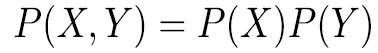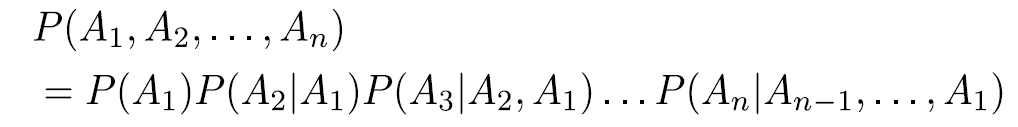LEC 02: Probability
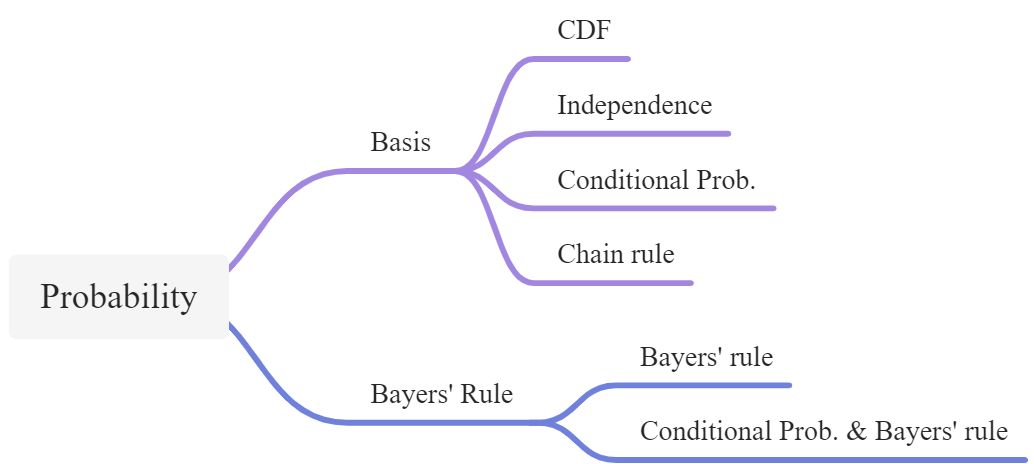
Probability basis
Cumulative Distribution Func. (CDF) 累计分布函数
Independence
Conditional Probability

leads to conditional independence 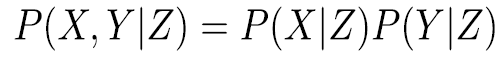
Chain rule
Bayes’ Rule
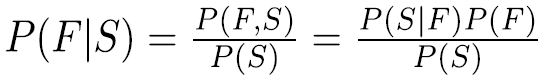
idea of Bayes’s rule: update probabilities from evidence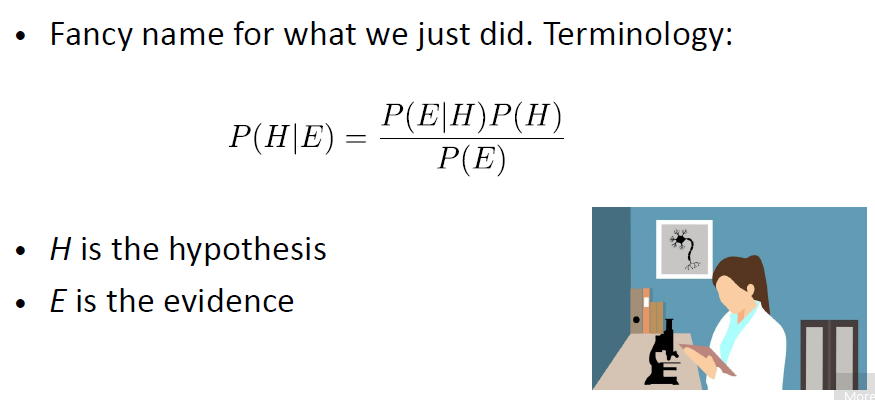
Prior: P(H) - estimate of the probability without evidence
Likelihood: P(E|H) - probability of evidence given a hypothesis
Posterior: P(H|E) - probability of hypothesis given evidence
Conditional Prob. & Bayes
LEC 03
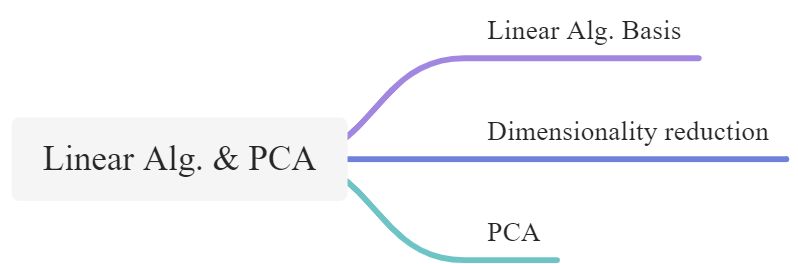
Linear Basis
vector products

Inner product defines “orthogonality” : 正交性, if
vector norms - size
dentity matrix
- like “1”
- multiplying by it gets back the same matrix or vector
- row & columns are the standard basis vectors
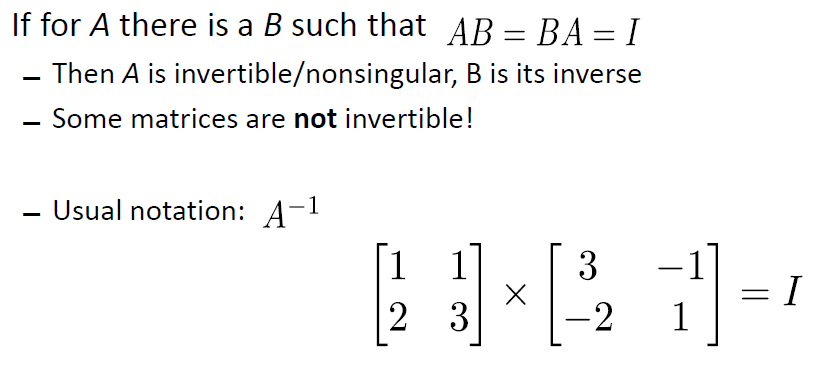
Inverses
Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors

Dimensionality Reduction
Why - 1) lots of features redundant 2) storage & computation costs
PCA
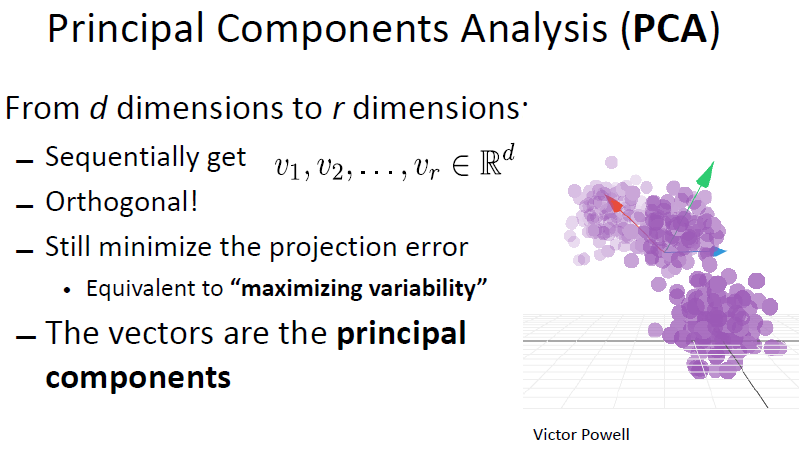
为什么样本在“协方差矩阵C的最大K个特征值所对应的特征向量”上的投影就是k维理想特征?
其中一种解释是: 最大方差理论:方差越大,信息量就越大。协方差矩阵的每一个特征向量就是一个投影面,每一个特征向量所对应的特征值就是原始特征投影到这个投影面之后的方差。由于投影过去之后,我们要尽可能保证信息不丢失,所以要选择具有较大方差的投影面对原始特征进行投影,也就是选择具有较大特征值的特征向量。然后将原始特征投影在这些特征向量上,投影后的值就是新的特征值。每一个投影面生成一个新的特征,k个投影面就生成k个新特征。
LEC 04 - Stats Math
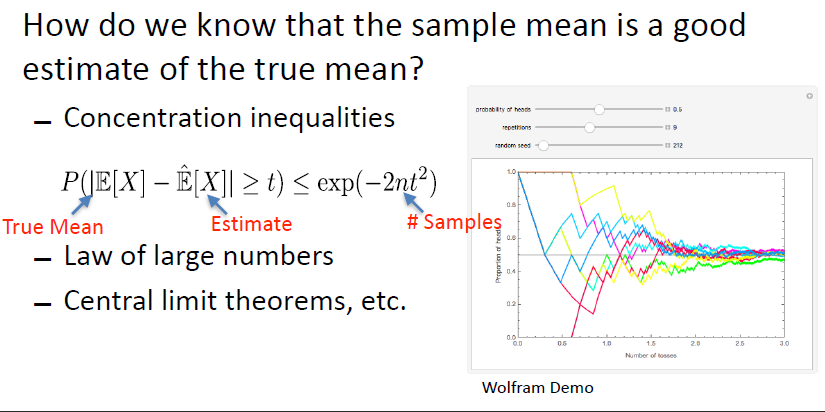
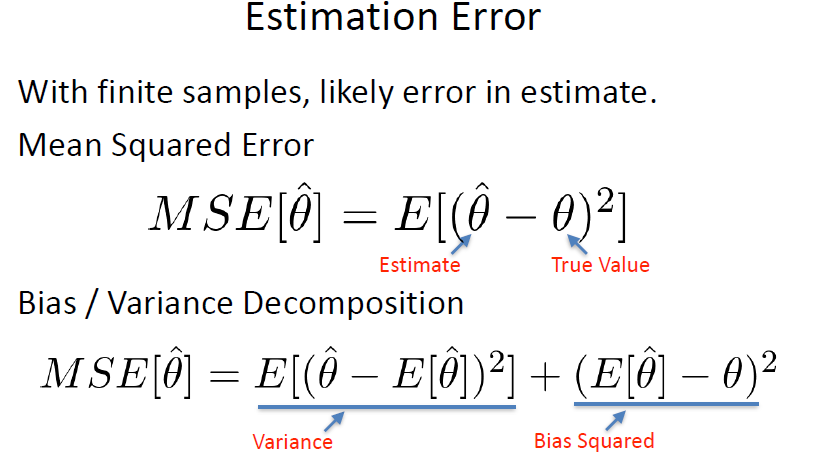
Sample and Estimation
estimate mean with sample mean
estimate error
LEC 05 - Logic
Conjuctive Normal Form - CNF 合取范式
QUIZ: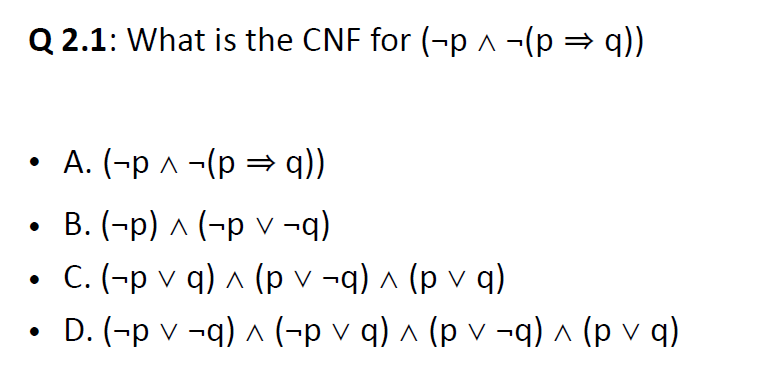
use equivbalences for connectives: p V (-q ^ q))
LEC 06 - NLP
Language models
basic idea - using probalilistic models to assign a probability to a sentence
chain rule: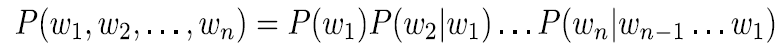
Training: Make Assumptions
Markov-type assumptions:
1) when k = 0: unigram model -
- full independece assumtion, present doesn’t depend on teh past :
- P(w1,w2, w3,…,wn) = P(w1)P(w2)…P(wn)
2) when k = n-1: n-gram model -
- for bigmra:
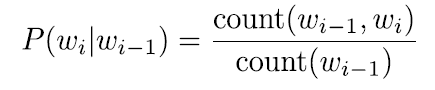
- multiply tiny numbers? - use logs; add instead of multiply
- n-grams with zero probability? - smoothing, 分母+V, 分子+1
- Smoothing is increasingly useful for n-grams when n gets larger
Perplexity
Perplexity is a measure of uncertainty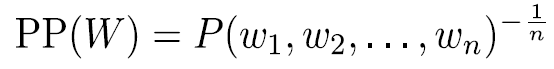
LEC 07 - Machine Learning Overview
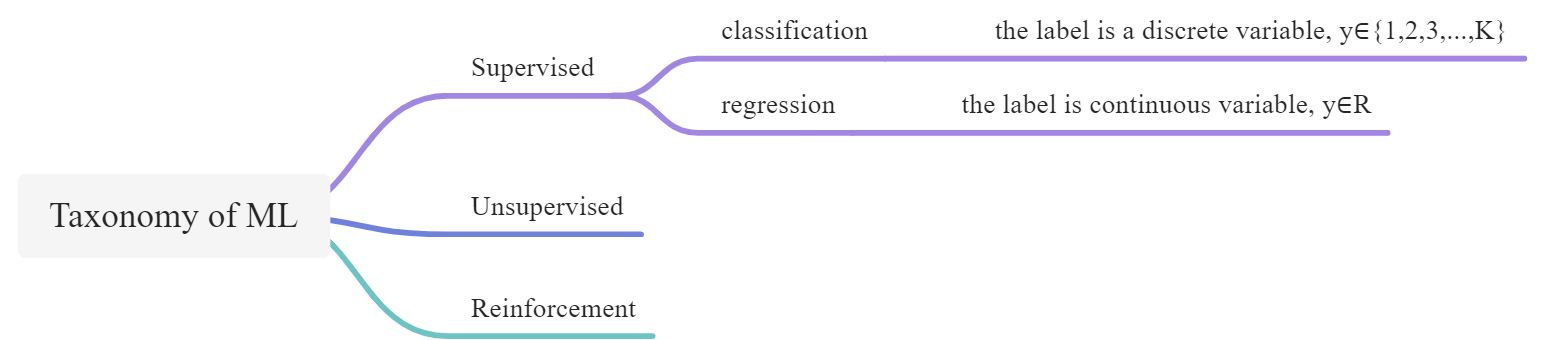
Supervised learning
- Classification: the label is a discrete variable, y∈{1,2,3,…,K}
- Regression: the label is continuous variable, y∈R
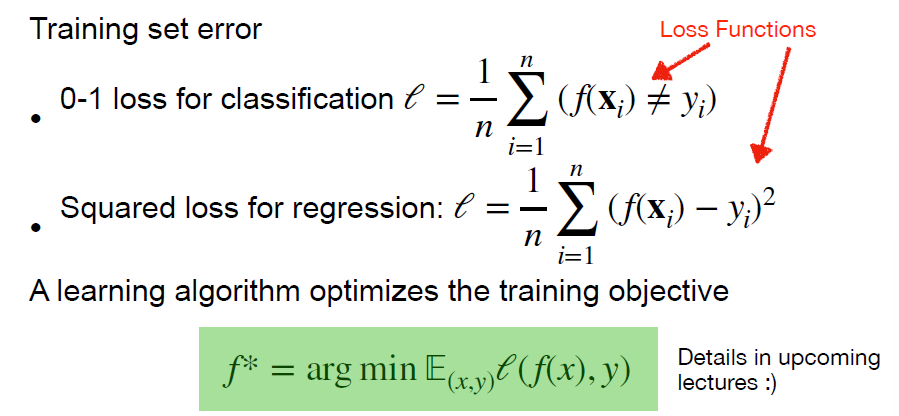
Training data is teh “experience“ given to a learning algorithm, learning a function mapping f: X -> Y, such that f(x) predicts the label y on future data x (not in traing data)
error
Unsupervised learning
given: dataset contains no label x1, x2,… xn
goal: discover new patterns and structures in the data
Clusters
- K-means clustering (do not confuse it with k-NN classifier)
- input a dataset x1, x2, …, xn, and assume the number of clusters k is given
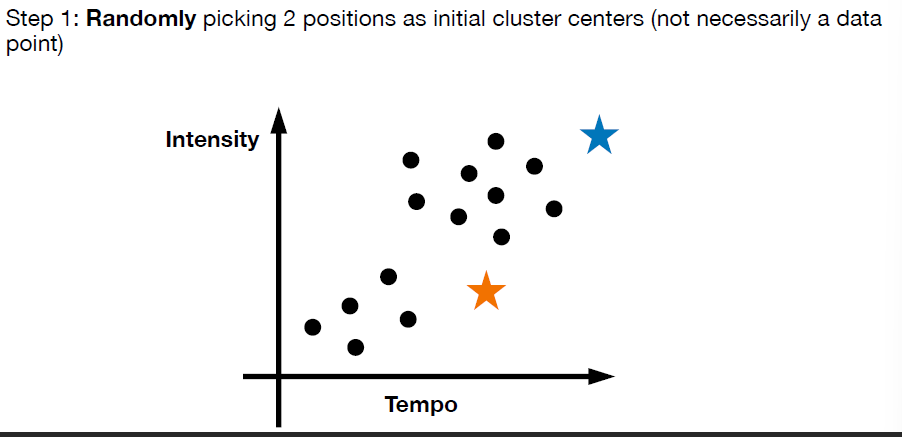

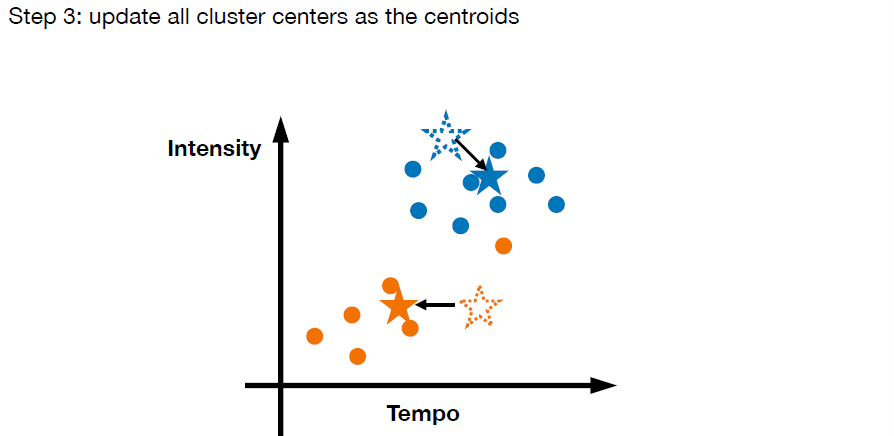

-
Reinforcement learning
learn from reward
- given: an agent that can take actions and a reward function specifiying how good an action is.
- Data: (x0,a0,r0), (x1,a1,r1) … (xn,an,rn)
- Goal: learn to choose actions that maximize future reward total
A* algorithm
For normal BFS:
frontier = Quene()frontier.put(start)reached = set()reached.add(start)while not frontiner.empty():current = frontiner.get()for next in graph.neighbours(current):if next no in reached:frontier.put(next)reached.add(next)
For normal BFS with back track:
frontier = Queue()frontier.put(start)came_from = dict{}came_from[start] = Nonewhile not frontier.empty():current = frontier.get()for next in graph.neighbors(current):if next not in came_from:frontier.put(next)came_from[next] = current
# initializefrontier = Queue()frontier.put(start)reached = set()reached.add(start)while not frontier.empty():current = frontier.get()for next in graph.neighbors(current):if next not in reached:frontier.put(next)reached.add(next)# BFS with trackfrontier = Queue()frontier.put(start)came_from = dict()came_from[start] = Nonewhile not frontier.empty():current = frontier.get()for next in graph.neighbors(current):if next not in came_from:frontier.put(next)came_from[next] = currentcurrent = goalpath = []while current != start:path.append(current)current = came_from[current]path.append(start)path.reverse()frontier = Queue()frontier.put(start)came_from = dict()came_from[start] = Nonewhile not frontier.empty():current = frontier.get()if current == goal:breakfor next in graph.neighbors(current):if next not in came_from:frontier.put(next)came_from[next] = current---# Dijkstrafrontier = PriorityQueue()frontier.put(start, 0)came_from = dict()cost_so_far = dict()came_from[start] = Nonecost_so_far[start] = 0while not frontier.empty():current = frontier.get()if current == goal:breakfor next in graph.neighbors(current):new_cost = cost_so_far[current] + graph.cost(current, next)if next not in cost_so_far or new_cost < cost_so_far[next]:cost_so_far[next] = new_costpriority = new_costfrontier.put(next, priority)came_from[next] = current---# greedyfrontier = PriorityQueue()frontier.put(start, 0)came_from = dict()came_from[start] = Nonewhile not frontier.empty():current = frontier.get()if current == goal:breakfor next in graph.neighbors(current):if next not in came_from:priority = heuristic(goal, next)frontier.put(next, priority)came_from[next] = current---# A*frontier = PriorityQueue()frontier.put(start, 0)came_from = dict()cost_so_far = dict()came_from[start] = Nonecost_so_far[start] = 0while not frontier.empty():current = frontier.get()if current == goal:breakfor next in graph.neighbors(current):next_cost = cost_so_far[current] + graph.cost(current,next)if next not in cost_so_far or new_cost < cost_so_far[next]:cost_so_far[next] = new_costpriority = new_cost + heuristic(goal, next)frontier.put(next, priority)came_from[next] = current