给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 target 。
找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ target 的长度最小的 连续子数组 [nums, nums, …, nums, nums] ,并返回其长度。如果不存在符合条件的子数组,返回 0 。
示例 1:
Input: target = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3]Output: 2Explanation: The subarray [4,3] has the minimal length under the problem constraint.
示例 2:
Input: target = 4, nums = [1,4,4]Output: 1
示例 3:
Input: target = 11, nums = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]Output: 0
提示:
- 1 ≤
target≤ 10; - 1 ≤
nums.length≤ 10; - 1 ≤
nums[i]≤ 10 - 如果你已经实现
O(n)时间复杂度的解法, 请尝试设计一个O(n log(n))时间复杂度的解法。
思路
本题有两个思路,一个是暴力穷举,一个是滑动窗口(类似于双指针)。
对于滑动窗口,借用代码随想录的示意图:
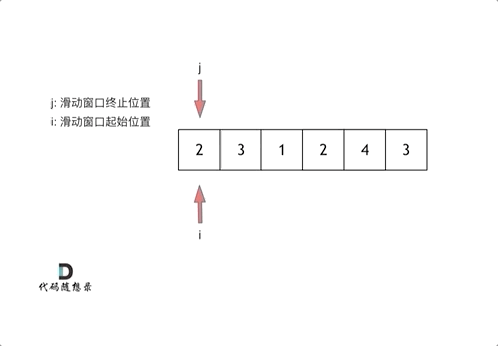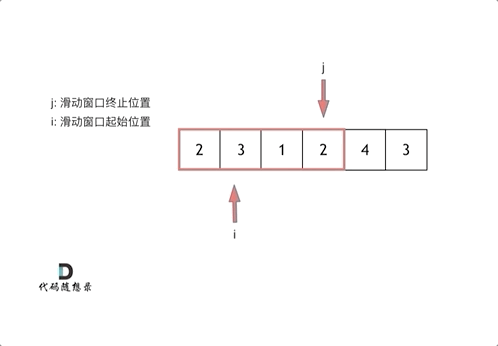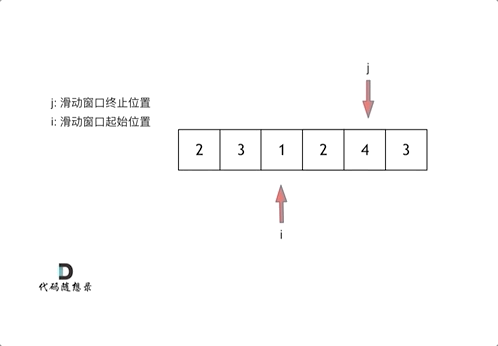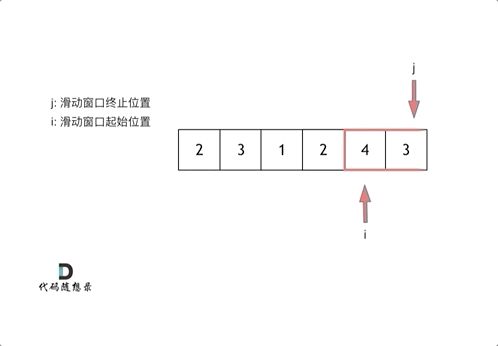
我们新建两个指针,一个start指向起点,一个end指向终点。两个指针构成的闭区间就是我们所说的窗口。
当区间的序列和 ≥ target时,我们就要把start指针向右移动。
如果最后start和end重合,且指向的值不是target,则我们认为找不到长度最小的子数组,返回0。
代码
Cpp:
// 4ms, 10.2MBclass Solution {public:int minSubArrayLen(int target, vector<int>& nums) {int start = 0, end = 0;unsigned cur_sum = 0;unsigned window_size = 0;unsigned result = 0xf << 15;for(end = 0; end < nums.size(); end++) {cur_sum += nums[end];while( cur_sum >= target ) {window_size = (end - start + 1);result = result < window_size ? result : window_size;cur_sum -= nums[start];start += 1;}}return (result == 0xf << 15 ? 0 : result);}};
Rust:
// 0ms, 2.3MBimpl Solution {pub fn min_sub_array_len(target: i32, nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {let mut start = 0;let mut end = 0;let mut cur_sum = 0;let mut windows_size = 0;let mut result = 0xf << 15;while end < nums.len() {cur_sum += nums[end];while cur_sum >= target {windows_size = (end - start + 1);result = if result < windows_size {result} else {windows_size};cur_sum -= nums[start];start += 1;}end += 1;}if result != 0xf << 15 {result as i32} else {0}}}

