总时间限制: 2000ms 单个测试点时间限制: 500ms 内存限制: 65536kB
描述
在韩国,有一种小的青蛙。每到晚上,这种青蛙会跳越稻田,从而踩踏稻子。农民在早上看到被踩踏的稻子,希望找到造成最大损害的那只青蛙经过的路径。每只青蛙总是沿着一条直线跳越稻田,而且每次跳跃的距离都相同。
稻子组成一个栅格,每棵稻子位于一个格点上。而青蛙总是从稻田的一侧跳进稻田,然后沿着某条直线穿越稻田,从另一侧跳出去
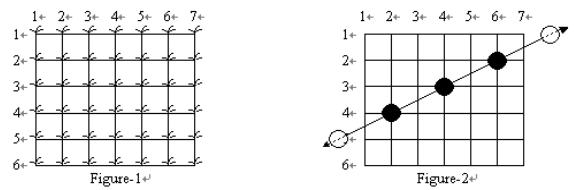
如下图所示,可能会有多只青蛙从稻田穿越。青蛙的每一跳都恰好踩在一棵水稻上,将这棵水稻拍倒。有些水稻可能被多只青蛙踩踏。当然,农民所见到的是图4中的情形,并看不到图3中的直线,也见不到别人家田里被踩踏的水稻。
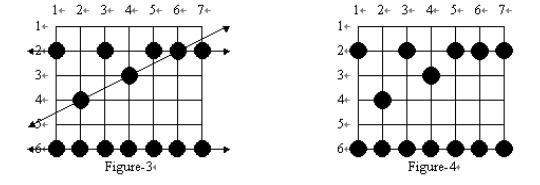
构造出青蛙穿越稻田时的行走路径,并且只关心那些在穿越稻田时至少踩踏了3棵水稻的青蛙。因此,每条青蛙行走路径上至少包括3棵被踩踏的水稻。而在一条青蛙行走路径的直线上,也可能会有些被踩踏的水稻不属于该行走路径
- 不是一条行走路径:只有两棵被踩踏的水稻;
- 是一条行走路径,但不包括(2,6)上的水道;
- 不是一条行走路径:虽然有3棵被踩踏的水稻,但这三棵水稻之间的距离间隔不相等。
请你写一个程序,确定:在一条青蛙行走路径中,最多有多少颗水稻被踩踏。例如,图4的答案是7,因为第6行上全部水稻恰好构成一条青蛙行走路径。
输入
从标准输入设备上读入数据。第一行上两个整数R、C,分别表示稻田中水稻的行数和列数,1≤R、C≤5000。第二行是一个整数N,表示被踩踏的水稻数量, 3≤N≤5000。在剩下的N行中,每行有两个整数,分别是一颗被踩踏水稻的行号(1~R)和列号(1~C),两个整数用一个空格隔开。而且,每棵被踩踏水稻只被列出一次。
输出
从标准输出设备上输出一个整数。如果在稻田中存在青蛙行走路径,则输出包含最多水稻的青蛙行走路径中的水稻数量,否则输出0。
样例输入
6 7142 16 64 22 52 62 73 46 16 22 36 36 46 56 7
样例输出
7
思路
我们枚举路径开始的2个点,由于两点确定一条直线,当开始的2个点被确定下来后,后面的很多因素也就被定下来了。
假设一只青蛙进入稻田后踩踏的前2个水稻分别是
#card=math&code=%28x_1%2C%20y_1%29)
#card=math&code=%28x_2%2C%20y_2%29)
青蛙下一跳的步长为:
- X方向:
- Y方向:
- X方向:
#card=math&code=%28x_1%20-%20dx%2C%20y_1%20-%20dy%29) 必须落在稻田外;
- 当青蛙在水稻田某一位置
#card=math&code=%28x%2C%20y%29)上时,下一跳踩踏的水稻坐标为:
#card=math&code=%28x%20%2B%20dx%2C%20y%20%2B%20dy%29)
- 将路径上的最后一棵水稻记作
#card=math&code=%28x_k%2C%20y_k%29),
#card=math&code=%28x_k%20%2B%20dx%2C%20y_k%20%2B%20dy%29) 需要落在稻田之外.
枚举的过程我们这样操作:
- 从输入的水稻中任取2棵,作为一只青蛙进入水稻后踩踏的前2棵水稻,看能否形成一条穿越稻田的路径
为了降低搜索空间,我们需要排除错误的答案。猜测
#card=math&code=%28X_1%2C%20Y_1%29)
#card=math&code=%28X_2%2C%20Y_2%29)
- 青蛙不能经过一跳从稻田外跳到
#card=math&code=%28X_1%2C%20Y_1%29)上;
- 按照
#card=math&code=%28X_1%2C%20Y_1%29),
#card=math&code=%28X_2%2C%20Y_2%29) 确定的步长,从
#card=math&code=%28X_1%2C%20Y_1%29) 出发,青蛙最多经过
#card=math&code=%28MAXSTEPS%20-%201%29) 步,就会跳到稻田之外, 其中
是当前已经找到的最好答案.
我们用面向对象的类来描述一个坐标点,并借助C++提供的函数来帮助我们简化代码。
代码
样例数据能得到答案,但是不知道为什么POJ没过。。。。
#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;class Plant {public:int x, y;};Plant plants[5001];int row = 0, col = 0, totalRice;int searchPath(Plant secarchPlant, int dx, int dy) {/* 判断从 searchPlant 开始,步长为 dx, dy, 那么最多能走几步 */Plant myPlant;myPlant.x = secarchPlant.x + dx;myPlant.y = secarchPlant.y + dy;int step = 2;while( myPlant.x <= row && myPlant.x >= 1 && myPlant.y <= col && myPlant.y >= 1 ) {if( !binary_search(plants, plants + totalRice, myPlant) ) {step = 0;break;}myPlant.x += dx;myPlant.y += dy;step++;}return step;}bool operator < (const Plant& p1, const Plant& p2) { // 配合sort函数if( p1.x == p2.x ) return p1.y < p2.y;return p1.x < p2.x;}int main() {cin >> row >> col >> totalRice;for(int i = 0; i < totalRice; i++)cin >> plants[i].x >> plants[i].y;// 将水稻按x坐标从小到大排序, x坐标相同按y从小到大排序sort(plants, plants + totalRice);// 枚举每一个点int max = 0, steps = 0;for(int i = 0; i < totalRice - 2; i++) { // plants[i]是第一个点for(int j = i + 1; j < totalRice - 1; j++) { // plant[j]是第二个点int dx = plants[j].x - plants[i].x;int dy = plants[j].y - plants[i].y;int previousX = plants[i].x - dx;int previousY = plants[i].y - dy;if(previousX <= row && previousX >= 1 && previousY <= col && previousY >= 1)continue; // 第2个点选的不合适if( plants[i].x + (max - 1) * dx > row )break; // 第1个点选的不合适previousY = plants[i].y + (max - 1) * dy;if( previousY > col || previousY < 1 )continue; // Y方向过早越界steps = searchPath(plants[j], dx, dy);if(steps > max) max = steps;}}if( max == 2) cout << 0 << endl;else cout << max << endl;return 0;}

