数字 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你设计一个函数,用于能够生成所有可能的并且 有效的 括号组合。
示例 1:
Input: n = 3Output: ["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]
示例 2:
Input: n = 1Output: ["()"]
提示:
- 1 ≤
n≤ 8
思路
本题可构建一棵求解树,如下图所示: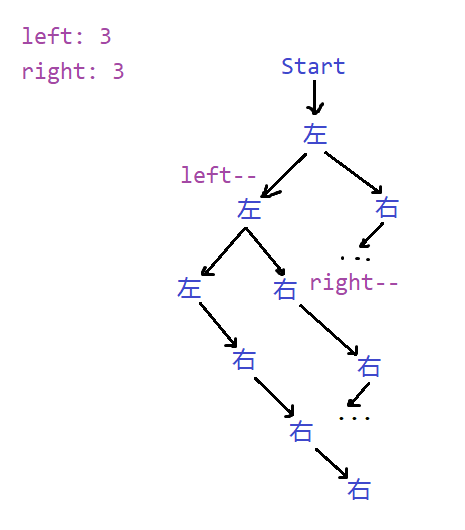
分析题目我们可以发现,在合法的括号中,第一个不能是右括号,或者说,当左括号的个数和右括号的个数相等时,我们不能选右括号。
DFS需要一个终止递归的条件,本题的终止条件是什么呢?因为括号是成对出现的,所以当path的长度等于2 * n时,我们就停止递归。例如n=3,那最终会生成长度为2 * 3 = 6的字符串。
我们分别为做左括号和右括号维护一个计数器。这个计数器的功能类似于bool[] visited数组。
代码
class Solution {public:vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {vector<string> answer;if(n == 0) return answer;if(n == 1) {answer.emplace_back( "()" );return answer;}int* visited = new int[n];for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) visited[i] = n;string path;string token = "()";dfs(n, answer, token, visited, path);delete[] visited;return answer;}void dfs(const int n,vector<string>& answer,const string& token,int visited[],string& path) {// 1. Exit conditionif( path.size() == 2 * n ) {answer.emplace_back( path );return;}// 2. Walk every node that not visitedif( visited[0] > 0 ) {string node = path + token[0];visited[0]--;dfs(n, answer, token, visited, node);visited[0]++;}if( visited[1] > 0 && visited[0] != visited[1] ) {string node = path + token[1];visited[1]--;dfs(n, answer, token, visited, node);visited[1]++;}}};

