文件:
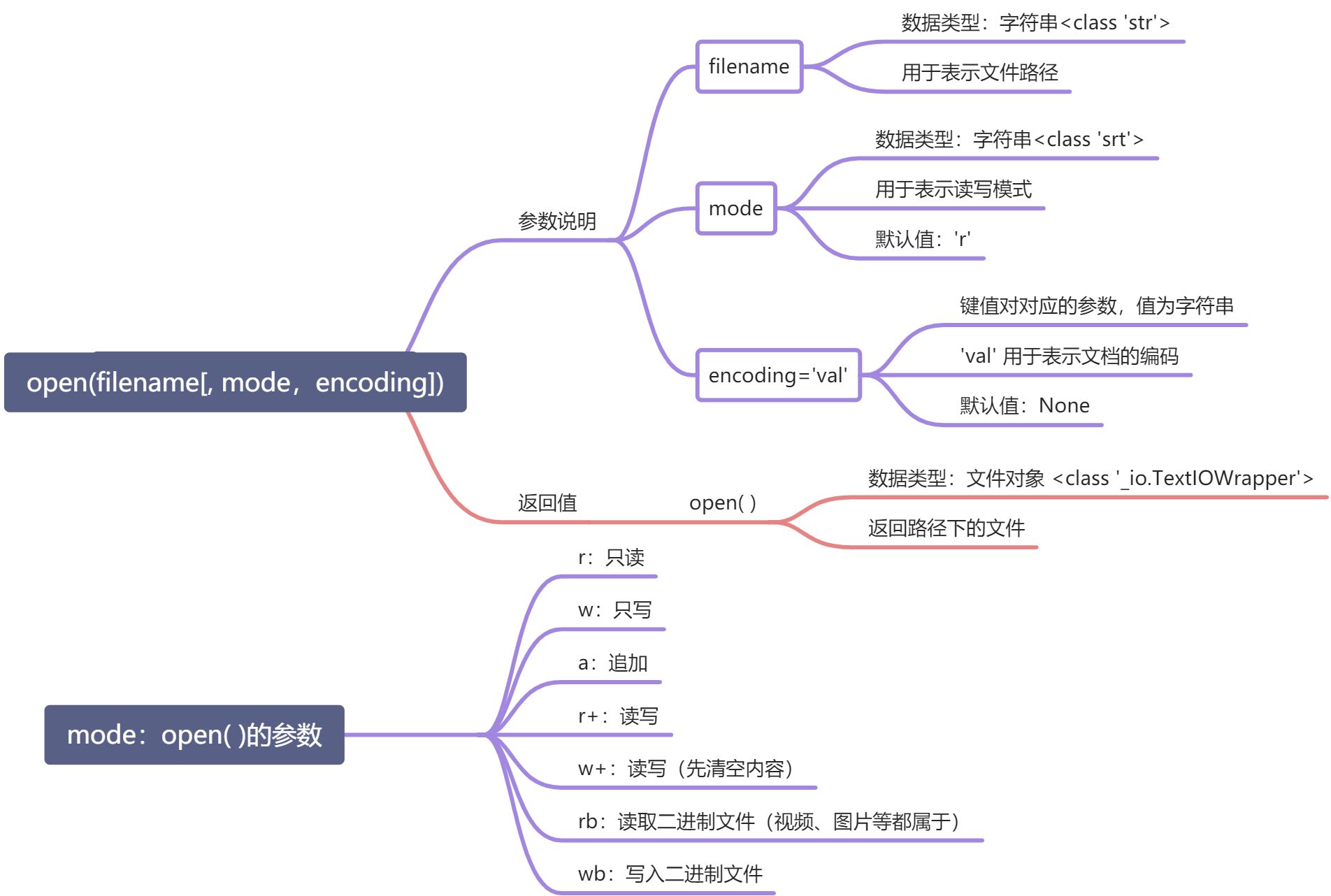
打开文件:open( )
open( )可以打开文件,如果文件不存在,会返回IOError异常
注意: 当文件被打开后完成了所需操作,必须把文件关掉
事实上open的参数有挺多的,但常用的也就思维导图里列出来的 要想了解更多,请参考官方文档:
open(file, mode=’r’, buffering=-1, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None, closefd=True, opener=None) https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/functions.html#open
 ```python
try:
f = open(“E:\MyFile.txt”, ‘r’) # 打开文件
print(“文件打开成功”)
f.close() # 关闭文件(文件操作完成后一定要关闭)
except IOError:
print(“文件不存在”)
```python
try:
f = open(“E:\MyFile.txt”, ‘r’) # 打开文件
print(“文件打开成功”)
f.close() # 关闭文件(文件操作完成后一定要关闭)
except IOError:
print(“文件不存在”)
```python# 上面的写法有点繁琐,可以用with...as...代替#================================================with open("E:\MyFile.txt", 'r') as f:print("文件打开成功")f.close()
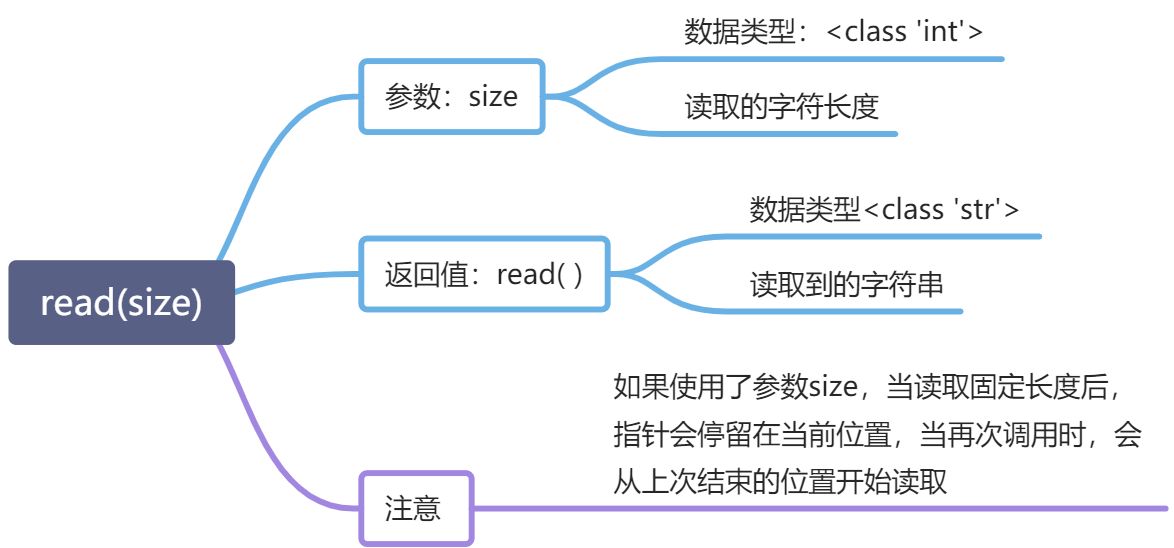
读取文件:read( )
读取全部:read( )【读取全部,返回一个字符串】 按行读取:readline( )【每次读取一行,返回一个列表】
 ```python
```python
read() 一次性读取全部
read(size) 读取不确定大小的文件
readline() 读取配置文件
=============================
with open(“E:\MyFile.txt”, ‘r’) as f: print(“文件打开成功”) print(f.read()) # 输出文件内容 f.close()
<a name="9e77631b"></a>#### 写入文件:write( )> 写入文件一定要注意 open(filename, mode) mode参数> mode> w:覆盖模式> a:追加模式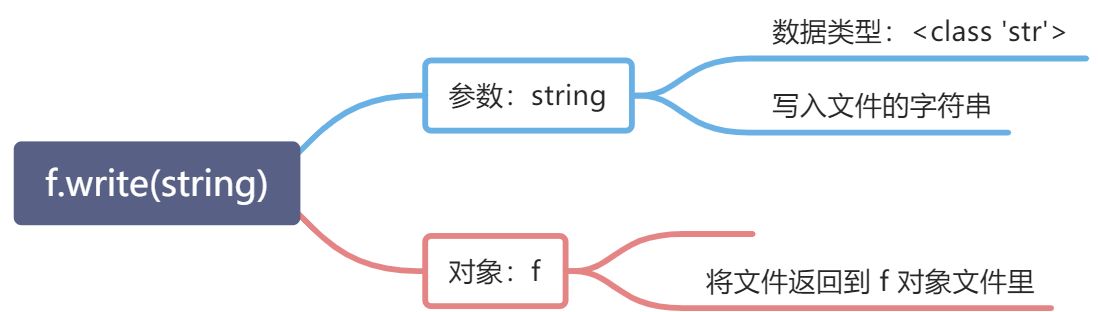```pythonwith open("E:\MyFile.txt", 'w') as f:f.write("追加到文件内的内容")f.close()
内存:
StringIO:
内存的字符串读写 (StringIO模块,可以把内存当做文件进行读写) (但无相打开和关闭) (BytesIO模块和SreingIO模块类似,但它是用来读写二进制文件的)
from io import StringIOf = StringIO() #创建一个文件对象f.write("Hibari") #写入print(f.getvalue()) #读取 读取的时候不要用read(),用getvalue()

