🥈Medium
给定一个二叉树,返回它的中序遍历。
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]1\2/3输出: [1,3,2]
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
题解
递归
使用递归算法,应该很简单,竟然还写不出来!!!太垃圾了吧😧
垃圾代码:
Python
错的!
# Definition for a binary tree node.# class TreeNode:# def __init__(self, x):# self.val = x# self.left = None# self.right = Noneclass Solution:def inorderTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:ans=[]if not root:return ansif root.left:self.inorderTraversal(root.left)ans.append(root.val)if root.right:self.inorderTraversal(root.right)return ans
正确的!
# Definition for a binary tree node.# class TreeNode:# def __init__(self, x):# self.val = x# self.left = None# self.right = Noneclass Solution:def inorderTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:ans=[]def inorder(node):if not node:returninorder(node.left)ans.append(node.val)inorder(node.right)inorder(root)return ans
JavaScript
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {const res = [];const inorder = (root) => {if (!root) {return;}inorder(root.left);res.push(root.val);inorder(root.right);}inorder(root);return res;};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
,其中 n 为二叉树节点的个数。二叉树的遍历中每个节点会被访问一次且只会被访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:
。空间复杂度取决于递归的栈深度,而栈深度在二叉树为一条链的情况下会达到
的级别。
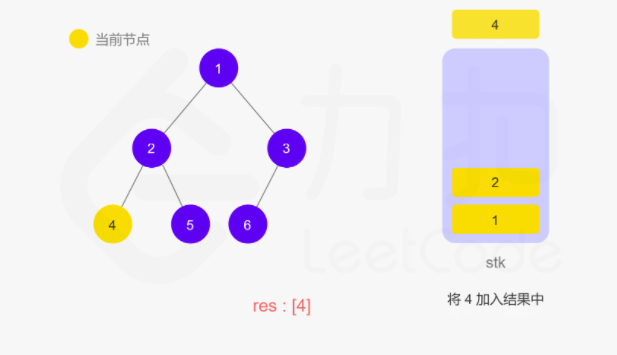
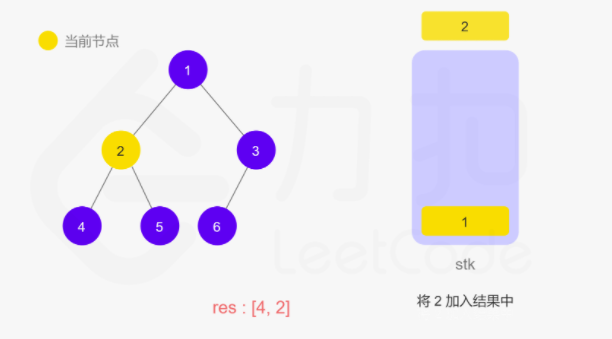
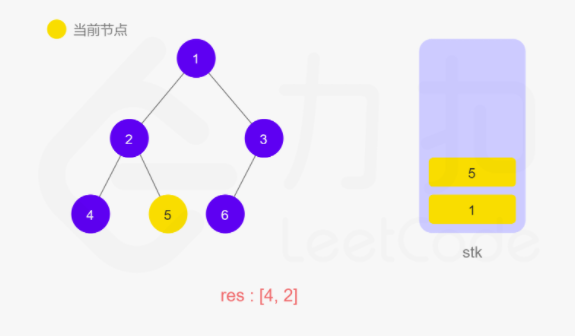
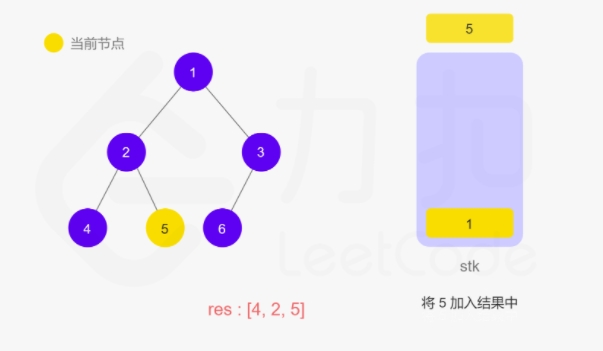
迭代
上面递归的操作也可以用栈来完成。两种方式等价的,只不过是迭代把递归中隐式维护的栈显式模拟出来。如下图所示: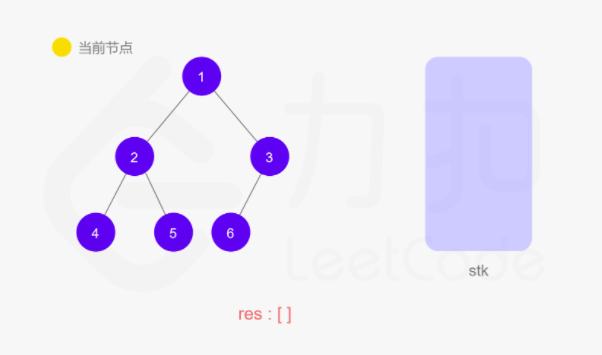
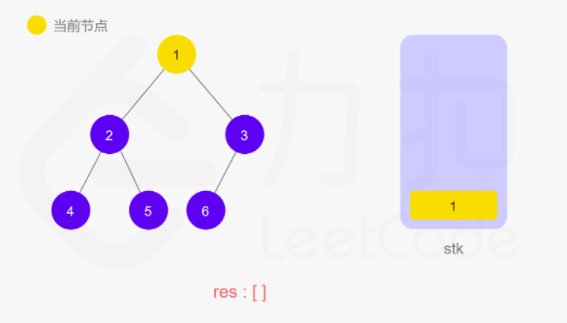
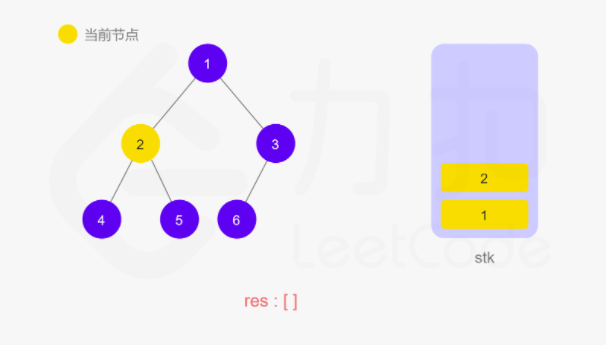
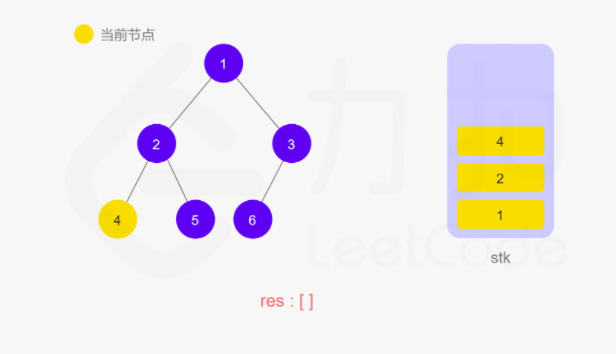
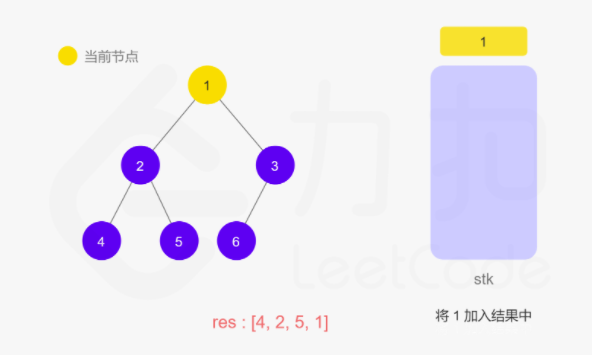
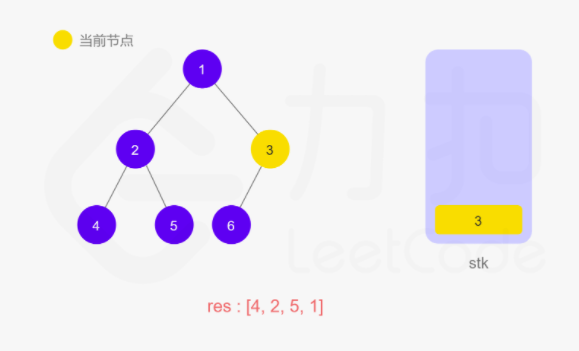
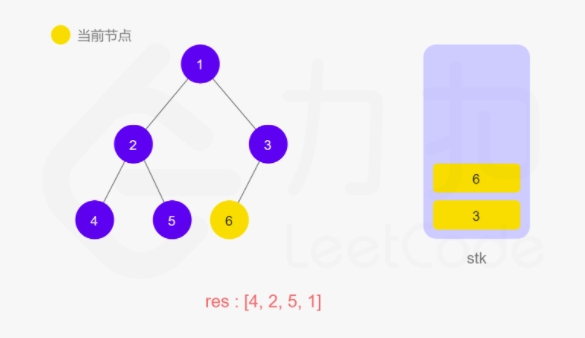
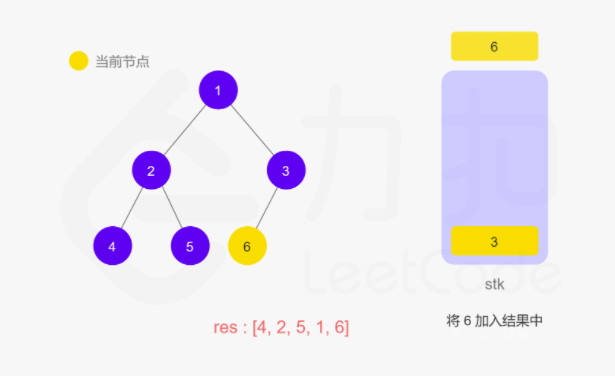
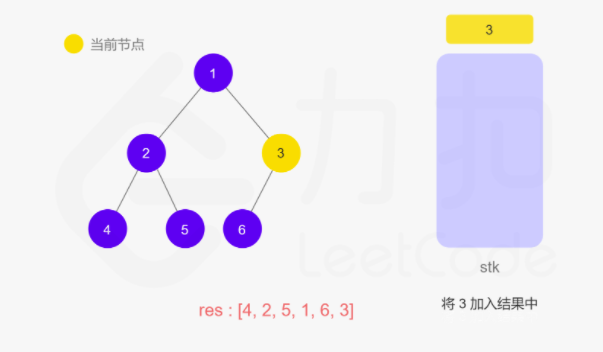
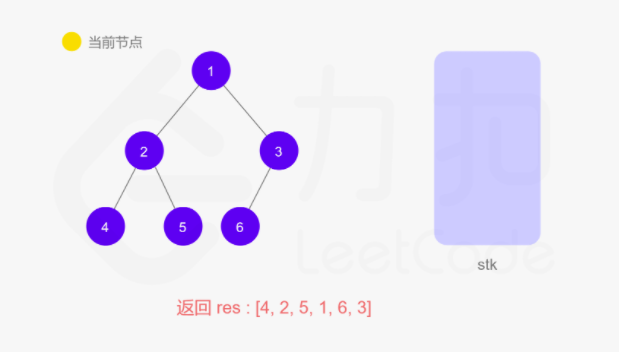
动图如下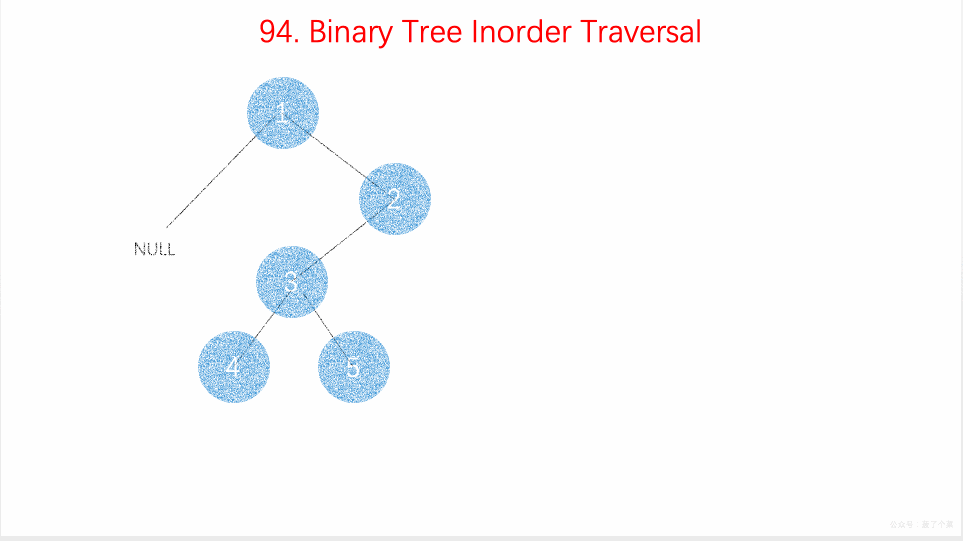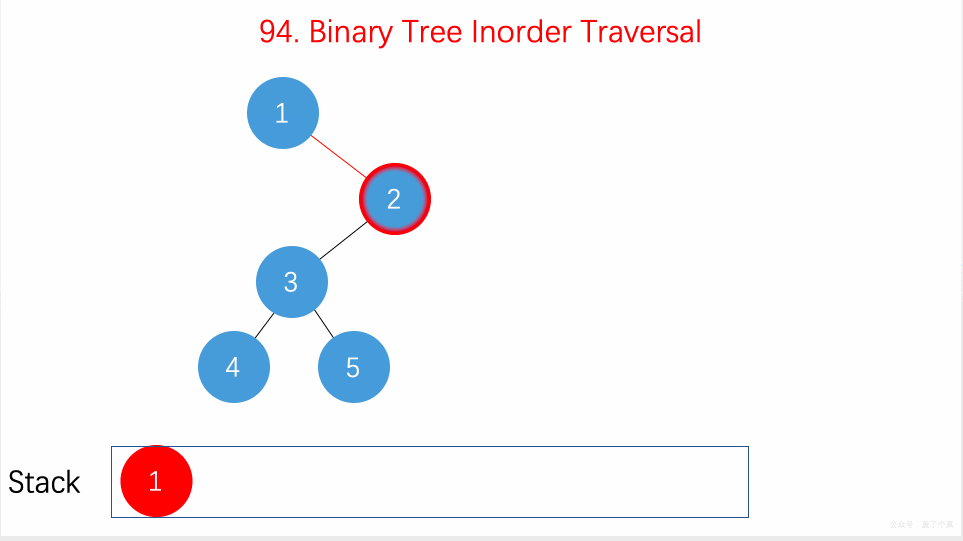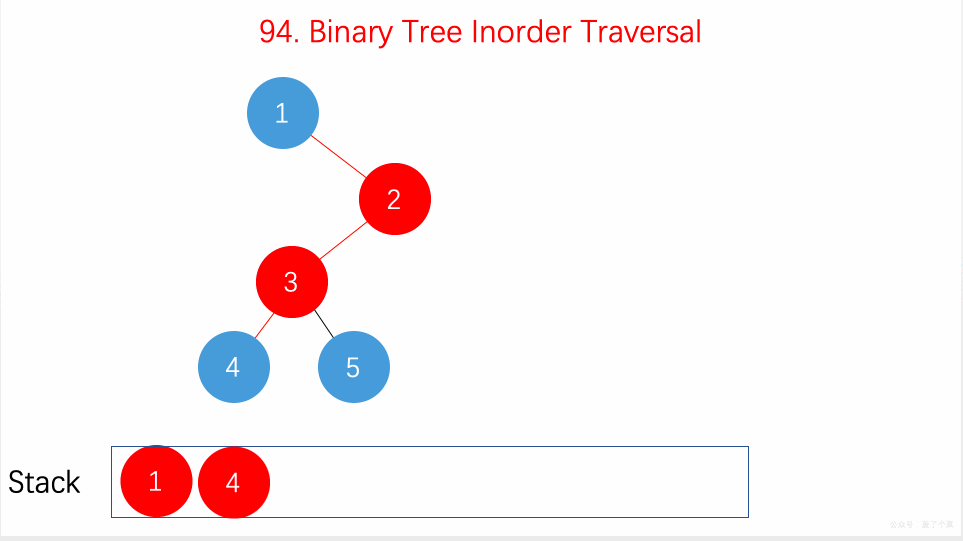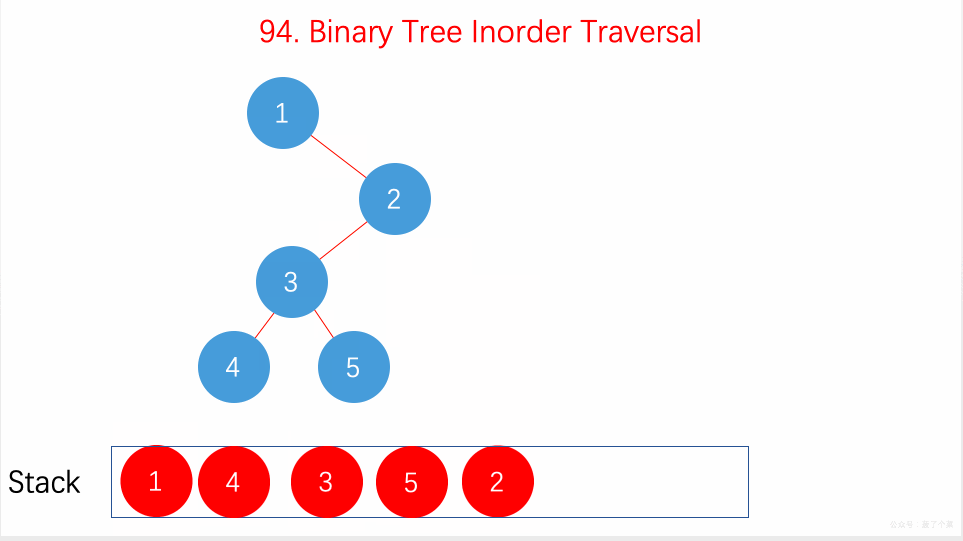
整体来说还是看节点是否有左子树,如果有就往下走,直到叶子节点,然后再返回中间结点和右子树。
Python
JavaScript
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {const res = [];const stk = [];while (root || stk.length) {// 把root节点的左子树全部加入while (root) {stk.push(root);root = root.left;}root = stk.pop();res.push(root.val);root = root.right;}return res;};

