在制备测序文库时,经常会增加PCR的步骤来扩增DNA片段。如何评估PCR的效果和影响,本文主要分享ENCODE中针对ChIP-Seq和ATAC-Seq标准来说明。
ENCODE中主要通过三个参数来反应Library Complexity:PCB1,PBC2和NRF。以下分别介绍各自的定义:
PCR Bottlenecking Coefficient 1 (PBC1)
- PBC1=M1/M_DISTINCT where
- M1: number of genomic locations where exactly one read maps uniquely
- M_DISTINCT: number of distinct genomic locations to which some read maps uniquely
PCR Bottlenecking Coefficient 2 (PBC2)
- PBC2= M1/M2 where
- M1: number of genomic locations where only one read maps uniquely
- M2: number of genomic locations where two reads map uniquely
Non-Redundant Fraction (NRF) - Number of distinct uniquely mapping reads (i.e. after removing duplicates) / Total number of reads.
如何计算这三个数值呢,在我们拿到比对的结果后(SAM或者BAM文件)
对于single end测序,以align.bam为例:
bedtools bamtobed -i align.bam | \awk \'BEGIN{OFS="\t"}{print $1,$2,$3,$6}\' | \grep -v \'chrM\' | sort | uniq -c | \awk \'BEGIN{mt=0;m0=0;m1=0;m2=0} ($1==1){m1=m1 1} ($1==2){m2=m2 1} {m0=m0 1} {mt=mt $1} END{m1_m2=-1.0; if(m2>0) m1_m2=m1/m2; printf "%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%f\t%f\t%f\n",mt,m0,m1,m2,m0/mt,m1/m0,m1_m2}\' > pbc_qc.txt
对于pair-end测序,以align.bam为例:
bedtools bamtobed -bedpe -i align.bam | \awk \'BEGIN{OFS="\t"}{print $1,$2,$4,$6,$9,$10}\' | \grep -v \'chrM\' | sort | uniq -c | \awk \'BEGIN{mt=0;m0=0;m1=0;m2=0} ($1==1){m1=m1 1} ($1==2){m2=m2 1} {m0=m0 1} {mt=mt $1} END{m1_m2=-1.0; if(m2>0) m1_m2=m1/m2; printf "%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\t%f\t%f\t%f\n",mt,m0,m1,m2,m0/mt,m1/m0,m1_m2}\' > pbc_qc.txt
最后文件中包含7列,分别为:
1)TotalReadPairs
2)DistinctReadPairs
3)OneReadPair
4)TwoReadPairs
5)NRF=Distinct/Total
6)PBC1=OnePair/Distinct
7)PBC2=OnePair/TwoPair
对于ChIP-seq结果解读: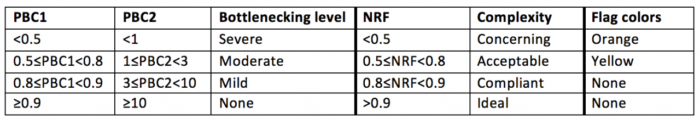
对于ATAC-Seq结果解读: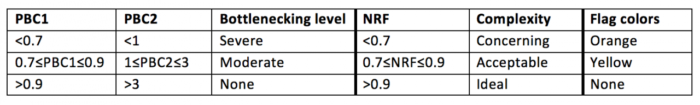
- 本文由 XP
- 转载请务必保留本文链接:https://www.plob.org/article/10866.html

