1. day04 新增和修改商品
2. 分布式ID生成解决方案
2.1. UUID
常见的方式。可以利用数据库也可以利用程序生成,一般来说全球唯一。
优点:
1)简单,代码方便。
2)生成ID性能非常好,基本不会有性能问题。
3)全球唯一,在遇见数据迁移,系统数据合并,或者数据库变更等情况下,可以从容应对。
缺点:
1)没有排序,无法保证趋势递增。
2)UUID往往是使用字符串存储,查询的效率比较低。
3)存储空间比较大,如果是海量数据库,就需要考虑存储量的问题。
4)传输数据量大
5)不可读。
2.2. Redis
当使用数据库来生成ID性能不够要求的时候,我们可以尝试使用Redis来生成ID。这主要依赖于Redis是单线程的,所以也可以用生成全局唯一的ID。可以用Redis的原子操作 INCR和INCRBY来实现。
优点:
1)不依赖于数据库,灵活方便,且性能优于数据库。
2)数字ID天然排序,对分页或者需要排序的结果很有帮助。
缺点:
1)如果系统中没有Redis,还需要引入新的组件,增加系统复杂度。
2)需要编码和配置的工作量比较大。
3)网络传输造成性能下降。
2.3. snowflake
snowflake是Twitter开源的分布式ID生成算法,结果是一个long型的ID。其核心思想是:使用41bit作为毫秒数,10bit作为机器的ID(5个bit是数据中心,5个bit的机器ID),12bit作为毫秒内的流水号(意味着每个节点在每毫秒可以产生 4096 个 ID),最后还有一个符号位,永远是0
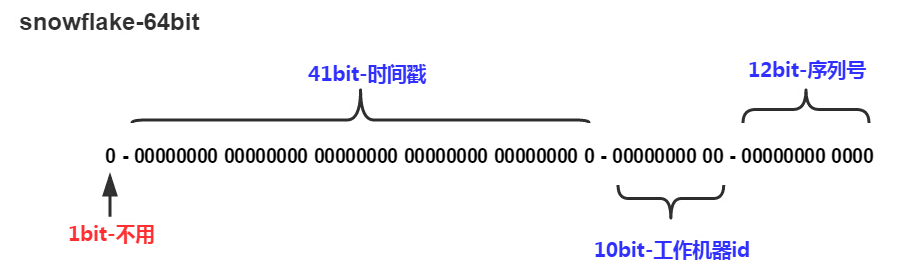
2.4. snowflake测试类
雪花算法编码
package com.changgou.util;import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;import java.net.InetAddress;import java.net.NetworkInterface;/*** <p>名称:IdWorker.java</p>* <p>描述:分布式自增长ID</p>*<pre>* Twitter的 Snowflake JAVA实现方案* </pre>* 核心代码为其IdWorker这个类实现,其原理结构如下,我分别用一个0表示一位,用—分割开部分的作用:* 1||0---0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0 --- 00000 ---00000 ---000000000000* 在上面的字符串中,第一位为未使用(实际上也可作为long的符号位),接下来的41位为毫秒级时间,* 然后5位datacenter标识位,5位机器ID(并不算标识符,实际是为线程标识),* 然后12位该毫秒内的当前毫秒内的计数,加起来刚好64位,为一个Long型。* 这样的好处是,整体上按照时间自增排序,并且整个分布式系统内不会产生ID碰撞(由datacenter和机器ID作区分),* 并且效率较高,经测试,snowflake每秒能够产生26万ID左右,完全满足需要。* <p>* 64位ID (42(毫秒)+5(机器ID)+5(业务编码)+12(重复累加))** @author Polim*/public class IdWorker {// 时间起始标记点,作为基准,一般取系统的最近时间(一旦确定不能变动)private final static long twepoch = 1288834974657L;// 机器标识位数private final static long workerIdBits = 5L;// 数据中心标识位数private final static long datacenterIdBits = 5L;// 机器ID最大值private final static long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);// 数据中心ID最大值private final static long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits);// 毫秒内自增位private final static long sequenceBits = 12L;// 机器ID偏左移12位private final static long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;// 数据中心ID左移17位private final static long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;// 时间毫秒左移22位private final static long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits;private final static long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits);/* 上次生产id时间戳 */private static long lastTimestamp = -1L;// 0,并发控制private long sequence = 0L;private final long workerId;// 数据标识id部分private final long datacenterId;public IdWorker(){this.datacenterId = getDatacenterId(maxDatacenterId);this.workerId = getMaxWorkerId(datacenterId, maxWorkerId);}/*** @param workerId* 工作机器ID* @param datacenterId* 序列号*/public IdWorker(long workerId, long datacenterId) {if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxWorkerId));}if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxDatacenterId));}this.workerId = workerId;this.datacenterId = datacenterId;}/*** 获取下一个ID** @return*/public synchronized long nextId() {long timestamp = timeGen();if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {throw new RuntimeException(String.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds", lastTimestamp - timestamp));}if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {// 当前毫秒内,则+1sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;if (sequence == 0) {// 当前毫秒内计数满了,则等待下一秒timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);}} else {sequence = 0L;}lastTimestamp = timestamp;// ID偏移组合生成最终的ID,并返回IDlong nextId = ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift)| (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift)| (workerId << workerIdShift) | sequence;return nextId;}private long tilNextMillis(final long lastTimestamp) {long timestamp = this.timeGen();while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {timestamp = this.timeGen();}return timestamp;}private long timeGen() {return System.currentTimeMillis();}/*** <p>* 获取 maxWorkerId* </p>*/protected static long getMaxWorkerId(long datacenterId, long maxWorkerId) {StringBuffer mpid = new StringBuffer();mpid.append(datacenterId);String name = ManagementFactory.getRuntimeMXBean().getName();if (!name.isEmpty()) {/** GET jvmPid*/mpid.append(name.split("@")[0]);}/** MAC + PID 的 hashcode 获取16个低位*/return (mpid.toString().hashCode() & 0xffff) % (maxWorkerId + 1);}/*** <p>* 数据标识id部分* </p>*/protected static long getDatacenterId(long maxDatacenterId) {long id = 0L;try {InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost();NetworkInterface network = NetworkInterface.getByInetAddress(ip);if (network == null) {id = 1L;} else {byte[] mac = network.getHardwareAddress();id = ((0x000000FF & (long) mac[mac.length - 1])| (0x0000FF00 & (((long) mac[mac.length - 2]) << 8))) >> 6;id = id % (maxDatacenterId + 1);}} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println(" getDatacenterId: " + e.getMessage());}return id;}public static void main(String[] args) {IdWorker idWorker=new IdWorker(0,0);for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){long nextId = idWorker.nextId();System.out.println(nextId);}}}
创建对象 传递机器id(唯一的) 和 序列化
IdWorker idWorker=new IdWorker(1,1);for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){long id = idWorker.nextId();System.out.println(id);}
输出结果为递增 不重复的long值
2.5. 微服务snowflake
IdWorker.java拷贝到changgou_common工程(公共工程)com.changgou.util包中
在changgou_service_goods的application.yml添加配置
workerId: 0datacenterId: 0
修改GoodsApplication(启动类),增加自动注入雪花算法类
package com.changgou;import com.changgou.util.IdWorker;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import tk.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;@SpringBootApplication@EnableEurekaClient@MapperScan(basePackages = {"com.changgou.goods.dao"})public class GoodsApplication {//从配置文件读取值@Value("${workerId}")private Integer workerId;@Value("${datacenterId}")private Integer datacenterId;public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(GoodsApplication.class);}@Beanpublic IdWorker idWorker() {return new IdWorker(workerId, datacenterId);}}
3. 新增和修改商品
3.1. SPU与SKU概念
SPU = Standard Product Unit (标准产品单位)
概念 : SPU 是商品信息聚合的最小单位,是一组可复用、易检索的标准化信息的集合,该集合描述了一个产品的特性。
通俗点讲,属性值、特性相同的货品就可以称为一个 SPU
例如:华为P30 就是一个 SPU
SKU=stock keeping unit( 库存量单位)
SKU 即库存进出计量的单位, 可以是以件、盒、托盘等为单位。
SKU 是物理上不可分割的最小存货单元。在使用时要根据不同业态,不同管理模式来处理。
在服装、鞋类商品中使用最多最普遍。
例如:华为P30 红色 64G 就是一个 SKU
3.2. 代码实现
前端传递给后端的数据格式 是一个spu对象和sku列表组成的对象
{"spu": {"name": "这个是商品名称","caption": "这个是副标题","brandId": 12,"category1Id": 558,"category2Id": 559,"category3Id": 560,"freightId": 10,"image": "http://www.changgou.com/image/1.jpg","images": "http://www.changgou.com/image/1.jpg,http://www.changgou.com/image/2.jpg","introduction": "这个是商品详情,html代码","paraItems": "{'出厂年份':'2019','赠品':'充电器'}","saleService": "七天包退,闪电退货","sn": "020102331","specItems": "{'颜色':['红','绿'],'机身内存':['64G','8G']}","templateId": 42},"skuList": [{"sn": "10192010292","num": 100,"alertNum": 20,"price": 900000,"spec": "{'颜色':'红','机身内存':'64G'}","image": "http://www.changgou.com/image/1.jpg","images": "http://www.changgou.com/image/1.jpg,http://www.changgou.com/image/2.jpg","status": "1","weight": 130},{"sn": "10192010293","num": 100,"alertNum": 20,"price": 600000,"spec": "{'颜色':'蓝','机身内存':'128G'}","image": "http://www.changgou.com/image/1.jpg","images": "http://www.changgou.com/image/1.jpg,http://www.changgou.com/image/2.jpg","status": "1","weight": 130}]}
3.3. SPU与SKU列表的保存
changgou_service_goods_api工程创建组合实体类Goods
package com.changgou.goods.pojo;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.List;public class Goods implements Serializable {//spuprivate Spu spu;//sku集合private List<Sku> skuList;public Spu getSpu() {return spu;}public void setSpu(Spu spu) {this.spu = spu;}public List<Sku> getSkuList() {return skuList;}public void setSkuList(List<Sku> skuList) {this.skuList = skuList;}}
changgou_service_goods工程SpuService 新增方法add 修改为Goods pojo
/**** 新增* @param goods*/void add(Goods goods);
SpuServiceImpl 修改add方法
@Autowiredprivate IdWorker idWorker;@Autowiredprivate CategoryMapper categoryMapper;@Autowiredprivate BrandMapper brandMapper;@Autowiredprivate SkuMapper skuMapper;@Transactional@Overridepublic void add(Goods goods) {//添加spuSpu spu = goods.getSpu();//设置分布式idspu.setId(String.valueOf(idWorker.nextId()));//设置删除状态spu.setIsDelete("0"); //未被删除//设置上架状态spu.setIsMarketable("0"); //未上架//审核状态spu.setStatus("0"); //未审核spuMapper.insertSelective(spu);//添加sku集合this.saveSkuList(goods);}//添加sku数据private void saveSkuList(Goods goods) {Spu spu = goods.getSpu();//查询分类对象Category category = categoryMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(spu.getCategory3Id());//查询品牌对象Brand brand = brandMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(spu.getBrandId());//获取sku集合List<Sku> skuList = goods.getSkuList();if (skuList != null) {//遍历集合 循环填充数据 并添加到数据库中for (Sku sku : skuList) {//设置skuIdsku.setId(String.valueOf(idWorker.nextId()));//设置sku规格数据if (StringUtils.isEmpty(sku.getSpec())) {sku.setSpec("{}");}//设置sku名称 spu名称+规格String name = spu.getName();//将规格json转为map 将map中的value进行拼接Map<String, String> specMap = JSON.parseObject(sku.getSpec(), Map.class);if (specMap != null && specMap.size() > 0) {for (String value : specMap.values()) {name += " " + value;}}sku.setName(name);//设置spu idsku.setSpuId(spu.getId());//设置创建和修改时间sku.setCreateTime(new Date());sku.setUpdateTime(new Date());//商品分类idsku.setCategoryId(category.getId());//设置商品分类名称sku.setCategoryName(category.getName());//设置品牌名称sku.setBrandName(brand.getName());//将sku添加到数据skuMapper.insertSelective(sku);}}}
修改controller层spu的add方法
/**** 新增数据* @param goods* @return*/@PostMappingpublic Result add(@RequestBody Goods goods){spuService.add(goods);return new Result(true,StatusCode.OK,"添加成功");}
3.4. 品牌与分类关联
将分类ID与SPU的品牌ID 一起插入到tb_category_brand表中
创建实体类
package com.changgou.goods.pojo;import javax.persistence.Id;import javax.persistence.Table;@Table(name = "tb_category_brand")public class CategoryBrand {//分类id@Idprivate Integer category_id;//品牌id@Idprivate Integer brandId;public Integer getCategory_id() {return category_id;}public void setCategory_id(Integer category_id) {this.category_id = category_id;}public Integer getBrandId() {return brandId;}public void setBrandId(Integer brandId) {this.brandId = brandId;}}
mapper层
package com.changgou.goods.dao;import com.changgou.goods.pojo.CategoryBrand;import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper;public interface CategoryBrandMapper extends Mapper<CategoryBrand> {}
SpuServiceImpl 注入 并封装CategoryBrand 判断表中是否有值 如无则插入
@Autowiredprivate CategoryBrandMapper categoryBrandMapper;//添加sku数据private void saveSkuList(Goods goods) {Spu spu = goods.getSpu();//查询分类对象Category category = categoryMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(spu.getCategory3Id());//查询品牌对象Brand brand = brandMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(spu.getBrandId());//获取品牌与分类的关联关系//查询关联表CategoryBrand categoryBrand = new CategoryBrand();categoryBrand.setBrandId(spu.getBrandId());categoryBrand.setCategory_id(spu.getCategory3Id());int count = categoryBrandMapper.selectCount(categoryBrand);if (count == 0) {//品牌和分类没有关联关系categoryBrandMapper.insert(categoryBrand);}//获取sku集合List<Sku> skuList = goods.getSkuList();if (skuList != null) {//遍历集合 循环填充数据 并添加到数据库中for (Sku sku : skuList) {//设置skuIdsku.setId(String.valueOf(idWorker.nextId()));//设置sku规格数据if (StringUtils.isEmpty(sku.getSpec())) {sku.setSpec("{}");}//设置sku名称 spu名称+规格String name = spu.getName();//将规格json转为map 将map中的value进行拼接Map<String, String> specMap = JSON.parseObject(sku.getSpec(), Map.class);if (specMap != null && specMap.size() > 0) {for (String value : specMap.values()) {name += " " + value;}}sku.setName(name);//设置spu idsku.setSpuId(spu.getId());//设置创建和修改时间sku.setCreateTime(new Date());sku.setUpdateTime(new Date());//商品分类idsku.setCategoryId(category.getId());//设置商品分类名称sku.setCategoryName(category.getName());//设置品牌名称sku.setBrandName(brand.getName());//将sku添加到数据skuMapper.insertSelective(sku);}}}
3.5. 根据id查询商品
changgou_service_goods工程SpuService新增方法定义
Goods findGoodsById(String id);
serviceimpl实现此方法
/*** 根据id查询spu和sku列表信息* @param id* @return*/@Overridepublic Goods findGoodsById(String id) {Goods goods =new Goods();//查询spu信息 封装到goods中Spu spu = spuMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);goods.setSpu(spu);//查询sku 封装Example example = new Example(Sku.class);Example.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();//根据spu进行sku列表查询criteria.andEqualTo("spuId",id);List<Sku> skus = skuMapper.selectByExample(example);goods.setSkuList(skus);return goods;}
修改SpuController的findById方法
/**** 根据ID查询数据* @param id* @return*/@GetMapping("/{id}")public Result findById(@PathVariable String id){// Spu spu = spuService.findById(id);Goods goods = spuService.findGoodsById(id);return new Result(true,StatusCode.OK,"查询成功",goods);}
3.6. 保存修改
changgou_service_goods工程SpuService修改方法定义
/**** 修改* @param goods*/void update(Goods goods);
changgou_service_goods工程SpuServiceImpl实现此方法
/*** 修改** @param goods*/@Transactional@Overridepublic void update(Goods goods) {//修改spuSpu spu = goods.getSpu();spuMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(spu);//修改sku 删除原有的sku列表 重新添加sku列表Example example=new Example(Sku.class);Example.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();criteria.andEqualTo("spuId",spu.getId());skuMapper.deleteByExample(example);//重新添加sku列表this.saveSkuList(goods);}
controller
/**** 修改数据* @param goods* @param id* @return*/@PutMapping(value="/{id}")public Result update(@RequestBody Goods goods,@PathVariable String id){spuService.update(goods);return new Result(true,StatusCode.OK,"修改成功");}
3.7. 商品审核和上下架
商品新增后,审核状态为0(未审核),默认为下架状态。
审核商品,需要校验是否是被删除的商品,如果未删除则修改审核状态为1,并自动上架
下架商品,需要校验是否是被删除的商品,如果未删除则修改上架状态为0
上架商品,需要审核状态为1,如果为1,则更改上下架状态为1
3.7.1. 商品审核
需要校验是否是被删除的商品,如果未删除则修改审核状态为1,并自动上架
SpuService新增方法
//商品审核并自动上架void audit(String id);
SpuServiceImpl实现方法
@Override@Transactionalpublic void audit(String id) {//查询spu对象Spu spu = spuMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);if (spu == null){throw new RuntimeException("当前商品不存在");}//判断当前spu是否处于删除状态if ("1".equals(spu.getIsDelete())){throw new RuntimeException("当前商品处于删除状态");}//不是删除状态 修改审核状态为1 上下架状态为1spu.setStatus("1");spu.setIsMarketable("1");//修改表数据spuMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(spu);}
SpuController实现方法
@PutMapping("/audit/{id}")public Result audit(@PathVariable("id") String id){spuService.audit(id);return new Result(true,StatusCode.OK,"商品审核成功");}
3.7.2. 下架商品
校验是否是被删除的商品,如果未删除则修改上架状态为0
SpuService新增方法
//商品下架void pull(String id);
SpuServiceImpl实现方法
@Override@Transactionalpublic void pull(String id) {//查询spuSpu spu = spuMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);if (spu == null){throw new RuntimeException("当前商品不存在");}//判断当前商品是否处于删除状态if ("1".equals(spu.getIsDelete())){throw new RuntimeException("当前商品处于删除状态");}//商品处于未删除状态 则修改上下架状态为已下架spu.setIsMarketable("0");spuMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(spu);}
controller
@PutMapping("/pull/{id}")public Result pull(@PathVariable("id") String id){spuService.pull(id);return new Result(true,StatusCode.OK,"商品下架成功");}
3.7.3. 上架商品
必须是通过审核的商品才能上架
SpuService新增方法
//商品上架void put(String id);
SpuServiceImpl 实现此方法
@Override@Transactionalpublic void put(String id) {//查询spuSpu spu = spuMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);if (spu == null){throw new RuntimeException("当前商品不存在");}//商品审核状态是否为已审核if ("0".equals(spu.getStatus())){throw new RuntimeException("当前商品未审核");}//上架状态改为1 已上架spu.setIsMarketable("1");spuMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(spu);}
SpuController新增方法
@PutMapping("/put/{id}")public Result put(@PathVariable("id") String id){spuService.put(id);return new Result(true,StatusCode.OK,"商品上架成功");}
3.8. 删除与还原商品
商品列表中的删除商品功能,并非真正的删除(物理删除),而是采用逻辑删除将删除标记的字段设置为1.
在回收站中有还原商品的功能,将删除标记的字段设置为0
在回收站中有删除商品的功能,是真正的物理删除,将数据从数据库中删除掉。
商品列表中的删除商品,执行逻辑删除,修改spu表is_delete字段为1
商品回收站中的还原商品,修改spu表is_delete字段为0
商品回收站中的删除商品,执行delete操作,进行物理删除
3.8.1. 逻辑删除商品
修改SpuServiceImpl的delete方法
/*** 删除** @param id*/@Override@Transactionalpublic void delete(String id) {//逻辑删除//查询spuSpu spu = spuMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);if (spu == null){throw new RuntimeException("当前商品不存在");}//当前商品是否处于下架状态if ("1".equals(spu.getIsMarketable())){throw new RuntimeException("当前商品必须处于下架状态才能删除");}//已下架商品 则修改逻辑删除状态spu.setIsDelete("1");spu.setStatus("0"); //未审核spuMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(spu);}
3.8.2. 商品还原
SpuService新增方法
//还原商品void restore(String id);
impl实现方法
@Override@Transactionalpublic void restore(String id) {//查询spuSpu spu = spuMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);if (spu == null) {throw new RuntimeException("当前商品不存在");}//当前商品已经删除if ("0".equals(spu.getIsDelete())) {throw new RuntimeException("当前商品未被删除");}//修改删除状态 和审核状态spu.setIsDelete("0");spu.setStatus("0"); //未审核spuMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(spu);}
SpuController新增方法
@PutMapping("/restore/{id}")public Result restore(@PathVariable("id") String id){spuService.restore(id);return new Result(true,StatusCode.OK,"商品还原成功");}
3.8.3. 物理删除
判断必须逻辑删除商品才能物理删除
service层
//物理删除商品void realDel(String id);
impl
@Override@Transactionalpublic void realDel(String id) {//查询spuSpu spu = spuMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);if (spu == null) {throw new RuntimeException("当前商品不存在");}//当前商品未删除if ("0".equals(spu.getIsDelete())) {throw new RuntimeException("当前商品未被删除");}//执行删除spuMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(id);}
controller
@DeleteMapping("/realDel/{id}")public Result realDel(@PathVariable("id") String id) {spuService.realDel(id);return new Result(true, StatusCode.OK, "商品删除成功");}

