5905. 到达目的地的第二短时间
城市用一个 双向连通 图表示,图中有 n 个节点,从 1 到 n 编号(包含 1 和 n)。图中的边用一个二维整数数组 edges 表示,其中每个 edges[i] = [u, v] 表示一条节点 u 和节点 v 之间的双向连通边。每组节点对由 最多一条 边连通,顶点不存在连接到自身的边。穿过任意一条边的时间是 time 分钟。
每个节点都有一个交通信号灯,每 change 分钟改变一次,从绿色变成红色,再由红色变成绿色,循环往复。所有信号灯都 同时 改变。你可以在 任何时候 进入某个节点,但是 只能 在节点 信号灯是绿色时 才能离开。如果信号灯是 绿色 ,你 不能 在节点等待,必须离开。
第二小的值 是 严格大于 最小值的所有值中最小的值。
- 例如,
[2, 3, 4]中第二小的值是3,而[2, 2, 4]中第二小的值是4。
给你 n、edges、time 和 change ,返回从节点 1 到节点 n 需要的 第二短时间 。
注意:
- 你可以 任意次 穿过任意顶点,包括
1和n。 你可以假设在 启程时 ,所有信号灯刚刚变成 绿色 。
示例 1:
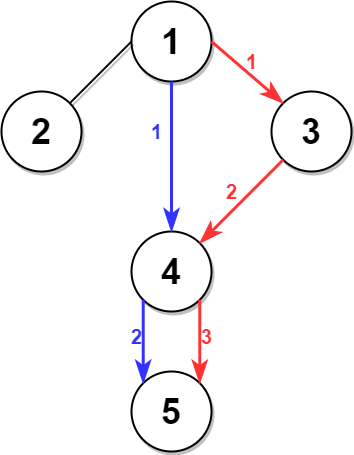
输入:n = 5, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[3,4],[4,5]], time = 3, change = 5
输出:13
解释:
上面的左图展现了给出的城市交通图。
右图中的蓝色路径是最短时间路径。
花费的时间是:
- 从节点 1 开始,总花费时间=0
- 1 -> 4:3 分钟,总花费时间=3
- 4 -> 5:3 分钟,总花费时间=6
因此需要的最小时间是 6 分钟。
右图中的红色路径是第二短时间路径。
- 从节点 1 开始,总花费时间=0
- 1 -> 3:3 分钟,总花费时间=3
- 3 -> 4:3 分钟,总花费时间=6
- 在节点 4 等待 4 分钟,总花费时间=10
- 4 -> 5:3 分钟,总花费时间=13
因此第二短时间是 13 分钟。
示例 2:
输入:n = 2, edges = [[1,2]], time = 3, change = 2
输出:11
解释:
最短时间路径是 1 -> 2 ,总花费时间 = 3 分钟
最短时间路径是 1 -> 2 -> 1 -> 2 ,总花费时间 = 11 分钟
提示:
2 <= n <= 10n - 1 <= edges.length <= min(2 * 10, n * (n - 1) / 2)edges[i].length == 21 <= u, v <= nu != v- 不含重复边
- 每个节点都可以从其他节点直接或者间接到达
1 <= time, change <= 10
方法1
边权相等,用bfs可以求单源最短路。
本题难点在于求第二短路!!!
用一个二维距离数组维护每个点到起点的最短距离和次短距离
更新方式
if (d[j][0] > x + 1) {d[j][1] = d[j][0];d[j][0] = x + 1;q.offer(new int[]{j, x + 1});} else if (d[j][0] < x + 1 && d[j][1] > x + 1) {d[j][1] = x + 1;q.offer(new int[]{j, x + 1});}
代码
class Solution {int[] h, e, ne;int idx = 0;public int secondMinimum(int n, int[][] edges, int time, int change) {int m = edges.length;h = new int[n + 1];e = new int[2 * m + 2];ne = new int[2 * m + 2];int[][] d = new int[n + 1][2];for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)Arrays.fill(d[i], 0x3f3f3f3f);Arrays.fill(h, -1);for (int[] p : edges) {int a = p[0], b = p[1];add(a, b);add(b, a);}Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();q.offer(new int[]{1, 0});while (!q.isEmpty()) {int[] p = q.poll();int cur = p[0];int x = p[1];for (int i = h[cur]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {int j = e[i];if (d[j][0] > x + 1) {d[j][1] = d[j][0];d[j][0] = x + 1;q.offer(new int[]{j, x + 1});} else if (d[j][0] < x + 1 && d[j][1] > x + 1) {d[j][1] = x + 1;q.offer(new int[]{j, x + 1});}}}int two = d[n][1] == 0x3f3f3f3f ? d[n][0] + 2 : d[n][1];int all = 0;for (int j = 0; j < two - 1; j++) {all += time;if ((all / change & 1) == 1) {all += change - all % change;}}return all + time;}void add(int a, int b) {e[idx] = b;ne[idx] = h[a];h[a] = idx++;}}

