1️⃣ 前言
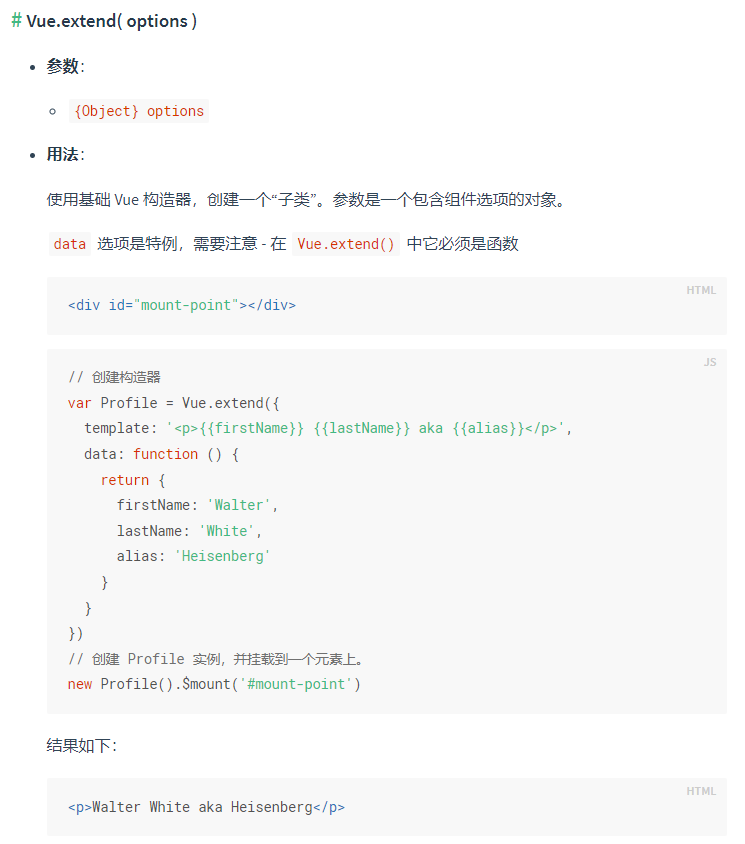
Vue.extend 是 Vue 里的一个全局 API,它提供了一种灵活的挂载组件的方式,这个 API 在日常开发中很少使用,毕竟只在碰到某些特殊的需求时它才能派上用场( 比如全局的弹窗提示组件 )
1️⃣ Vue.extend 定义
1️⃣ 源码分析
export function initExtend(Vue: GlobalAPI) {// 这个cid是一个全局唯一的递增的id// 缓存的时候会用到它Vue.cid = 0let cid = 1/*** 类继承*/Vue.extend = function(extendOptions: Object): Function {// extendOptions 就是我我们传入的组件optionsextendOptions = extendOptions || {}const Super = thisconst SuperId = Super.cid// 每次创建完 Sub 构造函数后,都会把这个函数储存在 extendOptions 上的 _Ctor 中// 下次如果用再同一个 extendOptions 创建 Sub 时// 就会直接从 _Ctor 返回const cachedCtors = extendOptions._Ctor || (extendOptions._Ctor = {})if (cachedCtors[SuperId]) {return cachedCtors[SuperId]}const name = extendOptions.name || Super.options.nameif (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && name) {validateComponentName(name)}// 创建 Sub 构造函数const Sub = function VueComponent(options) {this._init(options)}// 继承 Super,如果使用 Vue.extend,这里的 Super 就是 VueSub.prototype = Object.create(Super.prototype)Sub.prototype.constructor = SubSub.cid = cid++// 将组件的 options 和 Vue 的 options 合并,得到一个完整的 options// 可以理解为将 Vue 的一些全局的属性,比如全局注册的组件和 mixin,分给了 SubSub.options = mergeOptions(Super.options, extendOptions)Sub['super'] = Super// 下面两个设置了下代理,// 将 props 和 computed 代理到了原型上// 你可以不用关心这个if (Sub.options.props) {initProps(Sub)}if (Sub.options.computed) {initComputed(Sub)}// 继承 Vue 的 global-apiSub.extend = Super.extendSub.mixin = Super.mixinSub.use = Super.use// 继承 assets 的 api,比如注册组件,指令,过滤器ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function(type) {Sub[type] = Super[type]})// 在 components 里添加一个自己// 不是主要逻辑,可以先不管if (name) {Sub.options.components[name] = Sub}// 将这些 options 保存起来// 一会创建实例的时候会用到Sub.superOptions = Super.optionsSub.extendOptions = extendOptionsSub.sealedOptions = extend({}, Sub.options)// 设置缓存// 就是上文的缓存cachedCtors[SuperId] = Subreturn Sub}}function initProps(Comp) {const props = Comp.options.propsfor (const key in props) {proxy(Comp.prototype, `_props`, key)}}function initComputed(Comp) {const computed = Comp.options.computedfor (const key in computed) {defineComputed(Comp.prototype, key, computed[key])}}
其实这个 Vue.extend 做的事情很简单,就是继承 Vue,正如定义中说的那样,创建一个子类.<br />最终返回的这个 Sub 是:
const Sub = function VueComponent(options) {this._init(options)}
那么上文的例子中的 new Profile() 执行的就是这个方法了,因为继承了 Vue 的原型,这里的 _init 就是 Vue 原型上的 _init 方法
Vue.prototype._init = function(options?: Object) {const vm: Component = this// a uidvm._uid = uid++let startTag, endTag/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`mark(startTag)}vm._isVue = true// merge optionsif (options && options._isComponent) {initInternalComponent(vm, options)} else {vm.$options = mergeOptions(resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),options || {},vm)}/* istanbul ignore else */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {initProxy(vm)} else {vm._renderProxy = vm}// expose real selfvm._self = vmnextinitLifecycle(vm)initEvents(vm)initRender(vm)callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/propsinitState(vm)initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/propscallHook(vm, 'created')/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false)mark(endTag)measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag)}if (vm.$options.el) {vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)}}
这个函数里有很多逻辑,它主要做的事情就是初始化组件的事件,状态等,大多不是我们本次分析的重点,目前只需要关心里面的这一段代码:
if (options && options._isComponent) {initInternalComponent(vm, options)} else {vm.$options = mergeOptions(resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),options || {},vm)}
执行 new Profile() 的时候没有传任何参数,所以这里的 options 是 undefined,会走到 else 分值,然后 resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor)其实就是拿到 Sub.options 这个东西,你可以在上文的 Vue.extend 源码中找到它,然后将 Sub.options 和 new Profile() 传入的options合并,再赋值给实例的$options,所以如果 new Profile() 的时候传入了一个 options,这个 options 将会合并到 vm.$options上,然后在这个 _init 函数的最后判断了下vm.$options.el 是否存在,存在的话就执行 vm.$mount 将组件挂载到 el 上,因为我们没有传 options,所以这里的 el 肯定是不存在的,所以你才会看到例子中的 new Profile().$mount('#mount-point') 手动执行了 $mount 方法,其实经过这些分析你就会发现,我们直接执行 new Profile({ el: '#mount-point' }) 也是可以的,除了 el 也可以传其他参数,接着往下看就知道了。<br />$mount 方法会执行“挂载”,其实内部的整个过程是很复杂的,会执行 render、update、patch 等等,由于这些不是本次文章的重点,你只需要知道她会将组件的 dom 挂载到对应的 dom 节点上就行了,如$mount('#mount-point') 会把组件 dom 挂载到 #mount-point这个元素上。
1️⃣ 使用
经过上面的分析,你应该大致了解了Vue.extend的原理以及初始化过程,以及简单的使用,其实这个初始化和平时的new Vue()是一样的,毕竟两个执行的同一个方法。但是在实际的使用中,我们可能还需要给组件传 props,slots 以及绑定事件,下面我们来看下如何做到这些事情。
2️⃣ 使用 Prop
假如我们有一个 message 组件
<template><div class="message-box">{{ message }}</div></template><script>export default {props: {message: {type: String,default: ''}}}</script>
它需要一个 props 来显示这个 message,在使用 Vue.extend 时,要想给组件传参数,我们需要在实例化的时候传一个 propsData, 如:
const MessageBoxCtor = Vue.extend(MessageBox)new MessageBoxCtor({propsData: {message: 'hello'}}).$mount('#target')
你可能会不明白为什么要传propsData,没关系,接下来就来搞懂它,毕竟文章的目的就是彻底分析。
在上文的 _init 函数中,在合并完 $options 后,还执行了一个函数 initState(vm),它的作用就是初始化组件状态(props,computed,data):
export function initState(vm: Component) {vm._watchers = []const opts = vm.$optionsif (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)if (opts.data) {initData(vm)} else {observe((vm._data = {}), true /* asRootData */)}if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {initWatch(vm, opts.watch)}}
别的不看,只看这个:
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)
function initProps(vm: Component, propsOptions: Object) {const propsData = vm.$options.propsData || {}const props = (vm._props = {})// ...省略其他逻辑}
这里的 propsData 就是数据源,他会从 vm.$options.propsData 上取,上文说过在执行 _init 的时候 new MessageBoxCtor(options) 的 options 会被合并和 vm.$options 上,所以我们就可以在 options 中传入 propsData 属性,使得 initProps() 能取到这个值,从而进行 props 的初始化。
2️⃣ 绑定事件
可能有时候我们还想给组件绑定事件,其实这里应该很多小伙伴都知道怎么做,我们可以通过vm.$on给组件绑定事件,这个也是平时经常用到的一个 api
const MessageBoxCtor = Vue.extend(MessageBox)const messageBoxInstance = new MessageBoxCtor({propsData: {message: 'hello'}}).$mount('#target')messageBoxInstance.$on('some-event', () => {console.log('success')})
2️⃣ 使用示例
创建一个 hint 组件
<template><div class="hint" v-if="show" ref="modal"><div class="title">{{ title }}</div><div class="content">{{ content }}</div><div class="but"><div class="no" @click="cancel">{{ cancelText }}</div><div class="ok" @click="confirm">{{ confirmText }}</div></div></div></template><script>export default {data() {return {show: false,title: "",content: "",confirmText: "确定",cancelText: "取消",onConfirm: () => {// 确认执行函数this.$emit("confirm");},onCancel: () => {// 取消执行函数this.$emit("cancle");},};},methods: {// 取消cancel() {console.log("取消了吗?");this.onCancel("cancel");this.remove();},// 确认confirm() {console.log("确定了吗?");this.onConfirm("confirm");this.remove();},// 确认或取消后移除元素remove() {this.show = false;},},};</script><style lang="less">.hint {position: absolute;top: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;left: 0;margin: auto;width: 300px;height: 200px;background-color: #fff;box-shadow: 0 0 5px #ccc;border-radius: 10px;overflow: hidden;.title,.content {display: flex;align-items: center;justify-content: center;padding: 10px 0;font-size: 20px;}.but {cursor: pointer;width: 100%;height: 50px;position: absolute;bottom: 0;border-top: 1px solid #f5f5f5;display: flex;align-items: center;justify-content: space-around;.ok,.no {display: flex;align-items: center;justify-content: center;width: 50%;height: 100%;}.ok {background-color: rgb(83, 165, 241);}}}</style><template><div class="hint" v-if="show" ref="modal"><div class="title">{{ title }}</div><div class="content">{{ content }}</div><div class="but"><div class="no" @click="cancel">{{ cancelText }}</div><div class="ok" @click="confirm">{{ confirmText }}</div></div></div></template><script>export default {data() {return {show: false,title: "",content: "",confirmText: "确定",cancelText: "取消",onConfirm: () => {// 确认执行函数this.$emit("confirm");},onCancel: () => {// 取消执行函数this.$emit("cancle");},};},methods: {// 取消cancel() {console.log("取消了吗?");this.onCancel();this.remove();},// 确认confirm() {console.log("确定了吗?");this.onConfirm();this.remove();},// 确认或取消后移除元素remove() {this.show = false;},},};</script><style lang="less">.hint {position: absolute;top: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;left: 0;margin: auto;width: 300px;height: 200px;background-color: #fff;box-shadow: 0 0 5px #ccc;border-radius: 10px;overflow: hidden;.title,.content {display: flex;align-items: center;justify-content: center;padding: 10px 0;font-size: 20px;}.but {cursor: pointer;width: 100%;height: 50px;position: absolute;bottom: 0;border-top: 1px solid #f5f5f5;display: flex;align-items: center;justify-content: space-around;.ok,.no {display: flex;align-items: center;justify-content: center;width: 50%;height: 100%;}.ok {background-color: rgb(83, 165, 241);}}}</style>
在 main.js 中注册
import Vue from 'vue'import App from './App.vue'import hintComp from './view/hint.vue';Vue.config.productionTip = falsefunction hint(options) {// 返回一个 vue 子类const Hint = Vue.extend(hintComp);// 创建实例并且挂载到一个空的 div 上const app = new Hint().$mount(document.createElement('div'));// 初始化参数 - 将传入的参数赋值给实例的 datafor (let key in options) {app[key] = options[key];}// 将元素插入body中document.body.appendChild(app.$el);}// 添加的原型上Vue.prototype.$hint = hint;new Vue({render: h => h(App),}).$mount('#app')
在组件中使用
<template><div id="app"></div></template><script>export default {name: "App",components: {},mounted() {this.$hint({show: true,title: "这是标题",content: "这是内容这是内容这是内容",onCancel(v) {console.log(v);console.log("取消了!");},onConfirm(v) {console.log(v);console.log("确定了!");},});},};</script>