Mapping参数

analyzer
分词器,默认为standard analyzer,当该字段被索引和搜索时对字段进行分词处理
一般我们处理中文会选择ik分词器 ik_max_word, ik_smart
当我们进行全文本搜索的时候,会将检索的内容先进行分词,然后再进行匹配。默认情况下,检索内容使用的分词器会与字段指定的分词器一致,但如果设置了 search_analyzer,检索内容使用的分词器将会与 search_analyzer 设定的一致。
PUT analyzer_index{"mappings": {"properties": {"name": {"type": "text","analyzer": "simple","search_analyzer": "standard"}}}}
null_value
- 需要对null进行搜索
- 只有keyword类型支持设定null_value
如果需要对 null 值实现搜索的时候,需要设置字段的 null_value参数。null_value 参数默认值为 null,其允许用户使用指定值替换空值,以便它可以索引和搜索。
需要注意的是,null_value 只决定数据是如何索引的,不影响 _source 的内容, 并且 null_value 的值的类型需要与字段的类型一致,例如一个 long 类型的字段,其 null_value 的值不能为字符串。使用 “NULL” 显式值来代替 null,使用示例如下:
# 创建索引
PUT null_value_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": { "type": "keyword" },
"email": {
"type": "keyword",
"null_value": "NULL" # 使用 "NULL" 显式值
}
}
}
}
# 插入数据
PUT null_value_index/_doc/1
{
"id": "1",
"email": null
}
# 查询空值数据
GET null_value_index/_search
{
"query": {
"term": { "email": "NULL" } # 使用显式值来查询空值的文档
}
}
coerce
数据并不总是干净的。根据它的生成方式,数字可能会在JSON正文中呈现为真正的JSON数字,例如5,但它也可能呈现为字符串,例如”5”。或者,应该是整数的数字可以替代地呈现为浮点,例如5.0,或甚至”5.0”。
强制尝试清除脏值以适合字段的数据类型。例如:
- 字符串将被强制转换为数字。
- 浮点将被截断为整数值。
```java
PUT my_index
{
“mappings”: {
“_doc”: {
} } }"properties": { "number_one": { "type": "integer" }, "number_two": { "type": "integer", "coerce": false } }
PUT my_index/_doc/1 { “number_one”: “10” ① }
PUT my_index/_doc/2 { “number_two”: “10” ② }
> **coerce允许该设置对同一索引中的同名字段具有不同的设置。可以使用**[PUT映射API](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.4/indices-put-mapping.html)**在现有字段上更新其值。**
**Index-level default索引级默认**<br />index.mapping.coerce可以在索引级别设置该设置,以在所有映射类型中全局禁用强制:
```java
PUT my_index
{
"settings": {
"index.mapping.coerce": false
},
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"properties": {
"number_one": {
"type": "integer",
"coerce": true
},
"number_two": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
}
PUT my_index/_doc/1
{ "number_one": "10" }
PUT my_index/_doc/2
{ "number_two": "10" }
boost
dynamic
- Mapping中的字段类型一旦设定后,禁止直接修改,原因是:Lucene实现的倒排索引生成后不允许修改
- 只能新建一个索引,然后reindex数据
- 默认允许新增字段
- 通过dynamic参数来控制字段的新增:
- true(默认)允许自动新增字段
- false 不允许自动新增字段,但是文档可以正常写入,但无法对新增字段进行查询等操作
- strict 文档不能写入,报错
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"dynamic": false,
"properties": {
"user": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"social_networks": {
"dynamic": true,
"properties": {}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
定义后my_index这个索引下不能自动新增字段,但是在user.social_networks下可以自动新增子字段
copy_to
- 将该字段复制到目标字段,实现类似_all的作用
- 不会出现在_source中,只用来搜索
```json
DELETE my_index
PUT my_index
{
“mappings”: {
“doc”: {
} } }"properties": { "first_name": { "type": "text", "copy_to": "full_name" }, "last_name": { "type": "text", "copy_to": "full_name" }, "full_name": { "type": "text" } }
PUT my_index/doc/1 { “first_name”: “John”, “last_name”: “Smith” }
GET my_index/_search { “query”: { “match”: { “full_name”: { “query”: “John Smith”, “operator”: “and” } } } }
<a name="index"></a>
## index
- 控制当前字段是否索引,默认为true,即记录索引,false不记录,即不可搜索
<a name="index_options"></a>
## index_options
- index_options参数控制将哪些信息添加到倒排索引,以用于搜索和突出显示,可选的值有:docs,freqs,positions,offsets
- docs:只索引 doc id
- freqs:索引 doc id 和词频,平分时可能要用到词频
- positions:索引 doc id、词频、位置,做 proximity or phrase queries 时可能要用到位置信息
- offsets:索引doc id、词频、位置、开始偏移和结束偏移,高亮功能需要用到offsets
<a name="fielddata"></a>
## fielddata
- 是否预加载 fielddata,默认为false
- Elasticsearch第一次查询时完整加载这个字段所有 Segment 中的倒排索引到内存中
- 如果我们有一些 5 GB 的索引段,并希望加载 10 GB 的 fielddata 到内存中,这个过程可能会要数十秒
- 将 fielddate 设置为 true ,将载入 fielddata 的代价转移到索引刷新的时候,而不是查询时,从而大大提高了搜索体验
- 参考:[预加载 fielddata](https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/preload-fielddata.html)
<a name="eager_global_ordinals"></a>
## eager_global_ordinals
- 是否预构建全局序号,默认false
- 参考:[预构建全局序号(Eager global ordinals)](https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/preload-fielddata.html#global-ordinals)
<a name="doc_values"></a>
## doc_values
参考:[Doc Values and Fielddata](https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/docvalues-and-fielddata.html)
对数据进行检索的时候,倒排索引可以提高检索的效率,但是在对字段进行聚合、排序、使用脚本访问字段值等操作的时候,需要一种不同的数据结构来支持。<br />Doc values 是基于列式存储的结构,在索引数据的时候创建。它存储的值与 _source 中的值相同,**使用列式存储结构使得 Doc values 在处理聚合、排序操作上更高效**。Doc values 支持几乎所有的类型字段,但是 text 和 annotated_text 除外。<br />**Doc values 默认是开启的,保存 Doc values 结构需要很大的空间开销,如果某个字段不需要排序、聚合、使用脚本访问,那么应该禁用此字段的 Doc values 来节省磁盘空间**。其使用示例如下:
```c
PUT my-index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"status_code": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"session_id": {
"type": "keyword",
"doc_values": false
}
}
}
}
fields
- 该参数的目的是为了实现 multi-fields
- 一个字段,多种数据类型
- 譬如:一个字段 city 的数据类型为 text ,用于全文索引,可以通过 fields 为该字段定义 keyword 类型,用于排序和聚合
# 设置 mapping
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"raw": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
# 插入两条数据
PUT my_index/_doc/1
{
"city": "New York"
}
PUT my_index/_doc/2
{
"city": "York"
}
# 查询,city用于全文索引 match,city.raw用于排序和聚合
GET my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"city": "york"
}
},
"sort": {
"city.raw": "asc"
},
"aggs": {
"Cities": {
"terms": {
"field": "city.raw"
}
}
}
}
format
- 由于JSON没有date类型,Elasticsearch预先通过format参数定义时间格式,将匹配的字符串识别为date类型,转换为时间戳(单位:毫秒)
- format默认为:
strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis - Elasticsearch内建的时间格式:
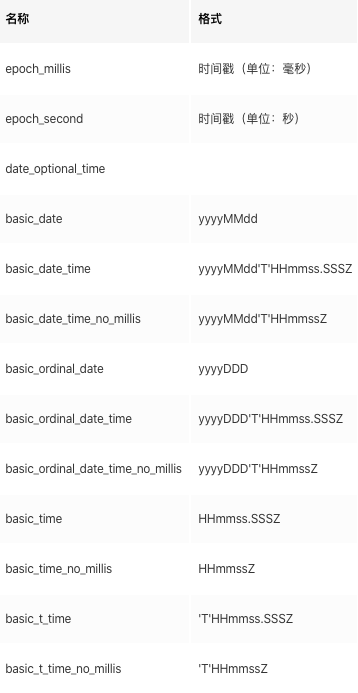
- 上述名称加前缀
strict_表示为严格格式 -
properties
用于_doc,object和nested类型的字段定义子字段 ```json PUT my_index { “mappings”: { “_doc”: {
"properties": { "manager": { "properties": { "age": { "type": "integer" }, "name": { "type": "text" } } }, "employees": { "type": "nested", "properties": { "age": { "type": "integer" }, "name": { "type": "text" } } } }} } }
PUT my_index/_doc/1 { “region”: “US”, “manager”: { “name”: “Alice White”, “age”: 30 }, “employees”: [ { “name”: “John Smith”, “age”: 34 }, { “name”: “Peter Brown”, “age”: 26 } ] }
<a name="normalizer"></a>
## normalizer
- 与 analyzer 类似,只不过 analyzer 用于 text 类型字段,分词产生多个 token,而 normalizer 用于 keyword 类型,只产生一个 token(整个字段的值作为一个token,而不是分词拆分为多个token)
- 定义一个自定义 normalizer,使用大写uppercase过滤器
PUT test_index_4 { “settings”: { “analysis”: { “normalizer”: { “my_normalizer”: { “type”: “custom”, “char_filter”: [], “filter”: [“uppercase”, “asciifolding”] } } } }, “mappings”: { “_doc”: { “properties”: { “foo”: { “type”: “keyword”, “normalizer”: “my_normalizer” } } } } }
插入数据
POST test_index_4/_doc/1 { “foo”: “hello world” }
POST test_index_4/_doc/2 { “foo”: “Hello World” }
POST test_index_4/_doc/3 { “foo”: “hello elasticsearch” }
搜索hello,结果为空,而不是3条!!
GET test_index_4/_search { “query”: { “match”: { “foo”: “hello” } } }
搜索 hello world,结果2条,1 和 2
GET test_index_4/_search { “query”: { “match”: { “foo”: “hello world” } } }
<a name="IxdG4"></a>
## _meta
允许您使用特殊的_meta字段在映射中存储所需的每种JSON数据。映射类型可以具有与之关联的自定义元数据。 Elasticsearch完全不使用这些,但是可以用于存储特定于应用程序的元数据
```json
PUT twitter
{
"mappings": {
"_meta" : {
"attr1": ["value1", "value2"],
"attr2": {
"attr3": "value3"
}
},
"properties": {
"content": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
这个 _meta 字段独立于任何的文档而存在。我们可以通过如下的方法来获取它:
GET twitter/_mapping
{
"twitter" : {
"mappings" : {
"_meta" : {
"attr2" : {
"attr3" : "value3"
},
"attr1" : [
"value1",
"value2"
]
},
"properties" : {
"content" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
}
}
}
在上面,我们可以看到返回的 _meta 字段。
我们也可以使用如下的方法来对它进行更新:
PUT twitter/_mapping
{
"_meta": {
"attr1": [
"value5",
"value6"
],
"attr2": {
"attr3": "value7"
}
},
"properties": {
"content": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
当 Elasticsearch 处理新的映射并找到 _meta 字段时,它将其存储在全局映射状态中,并将信息传播到所有集群节点。
_meta仅用于存储目的; 它不是索引和可搜索的。
其他字段
- coerce
- 强制类型转换,把json中的值转为ES中字段的数据类型,譬如:把字符串”5”转为integer的5
- coerce默认为 true
- 如果coerce设置为 false,当json的值与es字段类型不匹配将会 rejected
- 通过 “settings”: { “index.mapping.coerce”: false } 设置索引的 coerce
- enabled
- 是否索引,默认为 true
- 可以在_doc和字段两个粒度进行设置
- ignore_above
- 设置能被索引的字段的长度
- 超过这个长度,该字段将不被索引,所以无法搜索,但聚合的terms可以看到
- null_value
- 该字段定义遇到null值时的处理策略,默认为Null,即空值,此时ES会忽略该值
- 通过设定该值可以设定字段为 null 时的默认值
- ignore_malformed
- 当数据类型不匹配且 coerce 强制转换时,默认情况会抛出异常,并拒绝整个文档的插入
- 若设置该参数为 true,则忽略该异常,并强制赋值,但是不会被索引,其他字段则照常
- norms
- norms 存储各种标准化因子,为后续查询计算文档对该查询的匹配分数提供依据
- norms 参数对评分很有用,但需要占用大量的磁盘空间
- 如果不需要计算字段的评分,可以取消该字段 norms 的功能
- position_increment_gap
- 与 proximity queries(近似查询)和 phrase queries(短语查询)有关
- 默认值 100
- search_analyzer
- 搜索分词器,查询时使用
- 默认与 analyzer 一样
- similarity
- 设置相关度算法,ES5.x 和 ES6.x 默认的算法为 BM25
- 另外也可选择 classic 和 boolean
- store
- store 的意思是:是否在 _source 之外在独立存储一份,默认值为 false
- es在存储数据的时候把json对象存储到”_source”字段里,”_source”把所有字段保存为一份文档存储(读取需要1次IO),要取出某个字段则通过 source filtering 过滤
- 当字段比较多或者内容比较多,并且不需要取出所有字段的时候,可以把特定字段的store设置为true单独存储(读取需要1次IO),同时在_source设置exclude
- 关于该字段的理解,参考: es设置mapping store属性
- term_vector
- 与倒排索引相关

