一、字典Dictionary
ADT
template<class Key, class Elem, class KEComp, class EEComp>class Dictionary{public:virtual void clear() = 0; //重新初始化virtual bool insert(const Elem&) = 0; //插入一个元素virtual bool remove(const Key&, Elem&) = 0; //根据key删除元素//按照自定义规则删除一个元素,循环执行则最终会清空字典。virtual bool removeAny(Elem&) = 0;virtual bool find(const Key&, Elem&) const = 0; //根据key查找元素virtual int size() = 0; //元素总个数}
1、字典(无序顺序表)
template<class Key, class Elem, class KEComp, class KKComp>class UALdict : public Dictionary<Key, Elem, KEComp, KKComp>{private:AList<Elem>* list;public:UALdict(int size = DefaultListSize){list = new AList<Elem>(size);}~UALdict(){delete list;}void clear(){list.clear();}bool insert(const Elem& elem){return list->append(elem);}bool remove(const Key& key, Elem& elem){for(list->setStart(); list->getValue(e); list->next()){if(KEComp::eq(K, e)){list->remove(e);return true;}}return false;}//删除尾部元素bool removeAny(Elem& e){if(size() == 0) return false;list->setEnd();list->prev();list->remove(e);return true;}bool find(const Key& key, Elem& e){for(list->setStart(); list->getValue(e); list->next()){if(KEComp::eq(K, e)){return true;}}return false;}int size(){return list->leftLength() + list->rightLength();}}
2、字典(有序顺序表)
template<class Key, class Elem, class KEComp, class KKComp, class EEComp>class SALdict : public Dictionary<Key, Elem, KEComp, KKComp, EEComp>{private:AList<Elem>* list;public:SALdict(int size = DefaultListSize){list = new AList<Elem>(size);}~SALdict(){delete list;}void clear(){list.clear();}bool insert(const Elem& elem){return list->insert(elem);}bool remove(const Key& key, Elem& elem){for(list->setStart(); list->getValue(e); list->next()){if(KEComp::eq(K, e)){list->remove(e);return true;}}return false;}//删除尾部元素bool removeAny(Elem& e){if(size() == 0) return false;list->setEnd();list->prev();list->remove(e);return true;}//可以用上面无序一样的,但因为是有序,可以用二分查找bool find(const Key& key, Elem& e){int l = -1;int r = list->leftLength() + list->rightLength();while((l + 1) != r){int i = (l + r) / 2;list->setPos(i);list->getValue(e);if(KEComp::lt(K, e)) r = i;else if(KEComp::eq(K, e)) return true;else if(KEComp::lt(K, e)) l = i;}return false;}int size(){return list->leftLength() + list->rightLength();}}
二、栈Stack
在一端进行插入/删除的线性表,LIFO后进先出。
何必限制一端进行插入删除?
受限制的功能往往意味着更低的实现成本,而这些功能又刚好满足。
ADT
template<class Elem>class Stack<Elem>{public:virtual void clear() = 0; //重新初始化virtual bool push(const Elem& elem) = 0; //入栈virtual bool pop(Elem& elem) = 0; //出栈virtual bool topValue(Elem& elem) = 0; //栈顶值virtual int length() const = 0; //当前栈大小}
1、顺序栈
template<class Elem>class AStack<Elem> : public Stack<Elem>{private:int size; //当前栈大小int top; //栈顶位置,0表示栈空Elem *listArray; //栈空间:数组public:AStack(int s = DefaultListSize){listArray = new Elem[s];size = s;top = 0;}~AStack(){size = top = 0;delete[] listArray;}void clear(){top = 0;}bool push(const Elem& elem){if(top == size) return false;listArray[top++] = elem;return true;}bool pop(Elem& elem){if(top == 0) return false;elem = listArray[--top];return true;}bool topValue(Elem& elem){if(top == 0) return false;elem = listArray[top-1];return true;}int length() const{return top;}}
2、链式栈
template<class Elem>class LStack : public Stack<Elem>{private:Link<Elem>* top;int size; //当前栈大小public:LStack(int s = DefaultListSize){top = NULL;size = 0;}~LStack(){clear();}void clear(){Link<Elem>* temp = NULL;while(top != NULL){temp = top;top = top->next;delete temp;}size = 0;}bool push(const Elem& elem){top = new Link<Elem>(elem, top);size++;return true;}bool pop(Elem& elem){if(top == NULL) return false;elem = top->element;top = top->next;Link<Elem>* temp = top->next;delete top;top = temp;size --;return true;}bool topValue(Elem& elem){if(top == NULL) return false;elem = top->element;return true;}int length() const{return size;}}
3、顺序栈和链式栈比较
栈使用率不满时,顺序栈空间浪费。
链式栈有链接域,占空间,压栈入栈有内存分配,频繁的操作性能更低。
顺序栈的有数组的单向延伸性,两个栈,可以考虑一个数组,从两头往中间插入数据。
栈代替递归:汉诺塔
前面汉诺塔的递归算法用栈替换:
enum TOHop { DOMVE, DOTOH };class TOHobj{public:TOHop op;int num;Pole start, goal, temp;TOHobj(int num, Pole s, Pole g, Pole t){op = DOTOH;num = num;start = s;goal = g;temp = t;}TOHobj(Pole s, Pole g){op = DOMOVE;start = s;goal = g;}}void TOH(int num, Pole start, Pole goal, Pole temp, Stack<TOHobj*>& stack){stack.push(TOHobj(num, start, goal, temp));TOHobj *t;while(stack.pop(t)){if(t->op == DOMOVE){move(t->start, t->goal);}else if(t->num > 0){int num = t->num;Pole temp = t->temp;Pole goal = t->goal;Pole start = t->start;//压栈的顺序和调用顺序是相反的,所以下面三句也应该要反。stack.push(new THOobj(num - 1, temp, goal, start));stack.push(new THOobj(start, goal));stack.push(new THOobj(num - 1, start, temp, goal));}delete t;}}
三、队列Queue
ADT
template<class Elem>class Queue{public:virtual void clear() = 0; //重新初始化virtual bool enqueue(const Elem&) = 0;virtual bool dequeue(Elem&) = 0;virtual bool frontValue(Elem&) const = 0;virtual length() const = 0; //当前队列长度}
1、(顺序)队列
1、直接用数组的话,入队/出队会引起所有成员移动位置,性能会非常低。
2、队列数据放在数组中间,想法很好,性能很好,但是大小受限。
3、“环形”数组实现,不是数组真的环形,是以在队列位置mod模除队列长度来取数组地址。
4、队列长度n,数组长度必须是n+1,才好区分队列空和满的情况;当然也可以通过计数的方式。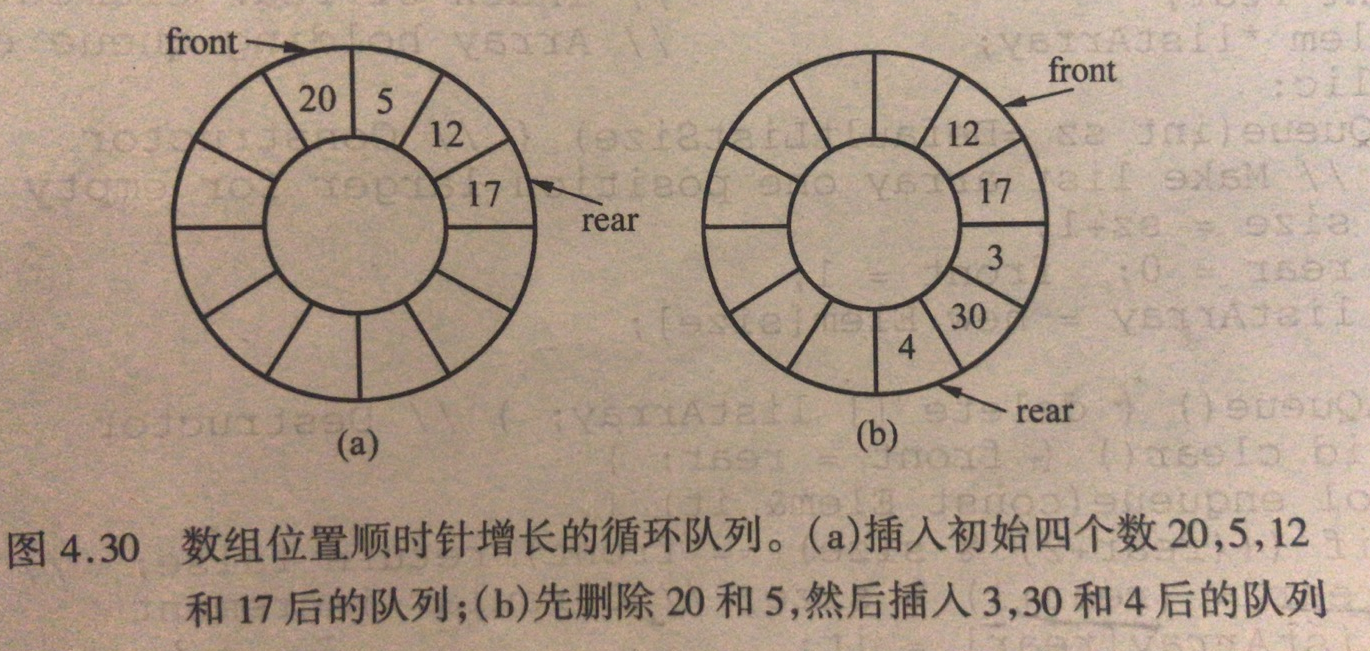
认真理解上图中文字。
template<class Elem>class AQueue : public Queue<Elem>{private:int size; //队列空间大小 + 1int front; //队首int rear; //队尾Elem *listArray; //队列空间public:AQueue(int size = DefaultListSize){this->size = size + 1;front = 1; //第一个元素从位置1开始插入rear = 0;listArray = new Elem[size + 1];}~AQueue(){delete[] listArray;}void clear(){front = rear;}bool enqueue(const Elem& elem){if ((rear + 2) % size == front) return false;rear = (rear + 1) % size;listArray[rear] = elem;return true;}bool dequeue(Elem& elem){if(length() == 0) return false;elem = listArray[front];front = (front + 1) % size;return true;}bool frontValue(Elem& elem) const{if(length() == 0) return false;elem = listArray[front];return true;}virtual int length() const{return ((rear + size) - front + 1) % size;}}
2、(链式)队列
template<class Elem>class LQueue : public Queue<Elem>{private:Link<Elem> *front; //队首Link<Elem> *rear; //队尾int size; //当前队列长度public:LQueue(int size = DefaultListSize){front = NULL;rear = NULL;size = 0;}~LQueue(){clear();}void clear(){Link<Elem> *temp = NULL;while(front != NULL){rear = front;front = front->next;delete rear;}rear = NULL;size = 0;}bool enqueue(const Elem& elem){if(size == 0){front = rear = new Link<Elem>(elem, NULL);}else{rear->next = new Link<Elem>(elem, NULL);rear = rear->next;}size++;return true;}bool dequeue(Elem& elem) const {if(size == 0) return false;elem = front->element;Link<Elem>* temp = front;front = front->next;if(front == NULL) rear = NULL;delete temp;size --;return true;}bool frontValue(Elem& elem) const {if(size == 0) return false;elem = front->element;return true;}int length() const{return size;}}

