1 线程的五大状态 & 线程方法
本文视频截图均来自【狂神说 Java】B 站视频。
线程的五大状态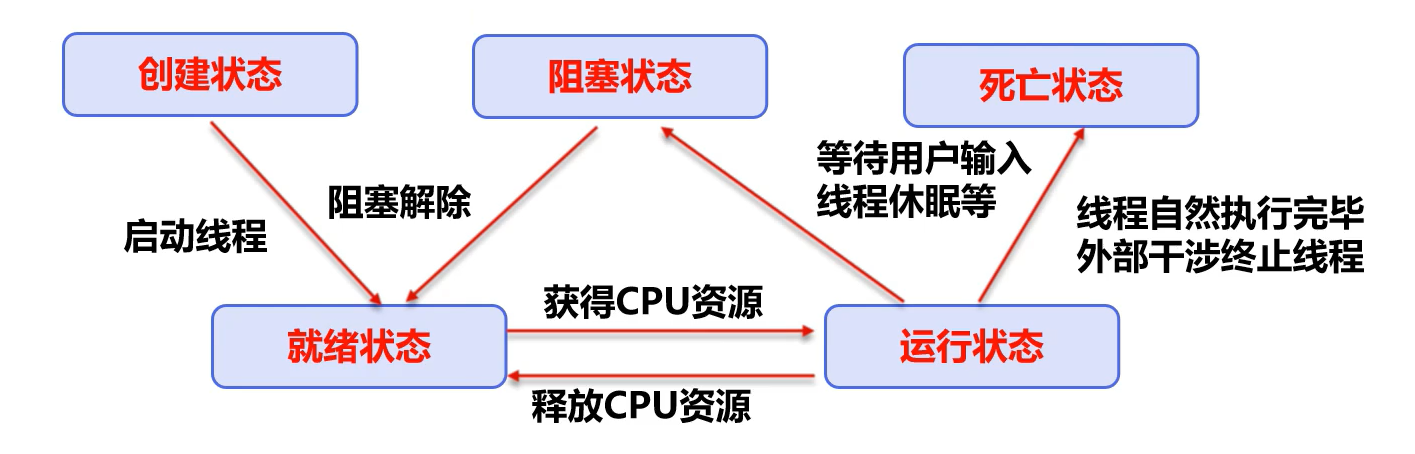
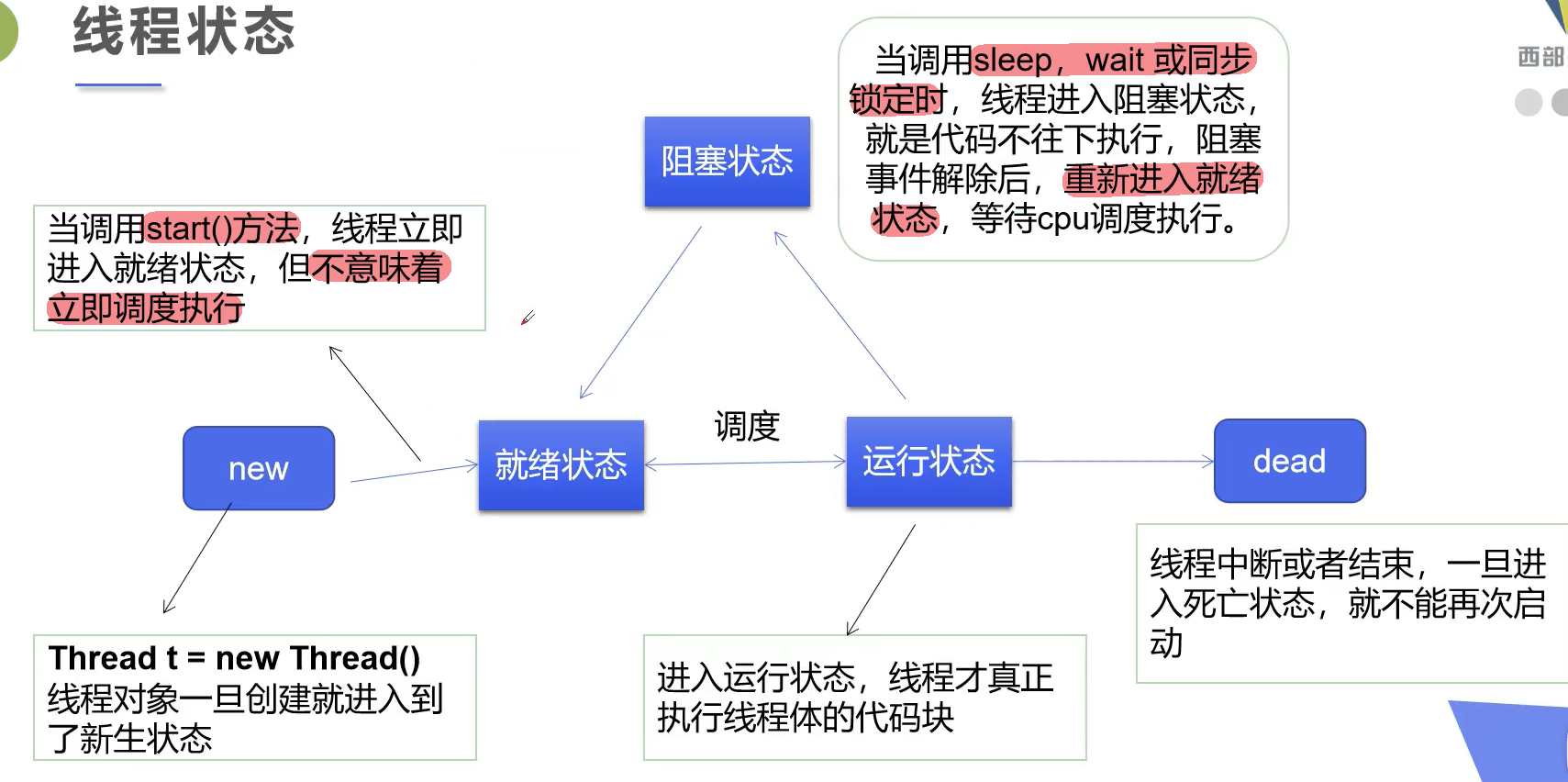
线程方法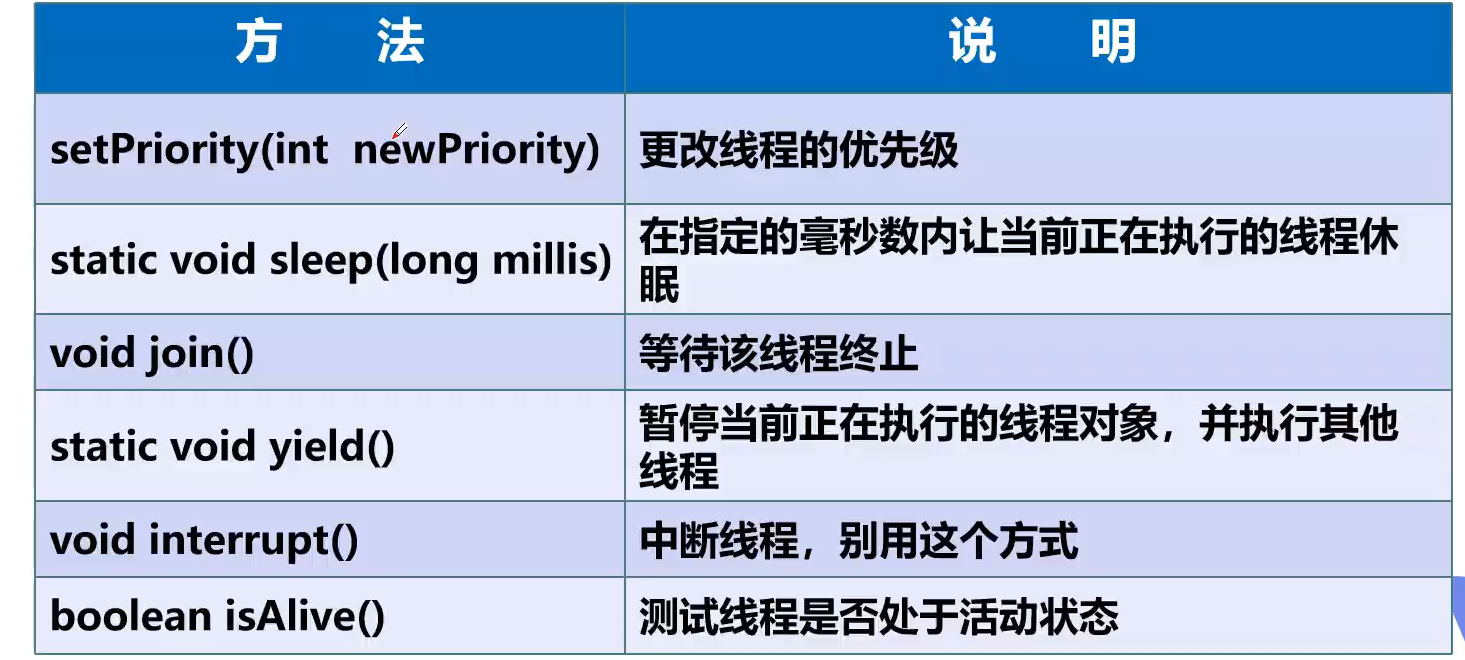
2 线程操作
2.1 线程停止
- 不推荐使用 JDK 提供的
stop(),destroy()方法(已废弃) - 推荐让线程自己停下来
- 建议使用一个标志位来终止线程,如当
flag=false时,终止线程
2.2 线程休眠 sleep
sleep()单位为毫秒sleep()存在InterruptedException异常,需要try-catch或者抛出异常(Idea 里面会自动识别并建议你这么做)sleep()后线程进入就绪状态- 每一个对象都有一个锁,
**sleep()**不会释放锁。
2.3 线程让出 CPU yield
yield()让线程进入就绪状态**yield()**不一定能让出 CPU,但是否延迟执行,由 CPU 调度决定
2.4 线程强制执行 join
- 如果子线程使用
join(),则主线程需要等待子线程结束后才能执行 join()可以实现线程的插队public class MyThread implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ==> " + i);try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public static void main(String[] args) {MyThread myThread = new MyThread();Thread t1 = new Thread(myThread, "Child thread");t1.start();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("Main thread ==> " + i);try {// 子线程通过 join 插队if (i == 2) {try {t1.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}}
执行结果:
Main thread ==> 0Child thread ==> 0Main thread ==> 1Child thread ==> 1Main thread ==> 2Child thread ==> 2Child thread ==> 3Child thread ==> 4Main thread ==> 3Main thread ==> 4
2.5 观测线程状态
- 通过
getState()获取线程状态 - JDK 官方文档关于线程状态的描述

BLOCKED阻塞状态:等待锁NEW新生状态:刚被创建,但还没有运行RUNNABLE就绪状态:Java 中为正在执行的线程TERMINATED终止状态:已经退出的线程TIMED_WAITING等待时间状态:正在等待另一个线程执行动作到达指定等待时间WAITING等待动作状态:正在等待另一个线程执行特定动作
public class TestState {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread(()->{System.out.println("Thread starts...");for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("Thread terminating...");});Thread.State state = thread.getState();System.out.println(state); // NEWthread.start();state = thread.getState();System.out.println(state); // RUNNABLEwhile (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}state = thread.getState();System.out.println(state); // TIMED_WAITING or TERMINATED}}}
退出之后的线程不能再启动,即处于TERMINATED状态的线程不能再执行start()。
3 守护线程
- 线程分为用户线程和守护线程
- 虚拟机必须保证用户线程执行完毕
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
- e.g. 后台记录操作日志、监控内存、垃圾回收
public class TestDaemon implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {System.out.println("Daemon running...");try {Thread.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public static void main(String[] args) {// 守护线程 daemonThread daemonThread = new Thread(new TestDaemon());daemonThread.setDaemon(true); // 设置守护线程daemonThread.start();// 用户线程 userThread userThread = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println("User running...");try {Thread.sleep(5);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});userThread.start();}}
执行结果:
Daemon running...Daemon running......User running...Daemon running...Daemon running......Daemon running...Daemon running...User running...Daemon running...Daemon running...Daemon running...Daemon running...Daemon running...Daemon running...
可以发现,在 User 线程结束后,守护线程又运行了一段时间才终止的。说明 Java 虚拟机并没有立即退出。

