
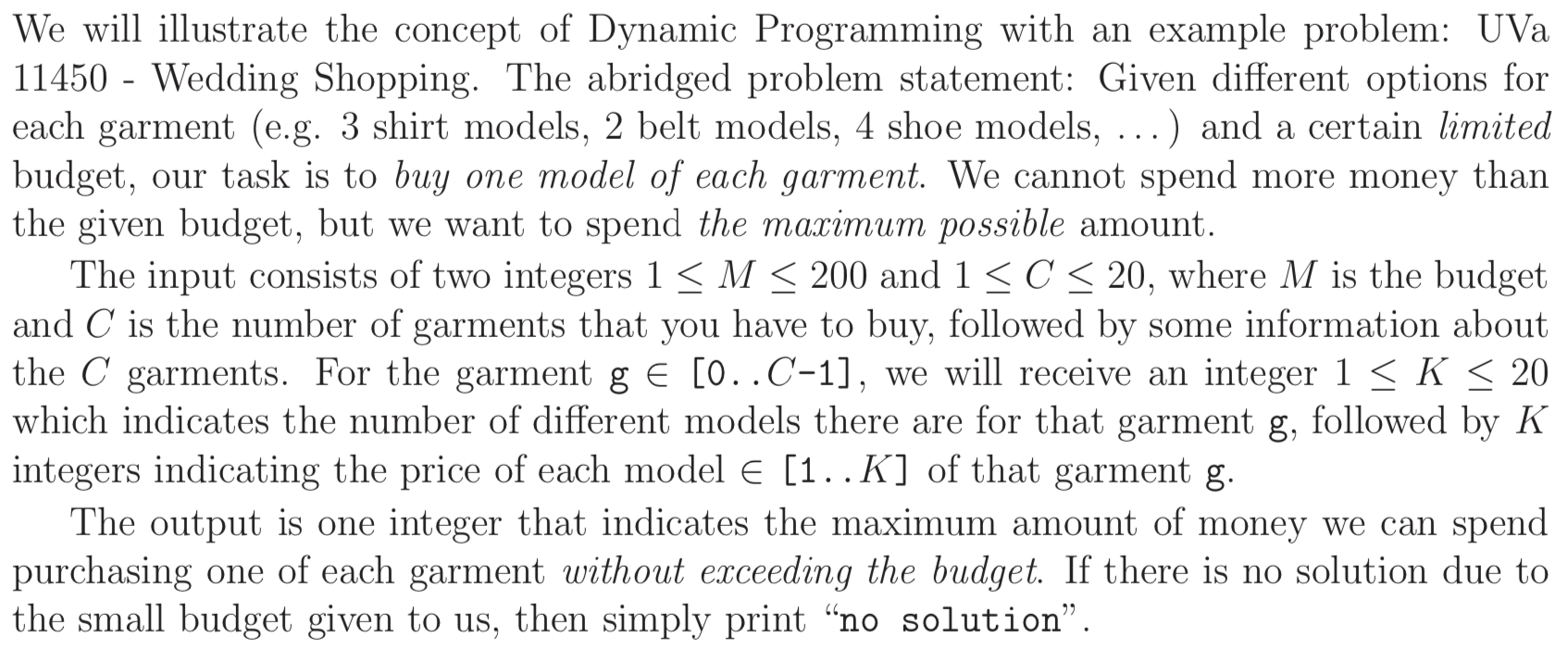
DP Illustration
// 先读题


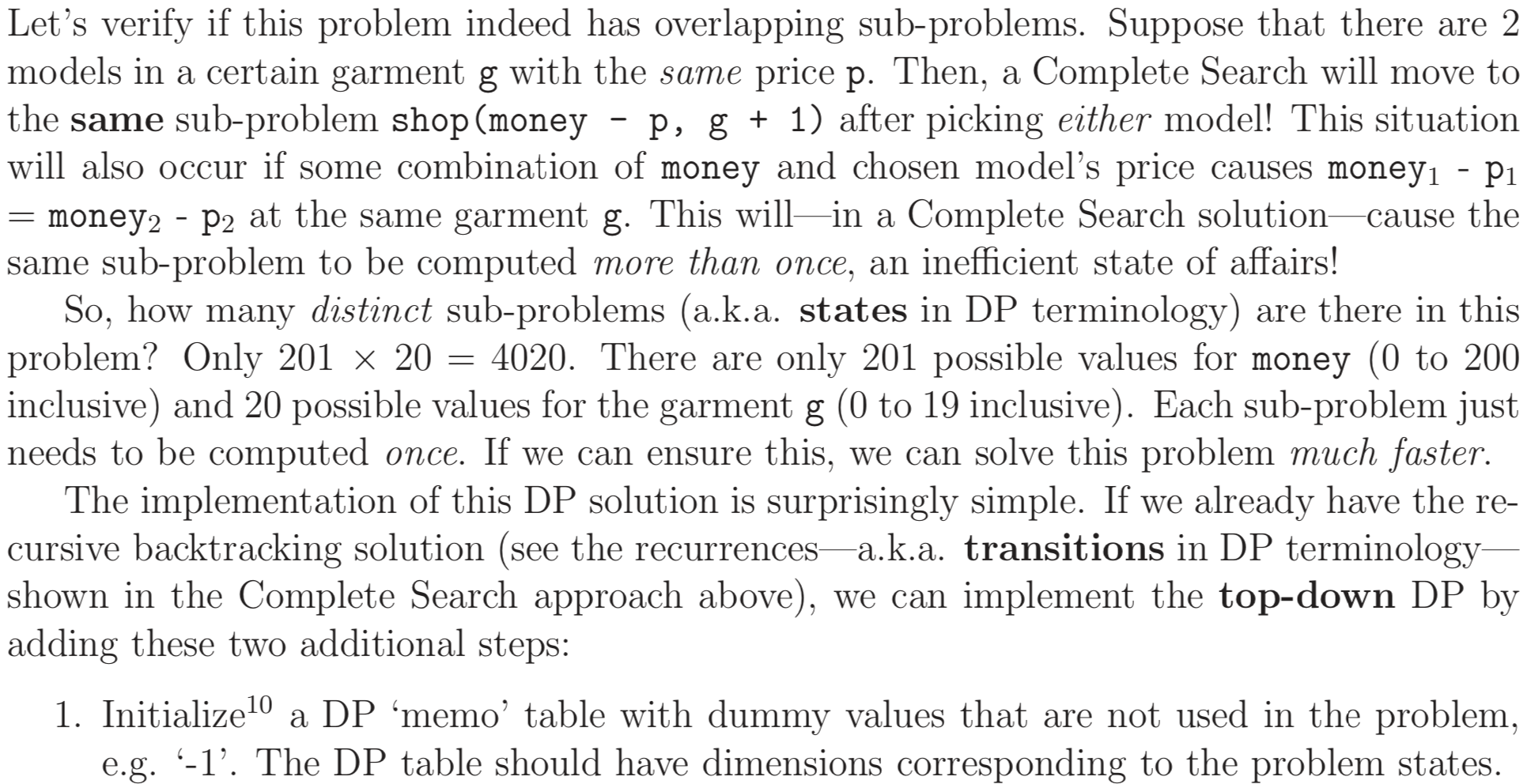
Complete Search(TLE)


Top-Down DP(AC)

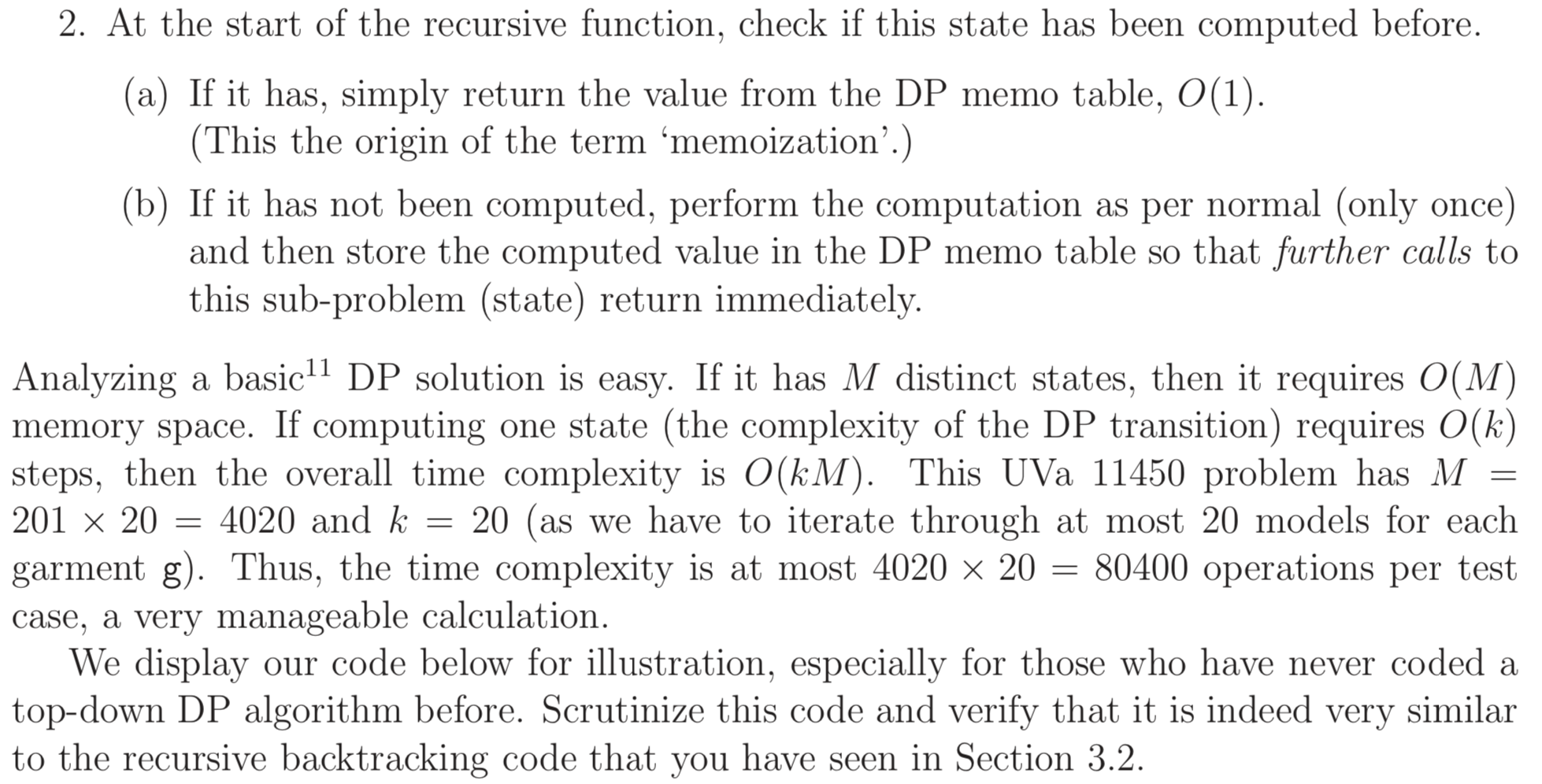
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int T, M, C;int price[25][25];int memo[25][210];int shop(int u, int remain){ if (remain < 0) return -1; if (u == C) return M - remain; int &ret = memo[u][remain]; if (ret != -1) return ret; for (int model = 1; model <= price[u][0]; model++) ret = max(ret, shop(u + 1, remain - price[u][model])); return ret;}int main(){ cin >> T; while (T--){ cin >> M >> C; for (int i = 0; i < C; i++){ cin >> price[i][0]; // 个数 for (int j = 1; j <= price[i][0]; j++) cin >> price[i][j]; } memset(memo, -1, sizeof memo); int ret = shop(0, M); if (ret < 0) cout << "no solution" << '\n'; else cout << ret << '\n'; } return 0;}
Bottom-Up DP(AC)


#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int T, M, C;int price[25][25];bool reachable[25][210];int main(){ cin >> T; while (T--){ cin >> M >> C; for (int i = 0; i < C; i++){ cin >> price[i][0]; for (int j = 1; j <= price[i][0]; j++) cin >> price[i][j]; } memset(reachable, false, sizeof reachable); // base cases for (int j = 1; j <= price[0][0]; j++) if (M - price[0][j] >= 0) reachable[0][M - price[0][j]] = true; for (int i = 1; i < C; i++) for (int money = 0; money < M; money++) if (reachable[i - 1][money]){ // 第i-1层的剩余money是可达的 for (int j = 1; j <= price[i][0]; j++) if (money >= price[i][j]) // 剩余money够买第j个物品的 reachable[i][money - price[i][j]] = true; } int money = 0; while (money <= M && !reachable[C - 1][money]) money++; if (money == M + 1) cout << "no solution" << '\n'; else cout << M - money << '\n'; } return 0;}

// 利用滚动数组优化#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int T, M, C;int price[25][25];bool reachable[2][210];int main(){ cin >> T; while (T--){ cin >> M >> C; for (int i = 0; i < C; i++){ cin >> price[i][0]; for (int j = 1; j <= price[i][0]; j++) cin >> price[i][j]; } memset(reachable, false, sizeof reachable); // base cases for (int j = 1; j <= price[0][0]; j++) if (M - price[0][j] >= 0) reachable[0 & 1][M - price[0][j]] = true; for (int i = 1; i < C; i++){ // 当前第i层的可达状态清空一下,避免和之前的混用 memset(reachable[i & 1], false, sizeof reachable[i & 1]); for (int money = 0; money < M; money++) if (reachable[(i - 1) & 1][money]){ // 第i-1层的剩余money是可达的 for (int j = 1; j <= price[i][0]; j++) if (money >= price[i][j]){ // 剩余money够买第j个物品的 reachable[i & 1][money - price[i][j]] = true; } } } int money = 0; while (money <= M && !reachable[(C - 1) & 1][money]) money++; if (money == M + 1) cout << "no solution" << '\n'; else cout << M - money << '\n'; } return 0;}// Note that for this problem, the memory savings are not significant. // For harder DP problems, // for example where there might be thousands of garment models instead of 20, // this space saving trick can be important.
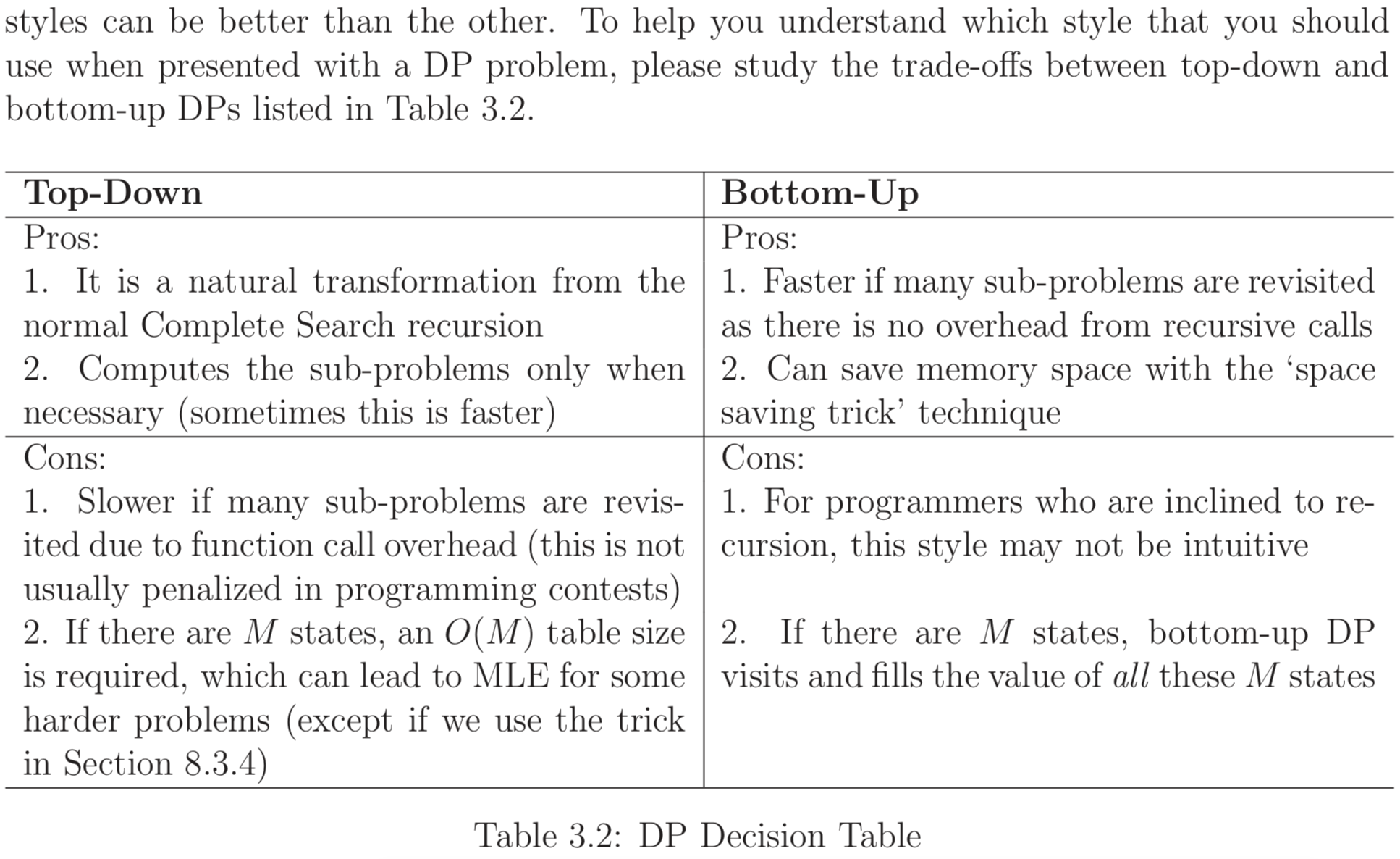
Top-Down verus Bottom-Up Dp

Displaying the Optimal Solution


#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int T, M, C;int price[25][25];int memo[25][210];int shop(int u, int remain){ if (remain < 0) return -1; if (u == C) return M - remain; int &ret = memo[u][remain]; if (ret != -1) return ret; for (int model = 1; model <= price[u][0]; model++) ret = max(ret, shop(u + 1, remain - price[u][model])); return ret;}void print_shop(int u, int remain){ if (remain < 0 || u == C) return ; for (int model = 1; model <= price[u][0]; model++){ if (shop(u + 1, remain - price[u][model]) == memo[u][remain]){ printf("%d%c", price[u][model], u == C - 1 ? '\n' : ' '); print_shop(u + 1, remain - price[u][model]); break; } }}int main(){ cin >> T; while (T--){ cin >> M >> C; for (int i = 0; i < C; i++){ cin >> price[i][0]; // 个数 for (int j = 1; j <= price[i][0]; j++) cin >> price[i][j]; } memset(memo, -1, sizeof memo); int ret = shop(0, M); if (ret < 0) cout << "no solution" << '\n'; else cout << ret << '\n'; print_shop(0, M); } return 0;}
Remarks Aboubt Dynamic Programming in Programming Contests





















