入门
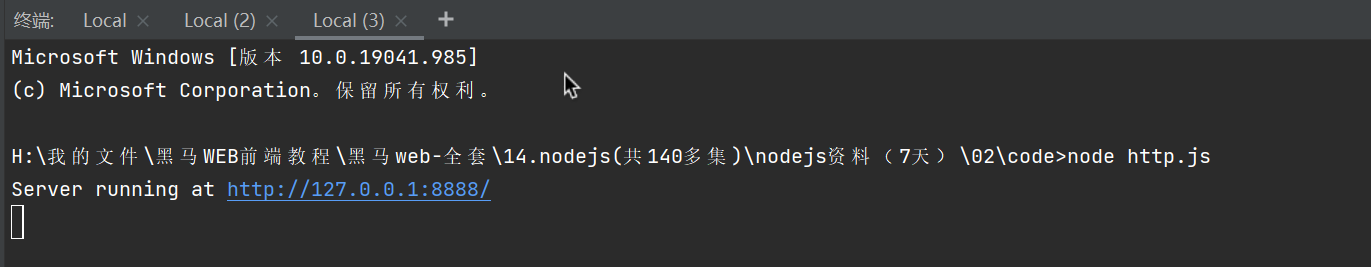
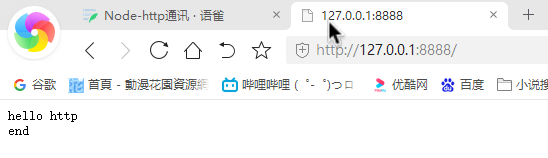
var http = require("http");http.createServer(function (req, res) {// 发送 HTTP 头部// HTTP 状态值: 200 : OK// 内容类型: text/plainres.writeHead(200, { "Content-type": "text/plain" });// 发送响应数据 "Hello World"//响应有两个方法res.write('hello http\n');//响应的内容res.end("end");//响应结束}).listen(8888);// 终端打印如下信息console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:8888/');
实战案例
服务端
创建一个服务端的代码
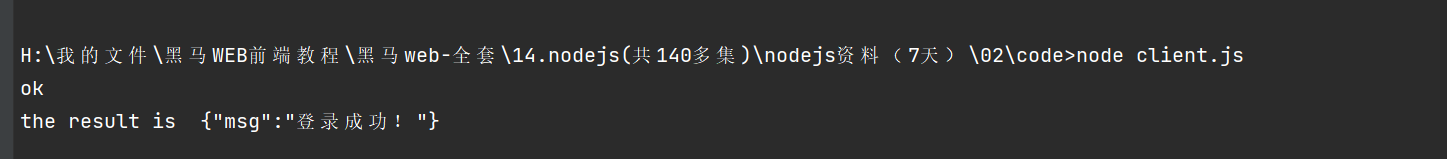
var url = require('url');var http = require('http');var server = http.createServer();function bizLogic (url) {if (url.path.toLowerCase() === '/login') {return {msg: '登录成功!'}} else if (url.path.toLowerCase() === '/user') {return {msg: [{name: '小明',class: '一年级1班'}, {name: '小红',class: '一年级3班'}]}} else {return {msg: 404}}}server.on('request', function (request, response) {if ('url' in request) {response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8'});response.write(JSON.stringify(bizLogic(url.parse(request.url))), 'utf8');} else {response.writeHead(404, {'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8'});response.write('找不到页面');}response.end();});server.listen(88, function () {console.log('服务器已经开始监听88端口');});
url.parse()方法
方法说明:
使用 url.parse()方法将路径解析为一个方便操作的对象。
第二个参数为 true 表示直接将查询字符串转为一个对象(通过query属性来访问),默认第二个参数为false。
当第二个参数为false时
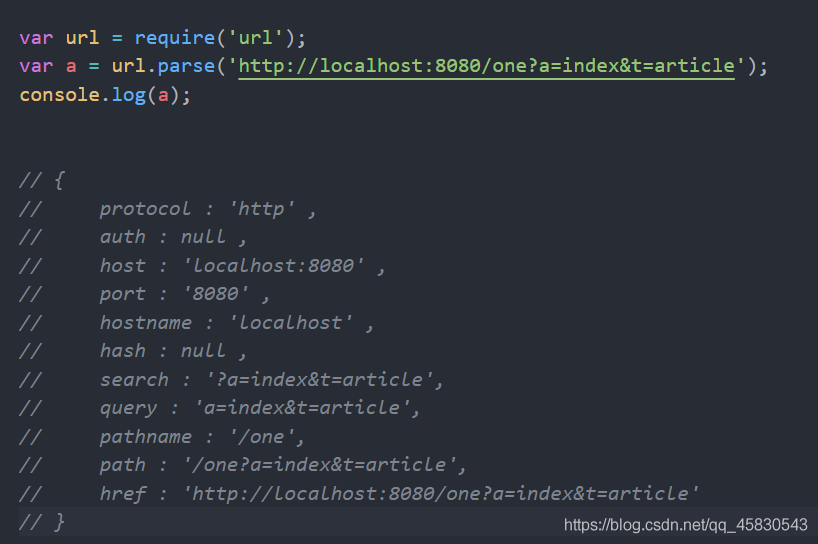
如上图,当url为http://localhost:8080/one?a=index&t=article时,
其中,pathname为不包含查询字符串的路径部分(即该路径不包含?后面的那些内容),query即是查询字符串部分。
当第二个参数为true时,
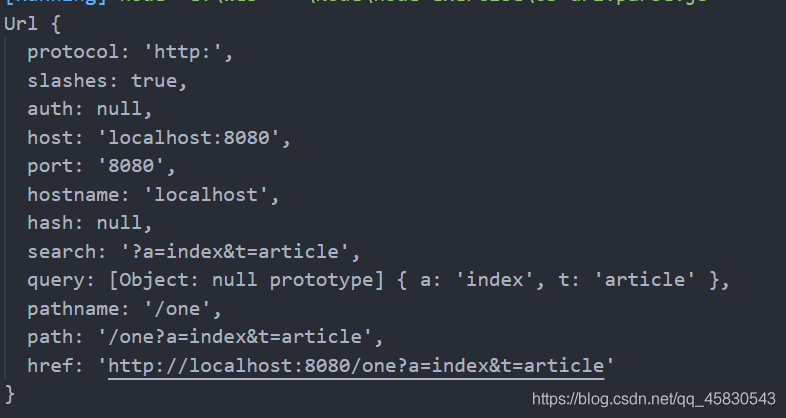
我们可以看到,第二个参数为true时,查询字符串被解析为一个对象了。
客户端
var http = require('http');var option, req;option = {host: '127.0.0.1',port: 88,path: '/login'};req = http.request(option, function (res) {if (res.statusCode === 200) {console.log('ok');}res.on('data', function (chunk) {console.log('the result is ', chunk.toString());});});req.on('error', function (error) {console.log('something is wrong:', error.message);});req.end();