概念
相比较于synchronized它具备如下特点:
- 可中断
- 可以设置超时时间;
- 可以设置公平锁(先到先得,而不是随机获取锁);
- 支持多个条件变量;
与synchronized一样,都支持可重入;
基本语法:
reentrantLock.lock();try{//临界区}finally{//释放锁reentrantLock.unlock();}
可重入
可重入是指同一个线程如果首次获得了这把锁,那么因为它是这把锁的拥有者,因此有权利再次获取这把锁。
如果是不可重入锁,那么第二次获得锁时,自己也会被锁挡住。
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();public static void main(String[] args) {method1();}public static void method1() {lock.lock();try {System.out.println("execute method1");method2();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public static void method2() {lock.lock();try {System.out.println("execute method2");method3();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public static void method3() {lock.lock();try {System.out.println("execute method3");} finally {lock.unlock();}}
输出
execute method1 execute method2 execute method3
可打断
private static void test1() {ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {log.debug("启动...");try {lock.lockInterruptibly();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();log.debug("等锁的过程中被打断");return;}try {log.debug("获得了锁");} finally {lock.unlock();}}, "t1");lock.lock();log.debug("获得了锁");t1.start();try {sleep(1);t1.interrupt();log.debug("执行打断");} finally {lock.unlock();}}
23:40:12.610 c.TestInterrupt [main] - 获得了锁23:40:12.612 c.TestInterrupt [t1] - 启动...23:40:13.615 c.TestInterrupt [main] - 执行打断23:40:13.616 c.TestInterrupt [t1] - 等锁的过程中被打断java.lang.InterruptedExceptionat java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.doAcquireInterruptibly(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java:898)at java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.acquireInterruptibly(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java:1222)at java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock.lockInterruptibly(ReentrantLock.java:335)at cn.itcast.n4.reentrant.TestInterrupt.lambda$test1$1(TestInterrupt.java:49)at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
注意如果是不可中断模式,那么即使使用了 interrupt 也不会让等待中断
private static void test2() {ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {log.debug("启动...");lock.lock();try {log.debug("获得了锁");} finally {lock.unlock();}}, "t1");lock.lock();log.debug("获得了锁");t1.start();try {sleep(1);t1.interrupt();log.debug("执行打断");sleep(1);} finally {log.debug("释放了锁");lock.unlock();}}
18:06:56.261 [main] c.TestInterrupt - 获得了锁18:06:56.265 [t1] c.TestInterrupt - 启动...18:06:57.266 [main] c.TestInterrupt - 执行打断 // 这时 t1 并没有被真正打断, 而是仍继续等待锁18:06:58.267 [main] c.TestInterrupt - 释放了锁18:06:58.267 [t1] c.TestInterrupt - 获得了锁
锁超时
private static void test2() {ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {log.debug("启动...");if (!lock.tryLock()) {log.debug("获取立刻失败,返回");return;}try {log.debug("获得了锁");} finally {lock.unlock();}}, "t1");lock.lock();log.debug("获得了锁");t1.start();try {sleep(2);} finally {lock.unlock();}}
18:15:02.918 [main] c.TestTimeout - 获得了锁18:15:02.921 [t1] c.TestTimeout - 启动...18:15:02.921 [t1] c.TestTimeout - 获取立刻失败,返回
private static void test1() {ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {log.debug("启动...");try {if (!lock.tryLock(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {log.debug("获取等待 1s 后失败,返回");return;}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {log.debug("获得了锁");} finally {lock.unlock();}}, "t1");lock.lock();log.debug("获得了锁");t1.start();try {sleep(2);} finally {lock.unlock();}}
18:19:40.537 [main] c.TestTimeout - 获得了锁18:19:40.544 [t1] c.TestTimeout - 启动...18:19:41.547 [t1] c.TestTimeout - 获取等待 1s 后失败,返回
公平锁
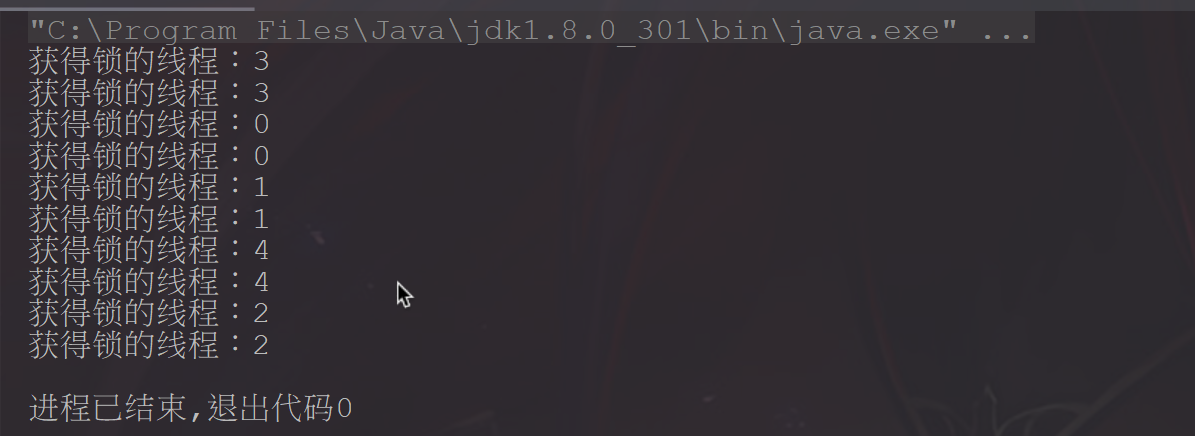
public class ReentrantLockFairTest {static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {new Thread(new ThreadDemo(i)).start();}}static class ThreadDemo implements Runnable {Integer id;public ThreadDemo(Integer id) {this.id = id;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {lock.lock();try {System.out.println("获得锁的线程:" + id);} finally {lock.unlock();}}}}}
公平锁结果: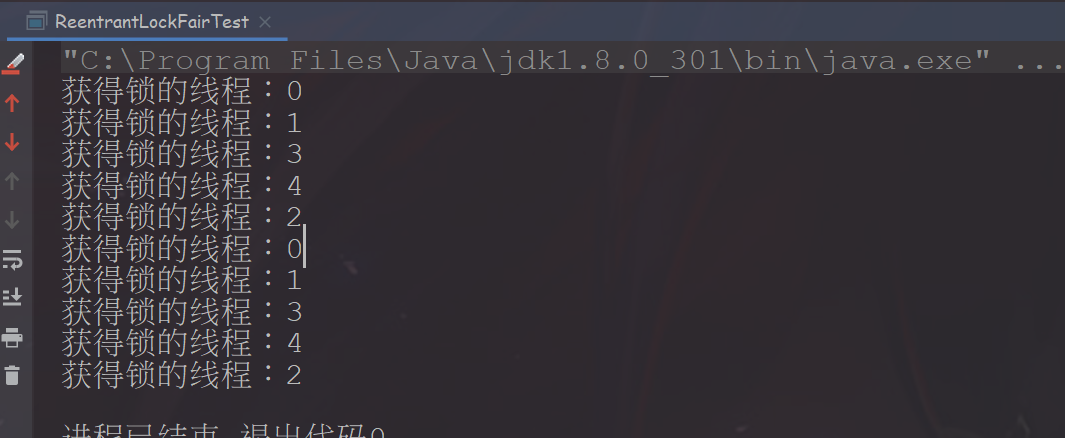
非公平锁结果: