给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
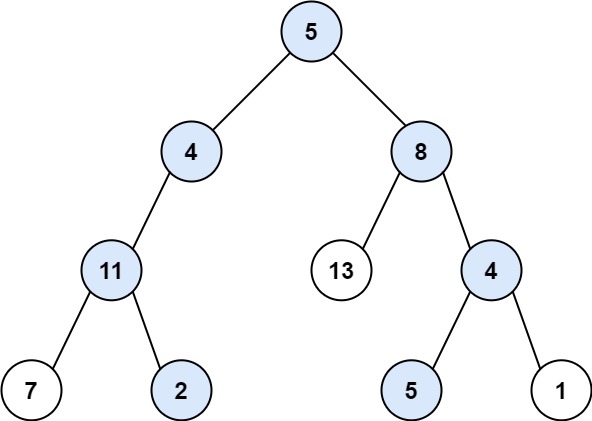
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22Output: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
示例 2:

Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5Output: []
示例 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0Output: []
提示:
- -1000 ≤
Node.val≤ 1000 - -1000 ≤
targetSum≤ 1000 - 树中节点总数在范围
[0, 5000]内
思路
先把根节点加入到path,然后进行左递归的DFS。
递归终止条件:访问到叶子节点(没有左右子树的节点)。
代码
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {vector<vector<int>> answer;if( root == nullptr ) return answer;vector<int> path;path.emplace_back( root->val );targetSum -= root->val;dfs(root, targetSum, answer, path);return answer;}void dfs(TreeNode* node, int targetSum, vector<vector<int>>& answer, vector<int>& path) {// 1. Exit condition: leaf nodeif( node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr ) {if( 0 == targetSum ) {answer.emplace_back( path );return;}}// 2. Walk every node that not visitedif( node->left != nullptr ) {path.emplace_back( node->left->val );dfs( node->left, targetSum - node->left->val, answer, path );path.pop_back();}if( node->right != nullptr ) {path.emplace_back( node->right->val );dfs( node->right, targetSum - node->right->val, answer, path );path.pop_back();}}};

