一、题目
Trie(发音类似 “try”)或者说 前缀树 是一种树形数据结构,用于高效地存储和检索字符串数据集中的键。这一数据结构有相当多的应用情景,例如自动补完和拼写检查。
请你实现 Trie 类:
Trie() 初始化前缀树对象。
void insert(String word) 向前缀树中插入字符串 word 。
boolean search(String word) 如果字符串 word 在前缀树中,返回 true(即,在检索之前已经插入);否则,返回 false 。
boolean startsWith(String prefix) 如果之前已经插入的字符串 word 的前缀之一为 prefix ,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
二、思路
题中已叙述清楚前缀树的功能,其目的主要是可以通过给定字符串s,根据放置入数据结构中的字符串进行查询:
1)查询是否存在和字符串s一模一样的字符串
2)查询数据结构中是否存在前缀为字符串s的串
准确理解题意的基础上,对进行数据结构的构思:
1)整个数据结构为以字符为节点的树,便于做上述的第二种查询
2)由于会存在放入的多个字符串共用同一前缀的情况,可以设定一个path值,用以代表共用该字符的字符串数量,如图: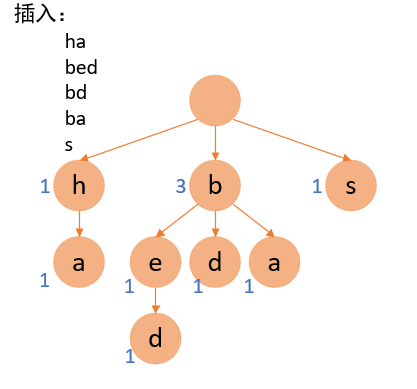
3)当数据结构如上所示时,当插入一个字符串如“b”时,那就无法区分结尾,此时可以再设计一个end值,以此代表有多少个字符串以当前字符结尾
4)每一个节点的孩子节点最多有26个,可是开辟数组进行保存会很大程度浪费空间,可以使用了Map的键值对实现孩子节点的存放(另一种实现是建立一个容量为26的数组进行实现)
三、实现
于是可以将对象初始化为:
class Trie {public int end;public int path;public Map<Character, Trie> next;/** Initialize your data structure here. */public Trie() {end = 0;path = 0;next = new HashMap<>();}}
插入函数为:
public void insert(String word) {char[] cWords = word.toCharArray();Trie node = this;for (char cWord : cWords) {if (!node.next.containsKey(cWord)) {node.next.put(cWord, new Trie());}node = node.next.get(cWord); // 获取孩子节点node.path++;}node.end++; // 标记该字符有字符串结尾}
第一种搜索函数(全匹配)为:
public boolean search(String word) {char[] cWords = word.toCharArray();Trie node = this;for (char cWord : cWords) {if (!node.next.containsKey(cWord)) { // 当不存在其中任一字符就判定不存在该字符串return false;}node = node.next.get(cWord);}return node.end > 0; // 遍历到word的最后一个字符,有字符串在此结尾,就存在word}
第二种搜索(前缀匹配)为:
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {char[] cWords = prefix.toCharArray();Trie node = this;for (char cWord : cWords) {if (!node.next.containsKey(cWord)) {return false;}node = node.next.get(cWord);}return true;}

