给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,树中每个节点都存放有一个 0 到 9 之间的数字。
每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:
例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径 1 -> 2 -> 3 表示数字 123 。
计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 所有数字之和 。
叶节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
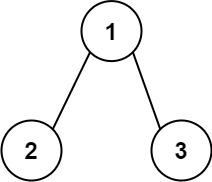
Input: root = [1,2,3]Output: 25Explanation:The root-to-leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12.The root-to-leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13.Therefore, sum = 12 + 13 = 25.
示例 2:
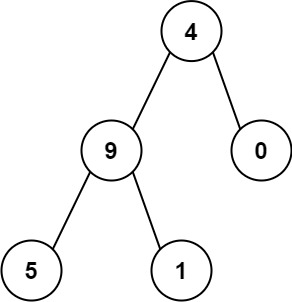
Input: root = [4,9,0,5,1]Output: 1026Explanation:The root-to-leaf path 4->9->5 represents the number 495.The root-to-leaf path 4->9->1 represents the number 491.The root-to-leaf path 4->0 represents the number 40.Therefore, sum = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026.
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 - 0 ≤
Node.val≤ 9 - 树的深度不超过
10
思路
从根节点开始来一个左递归深度优先搜索,当遇到叶子节点后停止递归。
到了叶子节点后,使用秦九邵算法计算path的值。
代码
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/class Solution {public:int sumNumbers(TreeNode* root) {if( root == nullptr ) return 0;if( root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr ) return root->val;int sum = 0;vector<int> path;path.emplace_back( root->val );dfs(root, path, sum);return sum;}void dfs(TreeNode* node, vector<int>& path, int& sum) {// 1. Exit condition: leaf nodeif( node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr ) {sum += compute_sum(path);return;}// 2. Walk every node that not visitedif( node->left != nullptr ) {path.emplace_back( node->left->val );dfs(node->left, path, sum);path.pop_back();}if( node->right != nullptr ) {path.emplace_back( node->right->val );dfs(node->right, path, sum);path.pop_back();}}int compute_sum(vector<int>& path) {int sum = 0;for(int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) // QinJiuShao algorithm/Horner algorithmsum = sum * 10 + path[i];return sum;}};

