参考: https://blog.csdn.net/ivan820819/article/details/79744797
IOC概念
- IOC(Inversion of Control), 控制反转, 指获得依赖对象的过程被反转了, 由原来的自身管理(主动)变为由IOC容器注入(被动)
- DI(Dependency Injection), 依赖注入, 由IOC容器在运行期间, 动态的将依赖关系注入到对象中
- 依赖注入(DI)和控制反转(IOC)是从不同的角度的描述的同一件事情,就是指通过引入IOC容器,利用依赖关系注入的方式,实现对象之间的解耦。
核心: 借助于”第三方”实现具有依赖关系的对象之间的解耦.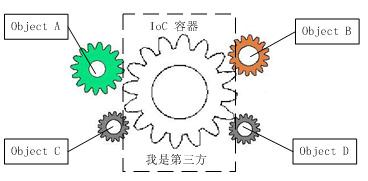
补充:
- IOC的实现策略有依赖查找和依赖注入
IOC职责
依赖处理依赖查找依赖注入生命周期管理容器托管的资源(Java Beans或其他资源)配置容器外部化配置托管的资源(Java Beans或其他资源)
依赖查找与依赖注入的对比

- 构造器注入与setter注入对比
构造器注入能够在构造期创建一个完整合法的对象, 更符合对象创建即不变的设计理念, 增强系统的稳定以及便利性.
Spring IOC 依赖查找
- 根据Bean名称查找
- 实时查找
- 延迟查找
- 根据Bean类型查找
- 单个Bean对象
- 集合Bean对象
- 根据Bean名称+类型查找
- 根据Java注解查找
- 单个Bean对象
- 集合Bean对象
public static void main(String[] args) {// 配置XML配置文件, 启动Spring应用上下文BeanFactory beanFactory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:META-INF/dependency-lookup-context.xml");// 通过名称查找// lookUpInRealTime(beanFactory);// lookUpInLazy(beanFactory);// 通过类型查找lookUpByType(beanFactory);lookUpByCollectionType(beanFactory);// 通过注解查找lookUpByAnnotation(beanFactory);}private static void lookUpInRealTime(BeanFactory beanFactory) {User user = (User) beanFactory.getBean("user");System.out.println("根据名称实时查找: " + user);}private static void lookUpInLazy(BeanFactory beanFactory) {ObjectFactory<User> objectFactory = (ObjectFactory<User>) beanFactory.getBean("objectFactory");User user = objectFactory.getObject();System.out.println("根据名称延迟查找: " + user);}private static void lookUpByType(BeanFactory beanFactory) {User user = beanFactory.getBean(User.class);System.out.println("根据类型实时查找: " + user);}private static void lookUpByCollectionType(BeanFactory beanFactory) {if (beanFactory instanceof ListableBeanFactory) {ListableBeanFactory listableBeanFactory = (ListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;Map<String, User> users = listableBeanFactory.getBeansOfType(User.class);System.out.println("根据类型查找集合对象: " + users);}}private static void lookUpByAnnotation(BeanFactory beanFactory) {if (beanFactory instanceof ListableBeanFactory) {ListableBeanFactory listableBeanFactory = (ListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;Map<String, User> users = (Map) listableBeanFactory.getBeansWithAnnotation(Super.class);System.out.println("根据类型查找集合对象: " + users);}}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttps://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttps://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><bean id="user" class="top.xinzhang0618.ioc.overview.domain.User" primary="true"><property name="id" value="1"/><property name="name" value="xinzhang"/></bean><bean id="objectFactory" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ObjectFactoryCreatingFactoryBean"><property name="targetBeanName" value="user"/></bean><bean id="superUser" class="top.xinzhang0618.ioc.overview.domain.SuperUser" parent="user"><property name="address" value="shenzhen"/></bean></beans>
实体如下
public class User {private Long id;private String name;...}@Superpublic class SuperUser extends User {private String address;...}/*** 标记超级*/@Target({ElementType.TYPE})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface Super {}
ObjectFactoryBean, FactoryBean, BeanFactory三者有什么区别?
ObjectFactory 通常是针对单类 Bean 做延迟获取的,BeanFactory 则是全局 Bean 管理的容器。
Spring IOC依赖注入
- 根据Bean名称注入
- 根据Bean类型注入
- 单个Bean对象
- 集合Bean对象
- 注入容器内建Bean对象
- 注入非Bean对象
- 注入类型
- 实时注入
- 延迟注入
如下示例, 可以手动配置, 也可以通过Autowire进行注入
<bean id="userRepository" class="org.geekbang.thinking.in.spring.ioc.overview.repository.UserRepository"autowire="byType"> <!-- Auto-Wiring --><!-- 手动配置 --><!-- <property name="users">--><!-- <util:list>--><!-- <ref bean="superUser" />--><!-- <ref bean="user" />--><!-- </util:list>--><!-- </property>--></bean>
Spring IOC依赖来源
- 自定义Bean(自己用xml配置或注解配置的bean)
- 内部容器依赖的Bean(非自己定义的Bean,spring容器初始化的Bean), 如Environment对象
内部容器所构建的依赖(非Bean,不可通过获取依赖查找Bean的方法来获取(getBean(XXX)))
public class UserRepository {private Collection<User> users; // 自定义 Beanprivate BeanFactory beanFactory; // 內建非 Bean 对象(依赖)...}
内建Bean和内建依赖如何区别?
实际上,内建的 Bean 是普通的 Spring Bean,包括 BeanDefinitions 和 Singleton Objects,而内建依赖则是通过 AutowireCapableBeanFactory 中的 resolveDependency 方法来注册,这并非是一个 Spring Bean,无法通过依赖查找获取~
内部容器构建的依赖指的是什么?
Spring IoC 底层容器就是指的 BeanFactory 的实现类,大多数情况是 DefaultListableBeanFactory 这个类,它来管理 Spring Beans,而 ApplicationContext 通常为开发人员接触到的 IoC 容器,它是一个 Facade,Wrap 了 BeanFactory 的实现。
Java Bean 是一种功能组件,它是 Java对象的方式封装, 所谓依赖就是被组合的对象。
Spring IOC配置元信息
- Bean定义配置
- 基于XML文件
- 基于Properties文件
- 基于JAVA注解
- 基于JAVA API
- IOC容器配置
- 基于XML文件
- 基于JAVA注解
- 基于JAVA API
- 外部化属性配置
- 基于JAVA注解, 比如@Value
Spring IOC容器
BeanFacrtory和ApplicationContext谁才是IOC容器?
官方文档如下图
简要翻译: BeanFactory提供了管理对象的一些高级配置特性, ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口, 它添加了:
- 更容易与Spring AOP的整合
- 消息资源的处理(用于国际化)
- 事件发布
- 应用级别的上下文, 比如应用在WEB应用的WebApplicationContext
总结: BeanFactory是个基本的IOC容器, ApplicationContext是在其基础上提供了更多企业级特性的超集.
分析下实现:
- ApplicationContext继承了BeanFactory
- ConfigurableApplicationContext中, 有个getBeanFactory()方法, 在AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中有实现, 返回的是AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext持有的DefaultListableBeanFactory
- 即ApplicationContext是委托DefaultListableBeanFactory来操作getBean等方法的
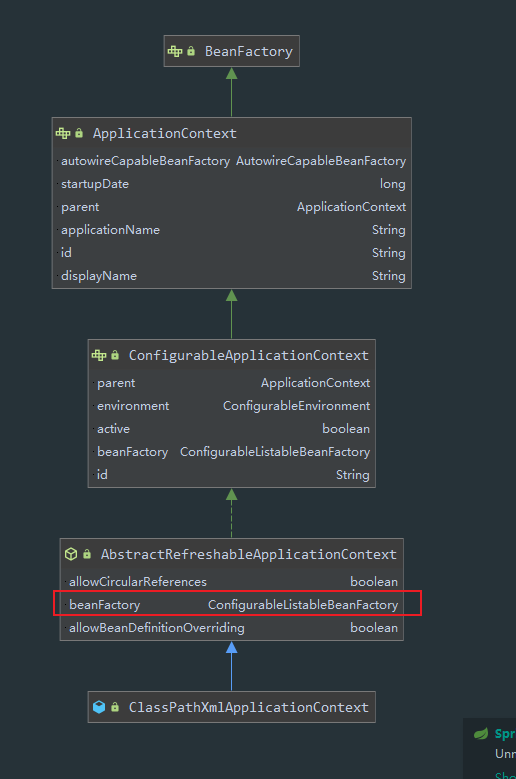
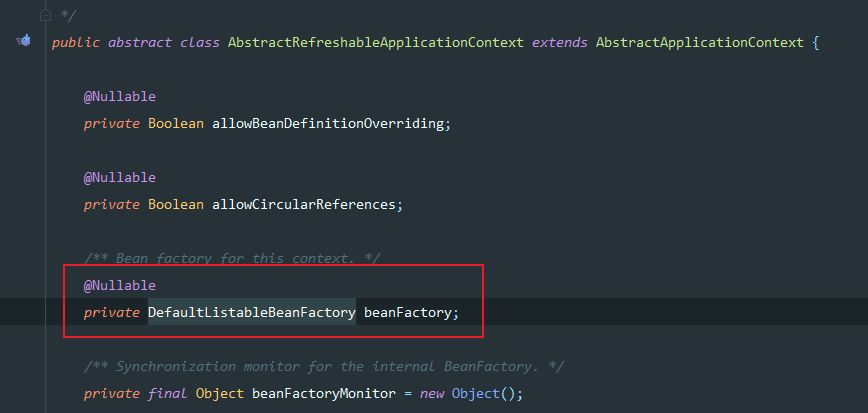
BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的关系,从设计模式上讲, 使用了代理模式,也使用了面门模式。
Spring应用上下文

使用Spring IOC
- BeanFactory是Spring底层的IOC容器
- ApplicationContext是具备应用特性的BeanFactory超集
两者的使用场景区别, 简单来说就是如果只用xml进行Bean的简单配置, 用BeanFactory即可, 如果要用到一些高级特性比如注解方式的Bean配置, 那么需要用ApplicationContext, 注解方式配置的demo如下
public class AnnotationApplicationContextAsIocContainerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建BeanFactory容器AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();// 将当前类作为配置类context.register(AnnotationApplicationContextAsIocContainerDemo.class);context.refresh();// 依赖查找集合对象lookUpByCollectionType(context);}@Beanpublic User user() {User user = new User();user.setId(1L);user.setName("hhh");return user;}private static void lookUpByCollectionType(BeanFactory beanFactory) {if (beanFactory instanceof ListableBeanFactory) {ListableBeanFactory listableBeanFactory = (ListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;Map<String, User> users = listableBeanFactory.getBeansOfType(User.class);System.out.println("根据类型查找集合对象: " + users);}}}
Spring IOC容器的生命周期
一般分三阶段: 启动, 运行, 停止
启动看applicationContext.refresh()方法
以下为AbstractApplicationContext源码, 可以看到启动有几个操作:
- 初始化BeanFactory
- 触发BeanFactory的后续处理
- 注册Bean的后续处理器
- 初始化国际化相关
- 初始化事件广播
- 注册监听器
…
@Overridepublic void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {// Prepare this context for refreshing.prepareRefresh();// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.// 这里加入了Bean以及内建的非Bean对象(如BeanFactory)等依赖prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);try {// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.// 这里可以自定义BeanFactory的拓展invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.// 这里可以自定义Bean的拓展registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Initialize message source for this context.initMessageSource();// Initialize event multicaster for this context.initApplicationEventMulticaster();// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.onRefresh();// Check for listener beans and register them.registerListeners();// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// Last step: publish corresponding event.finishRefresh();}catch (BeansException ex) {if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);}// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.destroyBeans();// Reset 'active' flag.cancelRefresh(ex);// Propagate exception to caller.throw ex;}finally {// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...resetCommonCaches();}}}
停止看applicationContext.close()方法
以下为AbstractApplicationContext源码, 可以看到停止主要有几个操作:
- 注销Bean
- 关闭BeanFactory
- 还有个onClose()空实现可以拓展
…
protected void doClose() {// Check whether an actual close attempt is necessary...if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Closing " + this);}LiveBeansView.unregisterApplicationContext(this);try {// Publish shutdown event.publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));}catch (Throwable ex) {logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex);}// Stop all Lifecycle beans, to avoid delays during individual destruction.if (this.lifecycleProcessor != null) {try {this.lifecycleProcessor.onClose();}catch (Throwable ex) {logger.warn("Exception thrown from LifecycleProcessor on context close", ex);}}// Destroy all cached singletons in the context's BeanFactory.destroyBeans();// Close the state of this context itself.closeBeanFactory();// Let subclasses do some final clean-up if they wish...onClose();// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.if (this.earlyApplicationListeners != null) {this.applicationListeners.clear();this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);}// Switch to inactive.this.active.set(false);}}
面试题
什么是Spring IOC容器?
Spring IOC容器是Spring使用依赖注入和依赖查找对IOC原则的一种实现, 同时Spring IOC还提供了一些其他的特性, 比如容器生命周期的管理, 容器的配置, 外部化配置等等.
BeanFactory与FactoryBean的区别?
BeanFactory是IOC底层容器, FactoryBean是创建Bean的一种方式, 帮助实现复杂的初始化逻辑
Spring Bean有两种实现,普通Bean,和工厂Bean(FactoryBean) 实现工厂Bean的方法就是pojo继承FactoryBean,并实现他的方法,当容器通过getBean()获取bean时,返回的是实现的getObject()方法所返回的对象

