服务管理
服务本质就是进程,但是是运行在后台的,通常会监听某个端口,等待其他程序的请求,因此又称为守护进程。
service 服务名 [start|stop|restart|reload|status]
在centos7.0后很多服务不再使用service 而是使用systemctl
可以使用 ls -l /etc/init.d/查看还在使用service的服务
使用setup可以查看系统的全部服务
chkconfig 管理service
chkconfig —list [|grep xxx] :查看服务
chkconfig 服务名 —list :查看服务
chkconfig —level 5 服务名 on/off 在某个级别把某个服务自启动打开或者关闭
通过chkconfig设置后,需要reboot后才能生效
systemctl 管理命令
systemctl [start|stop|restart|reload|status] 服务名
可以使用 ls -l /usr/lib/systemd/system查看使用systemctl管理的服务
systemctl设置服务的自启动状态
systemctl list-unit-files [|grep xxx]:查看服务的开机启动状态
systemctl enable 服务名 :设置服务开机启动
systemctl disable 服务名 :关闭服务开机启动
systemctl is-enabled 服务名 :查询某个服务是否开机自启动的
systemctl is-enabled firewalld :重启后不会失效
systemctl list-unit-files | grep firewalld
systemctl status firewalld
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl start firewalld : 重启后失效
netstat -anp | more
firewalld 防火墙
netstat -anp | more
firewall-cmd —permanent —add-port=端口/协议 : 打开端口
firewall-cmd —permanent —remove-port=端口/协议 : 删除端口
firewall-cmd —reload : 重载才能生效
firewall-cmd —query-port=端口/协议 : 查询
文件查看
将/etc/passwd下有出现root的行取出
[root@localhost ~]# grep root /etc/passwd root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
将/etc/passwd下没有出现root和nologin的行取出
[root@localhost ~]# grep -v root /etc/passwd | grep -v nologin sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt yyx:x:1000:1000:yyx:/home/yyx:/bin/bash
在根目录下查找文件名是yum.conf的文件
[root@localhost ~]# find / -name yum.conf /etc/yum.conf ……
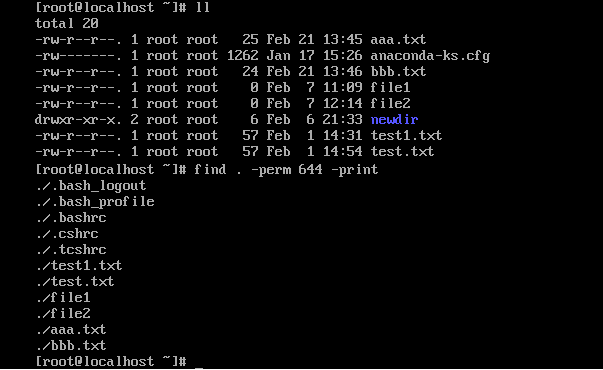
查找权限值为644 (-rw-r–r—)的文件,结果如图3-1所示。
[root@localhost test]#find . -perm 644 -print
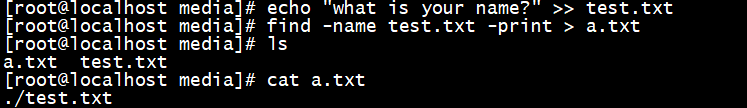
查找根目录下test.txt文件并输入到a.txt中,输入命令:
[root@localhost ~]# find -name test.txt -print > a.txt
在 ps aux的结果中查找test,使用ps aux | grep “test”命令。

将输出到显示器的“hello word”重定向输出到test.txt文件中
[root@localhost ~]# echo "hello word" >> ./test.txt
[root@localhost ~]# cat test.txt
what is your name?
hello word
信息查看
使用echo命令输出字符
[root@localhost ~]# echo "a\ndddd" a\ndddd[root@localhost ~]# echo -n "a\ndddd" a\ndddd[root@localhost ~]# [root@localhost ~]# echo -e "a\ndddd" a dddd
使用echo命令输出变量
[root@localhost ~]# echo $PATH /usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
使用默认格式查看当前系统的时间
[root@localhost ~]# date Fri Jan 29 17:47:13 EST 2021
查看今年的第几天
[root@localhost ~]# date "+%j" 029
按照“年-月-日 小时:分钟:秒”查看当前系统的时间
[root@localhost ~]# date "+%Y-%m-%d%H:%M:%S" 2021-01-2917:50:52
列出属于目前登录的PID与相关信息
[root@localhost ~]# ps -l F S UID PID PPID C PRI NI ADDR SZ WCHAN TTY TIME CMD 0 S 1000 5165 5158 0 80 0 - 29056 do_wai pts/0 00:00:00 bash 0 R 1000 8255 5165 0 80 0 - 38300 - pts/0 00:00:00 ps
显示指定用户信息(root)
[root@localhost ~]# ps -u root PID TTY TIME CMD 1 ? 00:00:04 systemd 2 ? 00:00:00 kthreadd 3 ? 00:00:00 ksoftirqd/0 5 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:0H ……
终止PID为4232的进程
[root@localhost ~]# kill 4232[root@localhost ~]# ps -u root
常见状态检测命令使用
启用和关闭网络接口。
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 down //关闭ens33网卡[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 up //启用ens33网卡
配置IP地址信息
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 192.168.148.10[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 192.168.148.10 netmask 255.255.255.0[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 192.168.148.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
更改MAC地址信息
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 down //关闭网卡[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 hw ether 00:AA:BB:CC:DD:EE //修改MAC地址[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 up //启动网卡
启动和关闭ARP协议
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 arp //开启ARP协议[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 -arp //关闭ARP协议
查看系统内核与系统版本信息
[root@localhost ~]# unameLinux[root@localhost ~]# uname -aLinux localhost.localdomain 3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Fri Apr 20 16:44:24 UTC 2018 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux[root@localhost ~]# uname -r3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64
显示当前系统未使用的和已使用的内存数目以MB为单位显示内存使用情况。
[root@localhost ~]# free -m[root@localhost ~]# free -m -t
查看系统总共运行了多长时间和系统的平均负载
[root@localhost ~]# uptime[root@localhost ~]# uptime -V[root@localhost ~]# uptime -s
显示当前登录的终端数(登录的用户名、终端设备、登录系统的时间)
[root@localhost ~]# who

