不变序列算法
此类算法不会修改算法所作用的容器或对象,适用于所有容器。它们的时间复杂度都是O(n)的。

min两个对象中较小的(可自定义比较器)max求两个对象中较大的(可自定义比较器)min_element求区间中的最小值(可自定义比较器)max_element求区间中的最大值(可自定义比较器)for_each对区间中的每个元素都做某种操作count计算区间中等于某值的元素个数count_if计算区间中符合某种条件的元素个数find再区间中查找等于某值的元素find_if在区间中查找符合某种条件的元素search在区间中查找另一个区间第一次出现的位置(可自定义比较器)search_n在区间中查找第一次出现等于某值的连续n个元素(可自定义比较器)equal判断两个区间是否相等(可自定义比较器)mismatch逐个比较两个区间的元素,返回第一次不相等的两个元素的位置(可自定义比较器)lexicographical_compare按字典序比较两个区间的大小(可自定义比较器)



min_element和max_element都是从第一个元素逐个比较到最后#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;class A {public:int n;A(int i):n(i) {}};bool operator<(const A & a1, const A & a2) {cout << "< called,a1=" << a1.n << " a2=" << a2.n << endl;if(a1.n == 3 && a2.n == 7)return true;return false;}void main() {A aa[] = {3, 5, 7, 2, 1};cout << min_element(aa, aa+5)->n << endl;cout << max_element(aa, aa+5)->n << endl;}/* 输出* < called, a1=5 a2=3* < called, a1=7 a2=3* < called, a1=2 a2=3* < called, a1=1 a2=3* 3* < called, a1=3 a2=5* < called, a1=3 a2=7* < called, a1=7 a2=2* < called, a1=7 a2=1* 7*/
变值算法
此类算法会修改源区间或目标区间元素的值。值被修改的那个区间,不可以是属于关联容器的
for_each对区间中的每个元素都做某种操作copy复制一个区间到别处copy_backward赋值一个区间到别处,但目标区间是从后往前被修改的transform将一个区间的元素变形后拷贝到另一个区间swap_ranges交换两个区间内容fill用某个值填充区间fill_n用某个值替换区间中的n个元素generate用某个操作的结果填充区间generate_n用某个操作的结果替换区间中n个元素replace将区间中的某个值替换为另一个值replace_if将区间中符合某种条件的元素值替换成另一个值

#include <vector>#include <iostream>#include <numeric>#include <list>#include <algorithm>#include <iterator>using namespace std;class CLessThan9 {public:bool operator()(int n) {return n < 9;}};void outputSquare(int value) {cout << value * value << " ";}int calCube(int value) {return value * value * value;}void main() {const int SIZE = 10;int a1[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};int a2[] = {100, 2, 8,1,50,3,8,9,10,2};vector<int> v(a1, a1 + SIZE);ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());cout << endl << "1) ";copy(v.begin(), v.end(), output); // 输出 5 4 1 3 7 8 9 10 6 2copy(a2, a2+SIZE, v.begin()); // copy的目标区间v必须有足够的区间,不然造成越界报错cout << endl << "2) ";cout << count(v.begin(), v.end(), 8); // 输出 2cout << endl << "3) "; // 输出 6cout << count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), ClessThan9()); // CLessThan9()是个对象cout << endl << "4) ";cout << *(min_element(v.begin(), v.end())); // 输出 1cout << endl << "5) ";cout << *(max_element(v.begin(), v.end())); // 输出 100cout << endl << "6) ";cout << accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0); // 求和cout << endl << "7) ";for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), outputSquare); // 输出 10000 4 ...vector<int> cubes(SIZE);transform(a1, a1+SIZE, cubes.begin(), calCube);cout << endl << "8) ";copy(cubes.begin(), cubes.end(), output); // 输出 1 8 27 64 ...}
copy函数要有想象力


void main() {
int a[4] = {1,2,3,4};
My_ostream_iterator
- 如何编写 `My_ostream_iterator` ?`copy` 的源代码:<br /><br />上面程序中调用语句 `copy(a, a+4, oit)` 实例化后得到的 `copy` 如下:```cppMy_ostream_iterator<int> copy(int * _F, int * _L, My_ostream_iterator<int> _X) {for(; _F != _L; ++_X, ++_F)*_X = *_F;return (_X);}
- 需要重载
++*=三个运算符- 因为赋值运算符
=的存在,*运算符需要返回引用
- 因为赋值运算符
- 在
=运算符中输出这个值就可以#include <iterator>using namespace std;class My_ostream_iterator: public iterator<output_iterator_tag, T> {private:string sep; // 分隔符ostream & os;public:My_ostream_iterator(ostream & o, string s):sep(s), os(o){}void operator ++(){}; // ++只需要定义就可以,不需要做什么My_ostream_iterator & operator * () {return * this;}My_ostream_iterator * operator = (const T & val) {os << val << sep; return *this;}};
删除算法

remove删除区间中等于某个值的元素unique删除元素中连续相等的元素,只留下一个(可自定义比较器)
算法都是
使用 unique 返回的迭代器减去 begin 就可以得到剩余的元素个数
void main() {int a[5] = {1,2,3,2,5};int b[6] = {1,2,3,2,5,6};ostream_iterator<int> oit(cout, ",");int * p = remove(a, a+5, 2);cout << "1) "; copy(a, a+5, oit); cout << endl; // 输出 1) 1,3,5,2,5cout << "2) " << p - a << endl; // 输出 2) 3vector<int> v(b, b+6);remove(v.begin(), v.end(), 2);cout << "3) "; copy(v.begin(), v.end(), oit); cout << endl; // 输出 3) 1,3,5,6,5,6cout << "4) "; cout << v.size() << endl; // v中元素没有减少,输出 4) 6}
变序算法

reverse颠倒区间的前后次序next_permutation将区间改为下一个排列(可自定义比较器)- 排列也是有大小顺序的
prev_permutation将区间改为上一个排列(可自定义比较器)random_shuffle随机打乱区间内元素的顺序partition把区间内满足某个条件的元素移到前面,不满足的移到后面



void main() {
string str = “231”;
char szStr[] = “324”;
while(next_permutation(str.begin(), str.end())) {
cout << str << endl;
}
cout << ““ << endl;
while(next_permutation(szStr, szStr+3)) {
cout << szStr << endl;
}
sort(str.begin(), str.end());
cout << ““ << endl;
while(next_permutation(str.begin(), str.end())) {
cout << str << endl;
}
}
/* 输出
- 312
- 321
- 342
- 423
- 432
- 132
- 213
- 231
- 312
- 321 */ ```
int main()
{
int a[] = {8, 7, 10};
list
return 0;
}
<a name="cBJu8"></a># 排序算法- `sort` (可自定义比较器)- `stable_sort` 从小到大并保持想等元素之间的相对次序(可自定义比较器)- `partial_sort` 对区间部分排序,直到最小的n个元素就位(可自定义比较器)- `nth_element` 对区间部分排序,使得第n小的元素(n从0开始算)就位,而且比它小的都在它前面,比它大的都在它后面(可自定义比较器)- `make_heap` 使区间成为一个“堆”(可自定义比较器)- `push_heap` 将元素加入一个是“堆”的区间(可自定义比较器)- `pop_heap` 类似上- `sort_heap` 将一个“堆”区间进行排序,排序后该区间就是普通的有序区间了,不再是“堆”了```cpp#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;class MyLess{public:bool operator()(int n1, int n2){return (n1 % 10) < (n2 % 10);}};int main(){int a[] = {14, 2, 9, 222, 77};sort(a, a + 5, MyLess());int i;for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i)cout << a[i] << " ";cout << endl;sort(a, a + 5, greater<int>());for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i)cout << a[i] << " ";return 0;}// 输出2 222 14 77 9222 77 14 9 2
有序区间算法

binary_search判断区间中是否包含某个元素includes判断是否一个区间中的每个元素,都在另一个区间中lower_bound查找最后一个不小于某值的元素的位置upper_bound查找第一个大于某值的元素的位置equal_range同时获取lower_bound和upper_boundmerge合并两个有序区间到第三个区间set_union将两个有序区间的并拷贝到第三个区间set_intersection将两个有序区间的交拷贝到第三个区间set_difference将两个有序区间的差拷贝到第三个区间set_symmetric_difference将两个有序区间的对称差拷贝到第三个区间
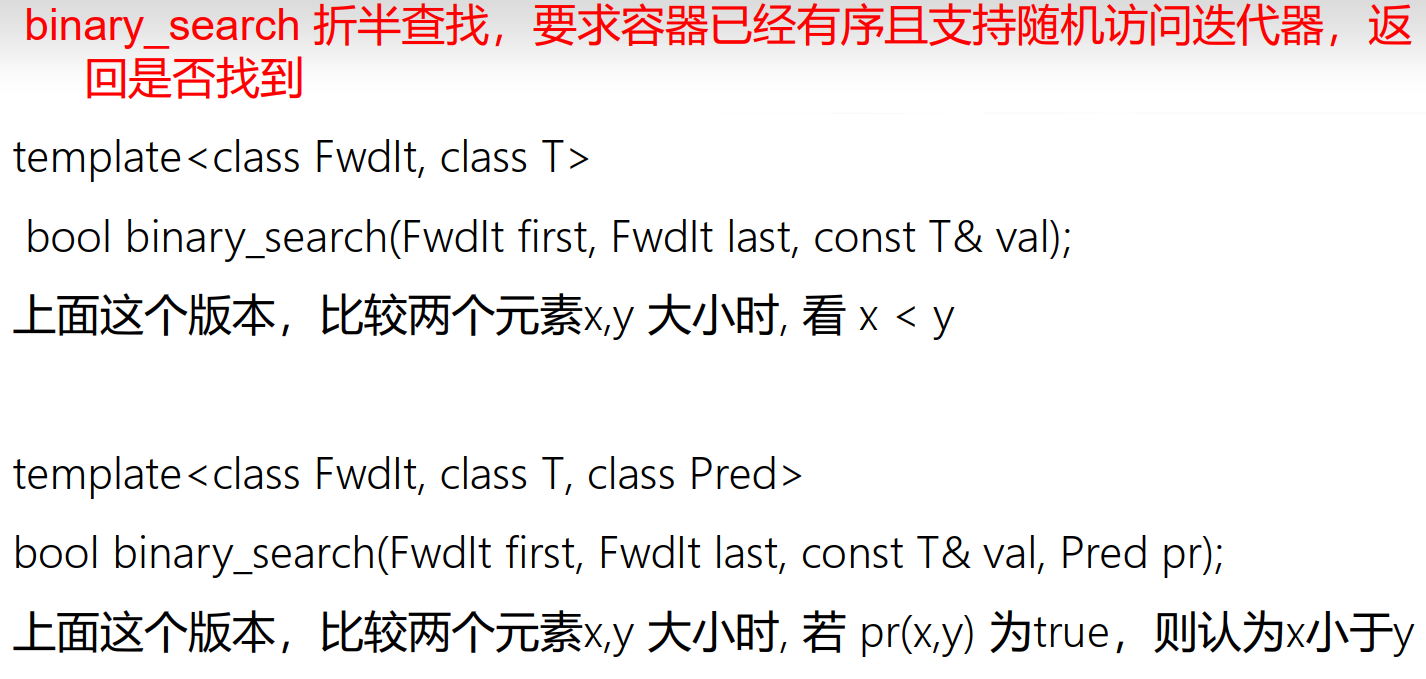
#include <vector>#include <bitset>#include <iostream>#include <numeric>#include <list>#include <algorithm>#include <iterator>using namespace std;bool Greater10(int n){return n > 10;}int main(){const int SIZE = 10;int a1[] = {2, 8, 1, 50, 3, 100, 8, 9, 10, 2};vector<int> v(a1, a1 + SIZE);ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");vector<int>::iterator loc;loc = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 10);if (loc != v.end()){cout << endl<< "1) " << loc - v.begin();}loc = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater10);if (loc != v.end())cout << endl<< "2) " << loc - v.begin();sort(v.begin(), v.end());if (binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9))cout << "3) "<< "9 found" << endl;return 0;}// 输出1) 82) 33) 9 found
bitset







