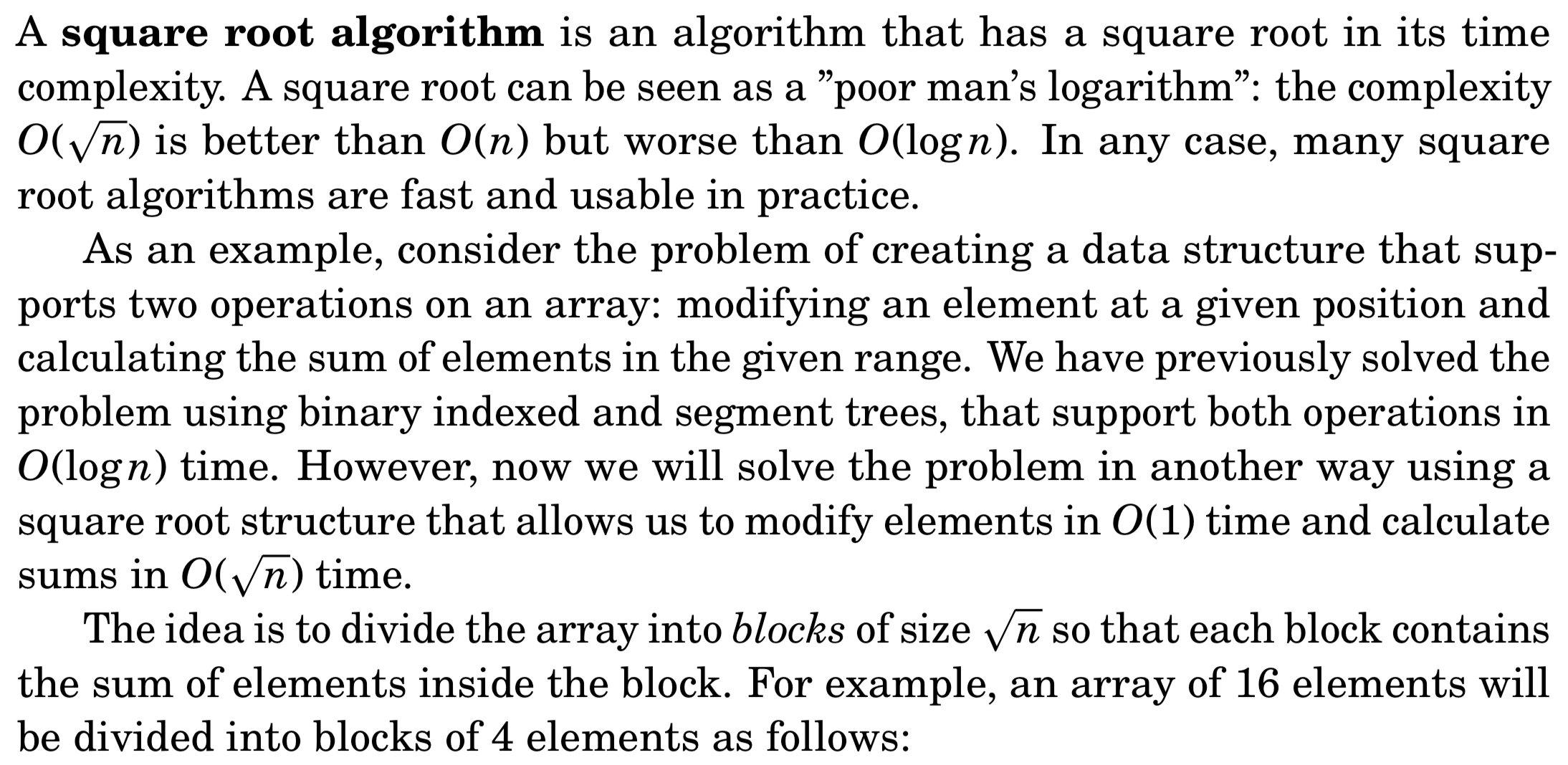
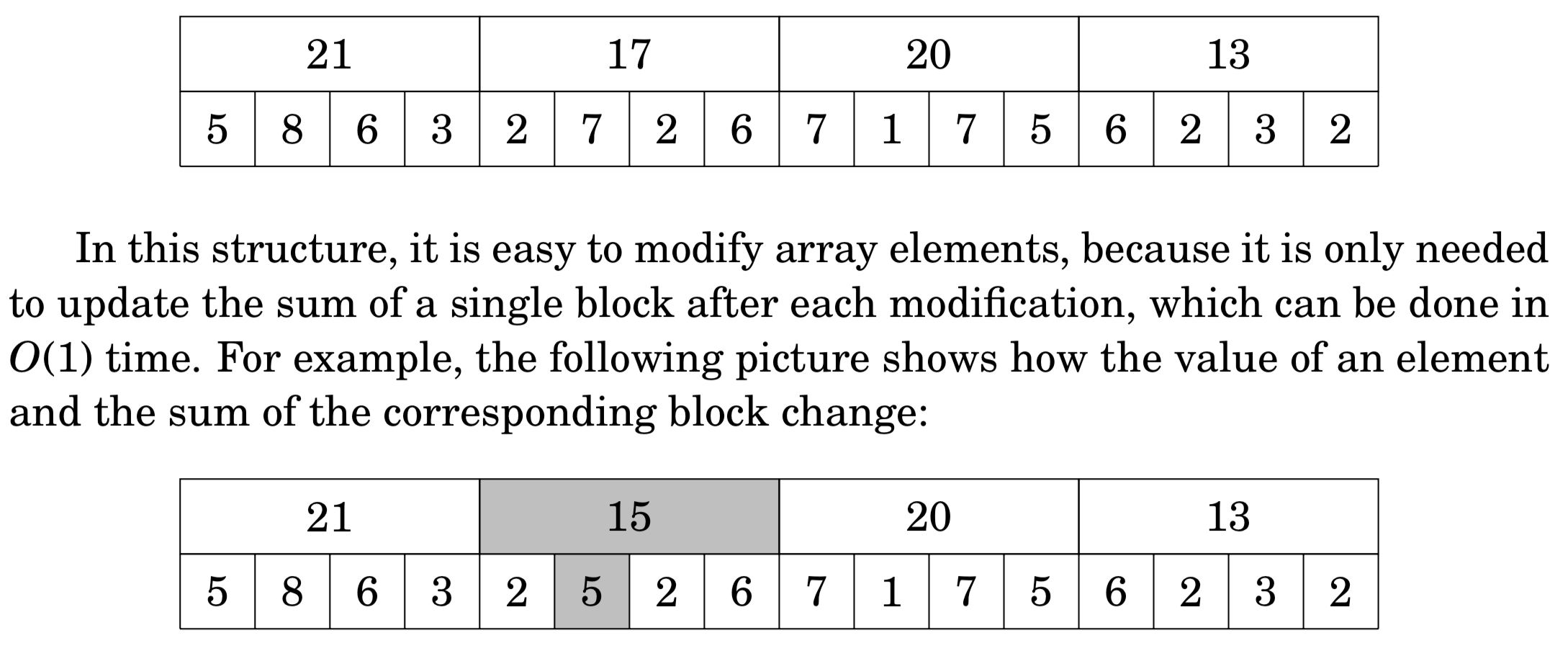
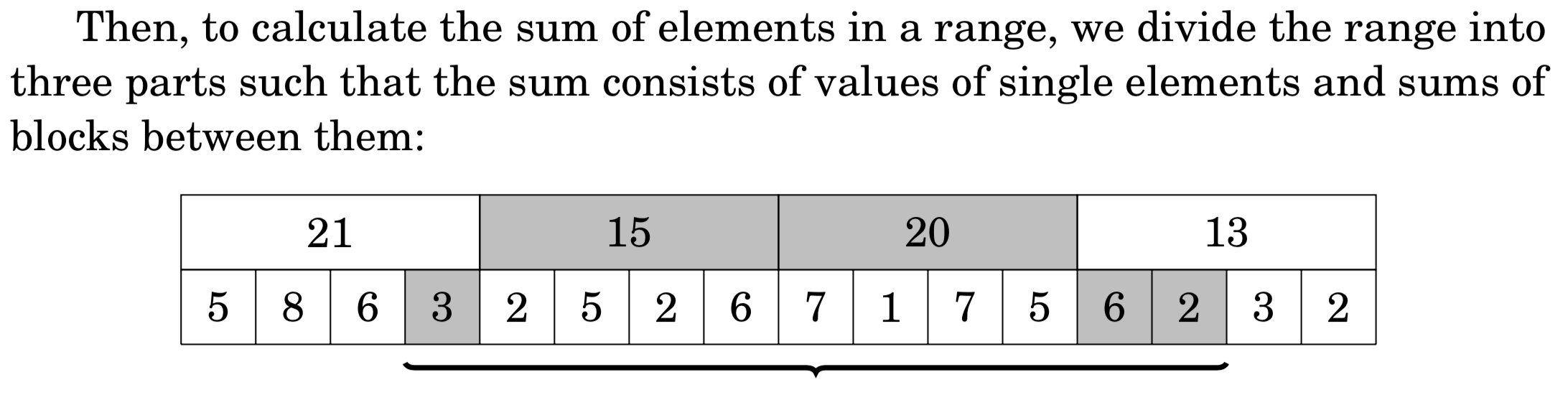
square root algorithm根号n算法
mo`s algorithm莫队
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/115243708
https://www.cnblogs.com/WAMonster/p/10118934.html
https://www.luogu.com.cn/blog/DPair2005/talk-talk-bruh-forces-in-oi
例题:奇数
询问离线后,排序的不同优化
// 询问离线后,排序的不同优化// 用时5038ms// 左端点在同一个块里的询问 ,我们按它们的 右端点升序排序// 否则我们按它们的 左端点升序排序struct node{int l, r, idx;bool operator< (const node &W) const{if (l / B == W.l / B) return r < W.r;return l < W.l;}}q[N];// 用时4879ms// 不难发现,排序的时候,我们每一个块都是按右端点升序排序的,// 这里显然只需要保证右端点单调就行了,所以降序排序也是对的。struct node{int l, r, idx;bool operator< (const node &W) const{if (l / B == W.l / B) return r > W.r;return l < W.l;}}q[N];// 用时3322ms// 然后我们又不难发现,每一次我们处理完左端点在某一个块中的所有询问后,// 右端点此时应该在序列的靠右端,处理下一个块时又回到最左端了,然后又不断往右,有一些浪费。// 所以我们考虑引入“奇偶块排序”,即对于左端点编号为奇数的块升序,左端点编号为偶数的块降序排序。// 关于小技巧的说明:对于两个区间交替的过程中,// r如果先回来,那么部分点就会被扫两次,// 那么对于r一正一逆的排序,就可以避免重复的情况struct node{int l, r, idx;bool operator< (const node &W) const{if (l / B != W.l / B) return l < W.l;if (l / B & 1) return r < W.r;return r > W.r;}}q[N];
没有离散化的AC代码,数据有点锅
// 没有离散化的#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10;int a[N], cnt[N], n, m;int B;int l = 1, r = 0;int ans[N], cur;struct node{int l, r, idx;bool operator< (const node &W) const{//if (l / B == W.l / B) return r > W.r;//return l < W.l;if (l / B != W.l / B) return l < W.l;if (l / B & 1) return r < W.r;return r > W.r;}}q[N];void add(int p){cnt[a[p]]++;if (cnt[a[p]] % 2 == 0) cur--;else cur++;}void del(int p){cnt[a[p]]--;if (cnt[a[p]] % 2 == 0) cur--;else cur++;}int main(){cin >> n;B = sqrt(n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);cin >> m;for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){scanf("%d%d", &q[i].l, &q[i].r);q[i].idx = i;}sort(q, q + m);for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){while (l > q[i].l) add(--l);while (r < q[i].r) add(++r);while (l < q[i].l) del(l++);while (r > q[i].r) del(r--);ans[q[i].idx] = cur;}for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) printf("%d\n", ans[i]);return 0;}
加入离散化后的AC代码
// 加入离散化#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10;int a[N], cnt[N], n, m;int B;int l = 1, r = 0;int ans[N], cur;int lsh[N];struct node{int l, r, idx;bool operator< (const node &W) const{if (l / B != W.l / B) return l < W.l;if (l / B & 1) return r < W.r;return r > W.r;}}q[N];void add(int p){cnt[a[p]]++;if (cnt[a[p]] % 2 == 0) cur--;else cur++;}void del(int p){cnt[a[p]]--;if (cnt[a[p]] % 2 == 0) cur--;else cur++;}int main(){cin >> n;B = sqrt(n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){scanf("%d", &a[i]);lsh[i] = a[i];}sort(lsh + 1, lsh + 1 + n);int num = unique(lsh + 1, lsh + 1 + n) - lsh - 1;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)a[i] = lower_bound(lsh+1, lsh+num+1, a[i]) - lsh; //解决掉a[i]<0的问题cin >> m;for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){scanf("%d%d", &q[i].l, &q[i].r);q[i].idx = i;}sort(q, q + m);for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){while (l > q[i].l) add(--l);while (r < q[i].r) add(++r);while (l < q[i].l) del(l++);while (r > q[i].r) del(r--);ans[q[i].idx] = cur;}for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) printf("%d\n", ans[i]);return 0;}
加入快读,用时3306ms
// 使用快读// 用时3306ms#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10;int a[N], cnt[N], n, m;int B;int l = 1, r = 0;int ans[N], cur;int lsh[N];inline int read(){int f = 1, x = 0;char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = x * 10 + c - '0';c = getchar();}return f * x;}struct node{int l, r, idx;bool operator< (const node &W) const{//if (l / B == W.l / B) return r < W.r;//return l < W.l;if (l / B != W.l / B) return l < W.l;if (l / B & 1) return r < W.r;return r > W.r;}}q[N];void add(int p){cnt[a[p]]++;if (cnt[a[p]] % 2 == 0) cur--;else cur++;}void del(int p){cnt[a[p]]--;if (cnt[a[p]] % 2 == 0) cur--;else cur++;}int main(){n = read();B = sqrt(n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){a[i] = read();lsh[i] = a[i];}sort(lsh + 1, lsh + 1 + n);int num = unique(lsh + 1, lsh + 1 + n) - lsh - 1;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)a[i] = lower_bound(lsh+1, lsh+num+1, a[i]) - lsh; //解决掉a[i]<0的问题m = read();for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){q[i].l = read(); q[i].r = read();q[i].idx = i;}sort(q, q + m);for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){while (l > q[i].l) add(--l);while (r < q[i].r) add(++r);while (l < q[i].l) del(l++);while (r > q[i].r) del(r--);ans[q[i].idx] = cur;}for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) printf("%d\n", ans[i]);return 0;}
加入inline,用时2606ms
在 c/c++ 中,为了解决一些频繁调用的小函数大量消耗栈空间(栈内存)的问题,特别的引入了 inline 修饰符,表示为内联函数。栈空间就是指放置程序的局部数据(也就是函数内数据)的内存空间。
// 使用inline// 用时2606ms#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10;int a[N], cnt[N], n, m;int B;int l = 1, r = 0;int ans[N], cur;int lsh[N];inline int read(){int f = 1, x = 0;char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = x * 10 + c - '0';c = getchar();}return f * x;}struct node{int l, r, idx;bool operator< (const node &W) const{//if (l / B == W.l / B) return r < W.r;//return l < W.l;if (l / B != W.l / B) return l < W.l;if (l / B & 1) return r < W.r;return r > W.r;}}q[N];inline void add(int p){cnt[a[p]]++;if (cnt[a[p]] % 2 == 0) cur--;else cur++;}inline void del(int p){cnt[a[p]]--;if (cnt[a[p]] % 2 == 0) cur--;else cur++;}int main(){n = read();B = sqrt(n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){a[i] = read();lsh[i] = a[i];}sort(lsh + 1, lsh + 1 + n);int num = unique(lsh + 1, lsh + 1 + n) - lsh - 1;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)a[i] = lower_bound(lsh+1, lsh+num+1, a[i]) - lsh; //解决掉a[i]<0的问题m = read();for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){q[i].l = read(); q[i].r = read();q[i].idx = i;}sort(q, q + m);for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){while (l > q[i].l) add(--l);while (r < q[i].r) add(++r);while (l < q[i].l) del(l++);while (r > q[i].r) del(r--);ans[q[i].idx] = cur;}for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) printf("%d\n", ans[i]);return 0;}
加入分块,用时2529ms
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10;int a[N], cnt[N], n, m;int B;int l = 1, r = 0;int ans[N], cur;int lsh[N];int bel[N];inline int read(){int f = 1, x = 0;char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = x * 10 + c - '0';c = getchar();}return f * x;}// [l, r]这个区间,进行查找// bel[l] bel[W.l]根据所在的块进行区分struct node{int l, r, idx;bool operator< (const node &W) const{if (bel[l] != bel[W.l]) return bel[l] < bel[W.l];if (bel[l] & 1) return r < W.r;return r > W.r;}}q[N];inline void add(int p){cnt[a[p]]++;if (cnt[a[p]] % 2 == 0) cur--;else cur++;}inline void del(int p){cnt[a[p]]--;if (cnt[a[p]] % 2 == 0) cur--;else cur++;}int main(){n = read();B = sqrt(n);// 分块for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) bel[i] = (i - 1) / B + 1;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){a[i] = read();lsh[i] = a[i];}sort(lsh + 1, lsh + 1 + n);int num = unique(lsh + 1, lsh + 1 + n) - lsh - 1;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)a[i] = lower_bound(lsh+1, lsh+num+1, a[i]) - lsh; //解决掉a[i]<0的问题m = read();for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){q[i].l = read(); q[i].r = read(); q[i].idx = i;}sort(q, q + m);for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){while (l > q[i].l) add(--l);while (r < q[i].r) add(++r);while (l < q[i].l) del(l++);while (r > q[i].r) del(r--);ans[q[i].idx] = cur;}for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) printf("%d\n", ans[i]);return 0;}
例题:索引



这道题目,本意是二分,我们在处理多次区间修改的过程中,可以用分块处理
// 分块#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int N = 1e7 + 10;int k, n, a[N];int bel[N], tag[N];int B;inline int read(){int f = 1, x = 0;char c = getchar();while (c < '0' || c > '9'){if (c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();}while (c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = x * 10 + c - '0';c = getchar();}return f * x;}// 核心是这个环节,特别有趣// 体现了O(n * sqrt(n))的思想void update(int l, int r, int c){for (int i = l; i <= min(bel[l] * B, r); i++) a[i] += c;if (bel[l] != bel[r]) for (int i = (bel[r]-1) * B + 1; i <= r; i++) a[i] += c;for (int i = bel[l] + 1; i <= bel[r] - 1; i++) tag[i] += c;}void ask(){int l = 1, r = n, best = 1;while (l < r){int mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1;if (a[mid] + tag[bel[mid]] <= 0) l = mid, best = mid;else r = mid - 1;}if (a[best] + tag[bel[best]] == 0) puts("YES");else puts("NO");//for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d ", a[i]);//puts("");}int main(){k = read(), n = read();B = sqrt(n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){a[i] = read() - i;bel[i] = (i - 1) / B + 1;}ask();for (int i = 2; i <= k; i++){int l = read(), r = read(), c = read();update(l, r, c);ask();}return 0;}