训练题:矩阵路径
- 时间复杂度:O(3kMN),k为字符串长度
- 空间复杂度:O(k) ```cpp
bool exist( vector
bool dfs( vector
char shit = board[i][j];board[i][j] = '*';if( dfs( board, word, countRow, countCol, wordSize, start + 1, i + 1, j ) ) { return true; }if( dfs( board, word, countRow, countCol, wordSize, start + 1, i - 1, j ) ) { return true; }if( dfs( board, word, countRow, countCol, wordSize, start + 1, i, j + 1 ) ) { return true; }if( dfs( board, word, countRow, countCol, wordSize, start + 1, i, j - 1 ) ) { return true; }board[i][j] = shit;return false;
}
<a name="pMpfj"></a># 训练题:顺时针打印矩阵题目:[http://t.cn/A6GkjcYi](http://t.cn/A6GkjcYi)<a name="caKLL"></a>## 方法一:模拟法- 时间复杂度:O(m*n)- 空间复杂度:O(m*n)模拟法,模拟顺时针的过程,递归模拟。```cppvector<int> spiralOrder( vector<vector<int>> &matrix ){if( matrix.empty() ) { return {}; }const auto countRow = matrix.size();const auto countCol = matrix[0].size();// 0:水平往右遍历// 1:垂直往下遍历// 2:水平往左遍历// 3:垂直往上遍历char direction = 0;vector<int> ret;ret.reserve( countRow * countCol );// 保存已经遍历的元素vector<vector<bool>> visited( countRow, vector<bool>( countCol, false ) );_print( matrix, visited, ret, countRow, countCol, direction, 0, 0 );return ret;}bool _print( vector<vector<int>> &matrix, vector<vector<bool>> &visited, vector<int> &container, const int &countRow, const int &countCol, char &direction, int i, int j ){// 索引已经越界或者已经被访问过了if( j >= countCol || j < 0 || i >= countRow || i < 0 || visited[i][j] ) { return false; }// 记录访问元素container.push_back( matrix[i][j] );visited[i][j] = true;// 先尝试继续相同方向的访问,如果失败了就切换到下一个方向尝试。if( direction % 4 == 0 && !_print( matrix, visited, container, countRow, countCol, direction, i, j + 1 ) ) { ++direction %= 4; }if( direction % 4 == 1 && !_print( matrix, visited, container, countRow, countCol, direction, i + 1, j ) ) { ++direction %= 4; }if( direction % 4 == 2 && !_print( matrix, visited, container, countRow, countCol, direction, i, j - 1 ) ) { ++direction %= 4; }if( direction % 4 == 3 && !_print( matrix, visited, container, countRow, countCol, direction, i - 1, j ) ) { ++direction %= 4; }if( direction % 4 == 0 && !_print( matrix, visited, container, countRow, countCol, direction, i, j + 1 ) ) { ++direction %= 4; }return true;}
方法二:层遍历
- 时间复杂度:O(m*n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
从外层往内层遍历,依次打印每层的上、右、下、左。
vector<int> spiralOrder( vector<vector<int>> &matrix ){if( matrix.empty() ) { return {}; }const auto countRow = matrix.size();const auto countCol = matrix[0].size();// 记录当前的层索引char left = 0;char right = countCol - 1;char top = 0;char bottom = countRow - 1;vector<int> ret;ret.reserve( countRow * countCol );while( true ){for( int tmp = left; tmp <= right; ++tmp ) { ret.push_back( matrix[top][tmp] ); }if( ++top > bottom ) { break; }for( int tmp = top; tmp <= bottom; ++tmp ) { ret.push_back( matrix[tmp][right] ); }if( --right < left ) { break; }for( int tmp = right; tmp >= left; --tmp ) { ret.push_back( matrix[bottom][tmp] ); }if( --bottom < top ) { break; }for( int tmp = bottom; tmp >= top; --tmp ) { ret.push_back( matrix[tmp][left] ); }if( ++left > right ) { break; }}return ret;}
训练题:旋转矩阵
方法一
- nums[i][j],旋转之后,到了nums[j][n - i - 1]的位置。
用一个相同大小的辅助数组保存旋转后的矩阵
时间复杂度:O(N)
-
方法二:模拟旋转
时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
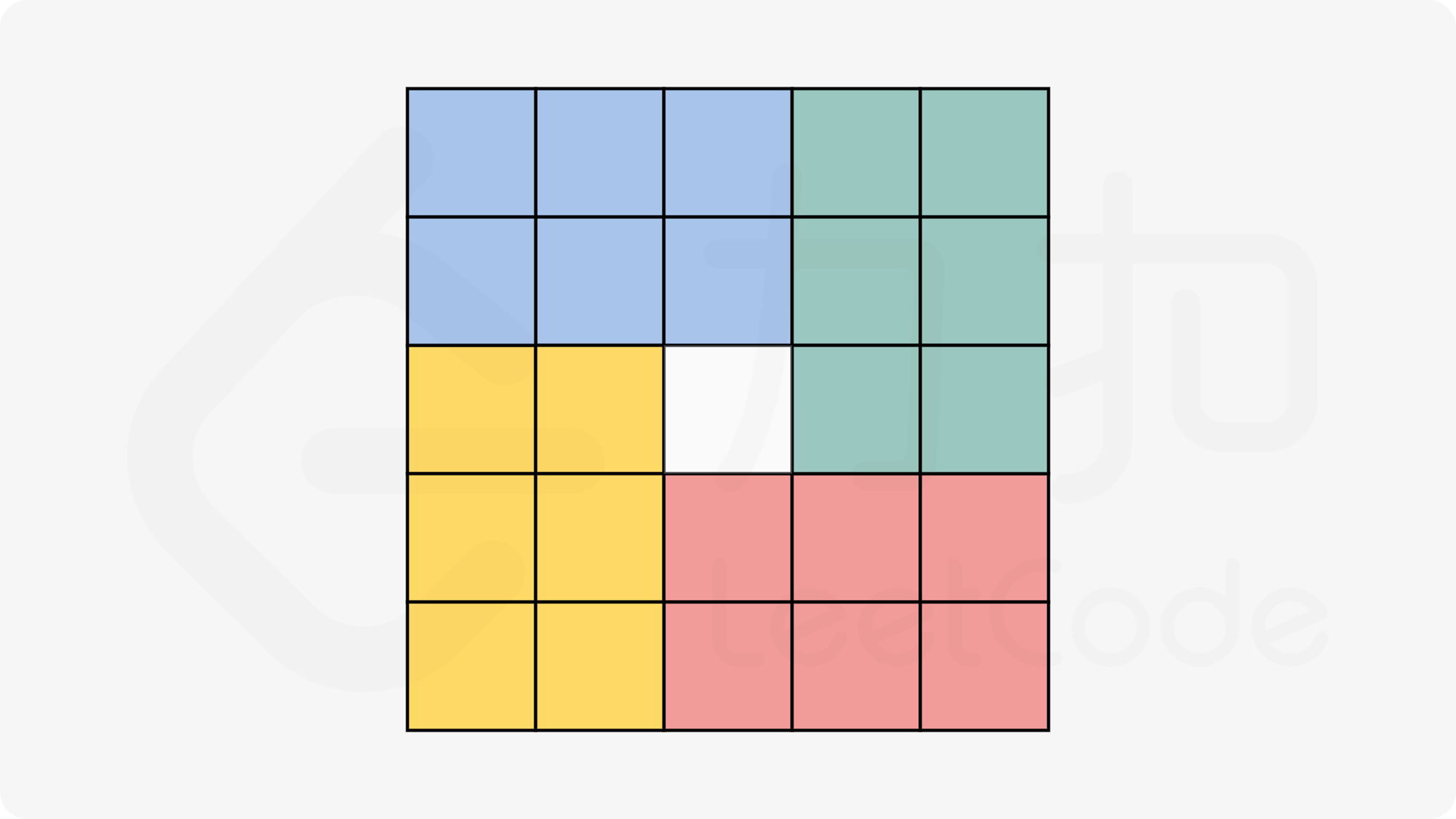
以nums[0][0]元素为例,旋转后到了右上角,这时如果我们再将右上角这个被覆盖之前的元素再旋转到右下角,以此类推,总共旋转4次,最后又旋转到了nums[0][0],这时我们就完成了四个角元素的旋转。我们称这个为一个循环循环。
以下图描述了n分别为奇数和偶数时,我们可以对这4个部分的每个元素进行一个旋转循环就完成了整个矩阵的旋转。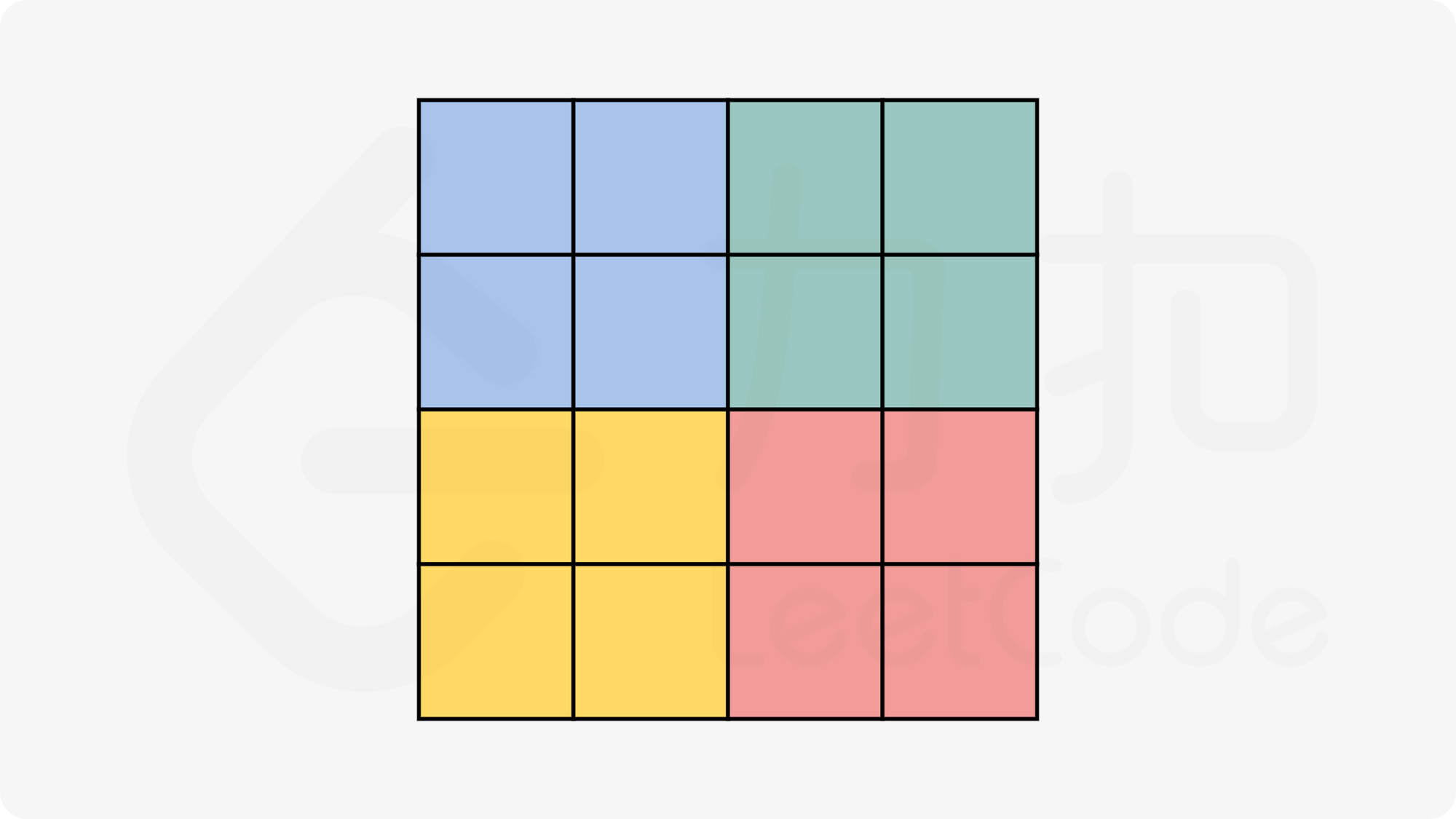
void rotate(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {if(matrix.size() < 2) return;const auto size = matrix.size();int startI = 0, startJ = 0, nextVal = 0, tmp;int row = 0, col = 0;if(size & 0x1){row = (size - 1) >> 1;col = (size + 1) >> 1;}else row = col = size >> 1;for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i){for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j){// 一个旋转循环startI = i, startJ = j;nextVal = matrix[i][j];while(true) {tmp = startI;startI = startJ;startJ = size - tmp - 1;tmp = matrix[startI][startJ];matrix[startI][startJ] = nextVal;nextVal = tmp;if(startI == i && startJ == j) break;}}}}
方法二:翻转代替旋转
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
旋转90° = 上下翻转 + 主对角线翻转。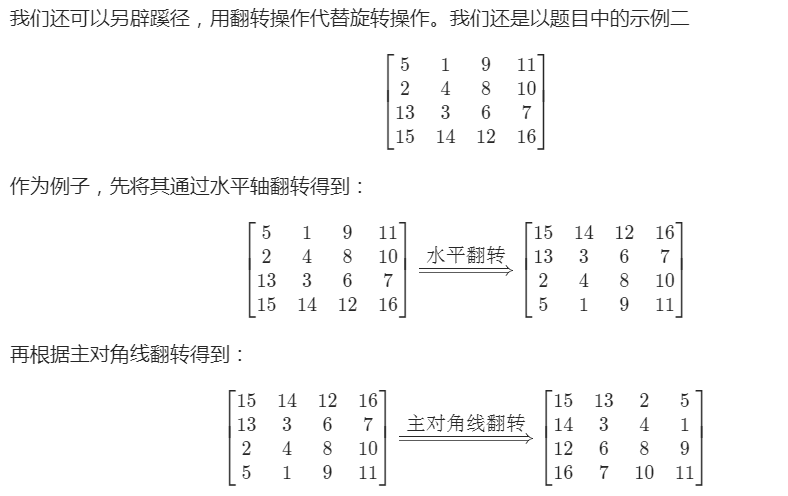
void rotate(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {if(matrix.size() < 2) return;const auto size = matrix.size();const auto size_2 = (size >> 1);// 上下翻转for(int row = 0; row < size_2; ++row){for(int col = 0; col < size; ++col)std::swap(matrix[row][col],matrix[size - 1 - row][col]);}// 主对角线翻转一次for(int row = 0; row < size; ++row){for(int col = row + 1; col < size; ++col)std::swap(matrix[row][col], matrix[col][row]);}}
训练题:矩阵找数
方法一:二叉搜索树
将矩阵逆时针旋转45°就是一个二叉搜索树。左节点<父节点<右节点。
我们从根节点(右上角位置)开始遍历查找,
bool findNumberIn2DArray(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {if( matrix.empty() || matrix[0].empty() ) { return false; }const auto n = matrix.size();for( int i = 0, j = matrix[0].size()-1; i < n && j >=0; ){if( matrix[i][j] > target ) { --j; }else if( matrix[i][j] < target ) { ++i; }else { return true; }}return false;}
方法二:同理
既然可以右上角,那也可以左下角。本质一样,只不过方向别扭。
bool findNumberIn2DArray(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {if( matrix.empty() || matrix[0].empty() ) { return false; }const auto m = matrix[0].size();for( int i = matrix.size() - 1, j = 0; i >= 0 && j < m; ){if( matrix[i][j] > target ) { --i; }else if( matrix[i][j] < target ) { ++j; }else { return true; }}return false;}

