializer = TweetSerializer(obj) # newreturn Response(serializer.data, status=200) # newelif action == "retweet":# ...# return Response(serializer.data, status=200)return Response(serializer.data, status=201) # status code from 200 to 201return Response({}, status=200)
to test, use
[root@localhost Twittme]# python3 ./manage.py testCreating test database for alias 'default'...System check identified no issues (0 silenced).........----------------------------------------------------------------------Ran 8 tests in 8.196sOKDestroying test database for alias 'default'...
so the process is a test database is created and used to test all 8 test cases (functions with test_ prefix) above.
Here we create a fail case, change /tweets/urls.py only for this test
urlpatterns = [# ...# path('action/', tweet_action_view),path('actions/', tweet_action_view),# ...]
to test
[root@localhost Twittme]# python3 ./manage.py testCreating test database for alias 'default'...System check identified no issues (0 silenced).FFF.....======================================================================FAIL: test_action_like (tweets.tests.TweetTestCase)----------------------------------------------------------------------Traceback (most recent call last):File "/root/SourceCode/Python/reactjs/Twittme/tweets/tests.py", line 49, in test_action_likeself.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)AssertionError: 404 != 200======================================================================FAIL: test_action_retweet (tweets.tests.TweetTestCase)----------------------------------------------------------------------Traceback (most recent call last):File "/root/SourceCode/Python/reactjs/Twittme/tweets/tests.py", line 68, in test_action_retweetself.assertEqual(response.status_code, 201)AssertionError: 404 != 201======================================================================FAIL: test_action_unlike (tweets.tests.TweetTestCase)----------------------------------------------------------------------Traceback (most recent call last):File "/root/SourceCode/Python/reactjs/Twittme/tweets/tests.py", line 57, in test_action_unlikeself.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)AssertionError: 404 != 200----------------------------------------------------------------------Ran 8 tests in 8.164sFAILED (failures=3)Destroying test database for alias 'default'...
so because url has been changes, 3 tests about “action” got failed, and detail lines are shown.
Under “System check identified no issues (0 silenced).”, we can see 8 letters corresponding to 8 test cases.
- all clear:
“……..”
- 3 fails:
“FFF…..”
So “.” means that test passed, “F” means failed.
- Remember to recover urls in /tweets/urls.py, and do the test again to check.
Verify or Install Node.js:
methods to install node.js varies.
nodejs homepage: https://nodejs.org/en/
I use “nvm(Node Version Manager)” to install node.js ```bash yum update
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/creationix/nvm/v0.35.1/install.sh | bash
nvm —version
0.35.1
nvm ls-remote # check available versions
nvm install 12.18.1
check versions:```bash[root@localhost ~]# npm --version6.14.5[root@localhost ~]# nvm --version0.35.1[root@localhost ~]# node --versionv12.18.1

