Pciutils源码分析
lspci是Linux下分析PCI设备的神器,简单分析下实现原理
源码下载: pciutils-3.7.0 或 github下载
pciutils提供了三种常用的工具:
lspci: displays detailed information about all PCI buses and devices. 查看PCI设备的信息
setpci: allows to read from and write to PCI device configuration registers. For example, you can adjust the latency timers with it. CAUTION: There is a couple of dangerous points and caveats, please read the manual page first! 允许读写PCI配置空间
update-pciids: download the current version of the pci.ids file. 更新最新版本的pci.ids文档 // /usr/share/misc/pci.ids 前边描述了已知设备得vendor ID和DeviceID 后边(List of known device classes, subclasses and programming interfaces) 描述了 class code组成方式
lspci
如何使用
其实最常用得办法就是查看配置空间
lspci | grep xxxx # 来查找设备得BDF号,grep是用来过滤其他设备, xxx可以是device号,也可以是Classcode对应类型设备(base) baiy@inno-MS-7B89:driver-test$ lspci | grep 148000:00.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 1480(base) baiy@inno-MS-7B89:driver-test$ sudo lspci -s 28:00.1 -xxxxvvvv # 用root用户来查看设备所有得配置空间详情28:00.1 Encryption controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 1486Subsystem: Micro-Star International Co., Ltd. [MSI] Device 7b89Control: I/O- Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx+Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort+ <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR- <PERR- INTx-Latency: 0, Cache Line Size: 64 bytesInterrupt: pin A routed to IRQ 90Region 2: Memory at f7300000 (32-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=1M]Region 5: Memory at f7408000 (32-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=8K]Capabilities: [48] Vendor Specific Information: Len=08 <?>Capabilities: [50] Power Management version 3Flags: PMEClk- DSI- D1- D2- AuxCurrent=0mA PME(D0-,D1-,D2-,D3hot-,D3cold-)Status: D0 NoSoftRst+ PME-Enable- DSel=0 DScale=0 PME-Capabilities: [64] Express (v2) Endpoint, MSI 00DevCap: MaxPayload 256 bytes, PhantFunc 0, Latency L0s <4us, L1 unlimitedExtTag+ AttnBtn- AttnInd- PwrInd- RBE+ FLReset+ SlotPowerLimit 0.000WDevCtl: Report errors: Correctable- Non-Fatal- Fatal- Unsupported-RlxdOrd+ ExtTag+ PhantFunc- AuxPwr- NoSnoop+ FLReset-MaxPayload 256 bytes, MaxReadReq 512 bytesDevSta: CorrErr+ UncorrErr- FatalErr- UnsuppReq+ AuxPwr- TransPend-LnkCap: Port #0, Speed 16GT/s, Width x16, ASPM L0s L1, Exit Latency L0s <64ns, L1 <1usClockPM- Surprise- LLActRep- BwNot- ASPMOptComp+LnkCtl: ASPM Disabled; RCB 64 bytes Disabled- CommClk+ExtSynch- ClockPM- AutWidDis- BWInt- AutBWInt-LnkSta: Speed 16GT/s, Width x16, TrErr- Train- SlotClk+ DLActive- BWMgmt- ABWMgmt-DevCap2: Completion Timeout: Range ABCD, TimeoutDis+, LTR-, OBFF Not SupportedDevCtl2: Completion Timeout: 50us to 50ms, TimeoutDis-, LTR-, OBFF DisabledLnkSta2: Current De-emphasis Level: -3.5dB, EqualizationComplete-, EqualizationPhase1-EqualizationPhase2-, EqualizationPhase3-, LinkEqualizationRequest-Capabilities: [a0] MSI: Enable- Count=1/1 Maskable- 64bit+Address: 0000000000000000 Data: 0000Capabilities: [c0] MSI-X: Enable+ Count=2 Masked-Vector table: BAR=5 offset=00000000PBA: BAR=5 offset=00001000Capabilities: [100 v1] Vendor Specific Information: ID=0001 Rev=1 Len=010 <?>Capabilities: [150 v2] Advanced Error ReportingUESta: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol-UEMsk: DLP- SDES- TLP- FCP- CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF- MalfTLP- ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol-UESvrt: DLP+ SDES+ TLP- FCP+ CmpltTO- CmpltAbrt- UnxCmplt- RxOF+ MalfTLP+ ECRC- UnsupReq- ACSViol-CESta: RxErr- BadTLP- BadDLLP- Rollover- Timeout- NonFatalErr+CEMsk: RxErr- BadTLP- BadDLLP- Rollover- Timeout- NonFatalErr+AERCap: First Error Pointer: 00, GenCap- CGenEn- ChkCap- ChkEn-Capabilities: [2a0 v1] Access Control ServicesACSCap: SrcValid- TransBlk- ReqRedir- CmpltRedir- UpstreamFwd- EgressCtrl- DirectTrans-ACSCtl: SrcValid- TransBlk- ReqRedir- CmpltRedir- UpstreamFwd- EgressCtrl- DirectTrans-Capabilities: [370 v1] Transaction Processing HintsDevice specific mode supportedSteering table in TPH capability structureKernel driver in use: ccpKernel modules: ccp00: 22 10 86 14 06 04 10 08 00 00 80 10 10 00 80 0010: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 30 f7 00 00 00 00......
baiy@ubuntu:pcie-test$ lspci -hBasic display modes:-mm Produce machine-readable output (single -m for an obsolete format)-t Show bus treeDisplay options:-v Be verbose (-vv for very verbose)-k Show kernel drivers handling each device-x Show hex-dump of the standard part of the config space-xxx Show hex-dump of the whole config space (dangerous; root only)-xxxx Show hex-dump of the 4096-byte extended config space (root only)-b Bus-centric view (addresses and IRQ's as seen by the bus)-D Always show domain numbersResolving of device ID's to names:-n Show numeric ID's-nn Show both textual and numeric ID's (names & numbers)-q Query the PCI ID database for unknown ID's via DNS-qq As above, but re-query locally cached entries-Q Query the PCI ID database for all ID's via DNSSelection of devices:-s [[[[<domain>]:]<bus>]:][<slot>][.[<func>]] Show only devices in selected slots-d [<vendor>]:[<device>][:<class>] Show only devices with specified ID'sOther options:-i <file> Use specified ID database instead of /usr/share/misc/pci.ids.gz-p <file> Look up kernel modules in a given file instead of default modules.pcimap-M Enable `bus mapping' mode (dangerous; root only)PCI access options:-A <method> Use the specified PCI access method (see `-A help' for a list)-O <par>=<val> Set PCI access parameter (see `-O help' for a list)-G Enable PCI access debugging-H <mode> Use direct hardware access (<mode> = 1 or 2)-F <file> Read PCI configuration dump from a given file
源码包编译
注:配置文件只需要看 lib/config.h即可
# 编译过程make 即可# 配置过程Makefile会调用lib/config.h lib/config.mk:cd lib && ./configurelib/configure会将当前所支持的配置写入到lib/config.h中
代码流程分析
main // lspci.cpacc = pci_alloc(); // ***分配自己的struct pci_access,也会初始化param表pci_methodspm_linux_sysfssysfs_config(pacc) // 这里吧所有支持方法的访问目录方式存在parm list,然后遍历// 在访问时,通过 sysfs_name(a)获取根目录// lib/configure:73:echo >>$c '#define PCI_PATH_SYS_BUS_PCI "/sys/bus/pci"'getopt(argc, argv, options) // 解析参数pci_init(pacc); // 初始化方法pci_init_v35(pacc); // 初始化方法表: 解析pci_methods 使用哪个接口scan_devices(); // 扫描所有设备 // sysfs_scansort_them(); // 快速排序show(); // 显示show_kernel_cleanup();pci_cleanup(pacc);解析参数中 -A,-O,-G等PCI access options参数:default分支:parse_generic_option(i, pacc, optarg) // 解析即可### 初始化方法接口pci_init(pacc);pci_init_v35(struct pci_access *a) //init.c// *** 获取pci接口,PCI_ACCESS_SYS_BUS_PCI=1,使用pci_methods->pm_linux_sysfsstruct pci_methods *m = pci_methods[probe_sequence[i]]; // ***获取方法pm_linux_sysfs->detect(); // 检查sysfs是否存在pm_linux_sysfs->init(); //a->methods->init(a);功能:清空未使用的变量// ******所以全局的操作方法接口使用如下**** !!!struct pci_methods pm_linux_sysfs = {"linux-sysfs", // name接口"The sys filesystem on Linux", // help接口sysfs_config, // config接口sysfs_detect, // detect接口sysfs_init, // init接口sysfs_cleanup, // cleanup接口sysfs_scan, // scan接口sysfs_fill_info, // fill_info接口sysfs_read, // read接口sysfs_write, // write接口sysfs_read_vpd, // read_vpd接口NULL, /* init_dev */ // init_dev接口sysfs_cleanup_dev // cleanup_dev接口};# 注: opt_map_mode暂时不考虑,help里边说有风险### 扫描设备接口scan_devicessysfs_scan// sysfs_config中获取的目录索引,然后查询dirsnprintf(dirname, sizeof(dirname), "%s/devices", sysfs_name(a));while ((entry = readdir(dir))){d = pci_alloc_dev(a); // 分配dev,并初始化pci_link_dev(a, d);(struct pci_access *)a->devices = d, 弄成链表,然后前插}for (p=pacc->devices; p; p=p->next) // 遍历scan_device(p)pci_read_block(p, 0, d->config, 64) # 预读取配置空间sysfs_readdo_read(d, fd, buf, len, pos);syscall(SYS_pread, fd, buf, size, where); // 调用系统调用,有点意思的操作方法 !!!!
获取厂家信息:
从pci.ids中进行对比,来查找厂家信息和设备信息。 pci的id表收录在 pci-ids.ucw.cz 中
PCI ID Project at The PCI ID Repository, 注册登陆后(公司是PCI-SIG组织成员),可以增加修改对应device id的描述信息,需要maintainer审批合入后,展示在PCI ID网站上 sudo update-pciids 命令可以更新pci.ids 在此位置/usr/share/misc/pci.ids可以查看更新后pci.ids文件
baiy@inno-NUC8i3BEH:pciutils-3.7.0$ sudo ./lspci -s 00:02.0 -mopt_machine is 1, verbose is 000:02.0 "VGA compatible controller" "Intel Corporation" "Device 3ea5" -r01 "Intel Corporation" "Device 2074"baiy@inno-NUC8i3BEH:pciutils-3.7.0$ sudo ./lspci -s 00:02.0 -mvopt_machine is 1, verbose is 1Device: 00:02.0Class: VGA compatible controllerVendor: Intel CorporationDevice: Device 3ea5SVendor: Intel CorporationSDevice: Device 2074Rev: 01showshow_device(d);show_machine(d); // verbose就是 -vvv中v的数量
获取pci详细信息
showshow_device(d);show_verbose(d); // verbose就是 -vvv中v的数量
opt_machine is 0, verbose is 300:02.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation Device 3ea5 (rev 01) (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])DeviceName: CPUSubsystem: Intel Corporation Device 2074Control: I/O+ Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx+Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR- <PERR- INTx-Latency: 0, Cache Line Size: 64 bytesInterrupt: pin A routed to IRQ 132Region 0: Memory at 90000000 (64-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=16M]Region 2: Memory at 80000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=256M]Region 4: I/O ports at 3000 [size=64]Expansion ROM at 000c0000 [virtual] [disabled] [size=128K]Capabilities: [40] Vendor Specific Information: Len=0c <?>Capabilities: [70] Express (v2) Root Complex Integrated Endpoint, MSI 00DevCap: MaxPayload 128 bytes, PhantFunc 0ExtTag- RBE+ FLReset+DevCtl: CorrErr- NonFatalErr- FatalErr- UnsupReq-RlxdOrd- ExtTag- PhantFunc- AuxPwr- NoSnoop- FLReset-MaxPayload 128 bytes, MaxReadReq 128 bytesDevSta: CorrErr- NonFatalErr- FatalErr- UnsupReq- AuxPwr- TransPend-DevCap2: Completion Timeout: Not Supported, TimeoutDis- NROPrPrP- LTR-10BitTagComp- 10BitTagReq- OBFF Not Supported, ExtFmt- EETLPPrefix-EmergencyPowerReduction Not Supported, EmergencyPowerReductionInit-FRS-AtomicOpsCap: 32bit- 64bit- 128bitCAS-DevCtl2: Completion Timeout: 50us to 50ms, TimeoutDis- LTR- OBFF Disabled,AtomicOpsCtl: ReqEn-Capabilities: [ac] MSI: Enable+ Count=1/1 Maskable- 64bit-Address: fee00018 Data: 0000Capabilities: [d0] Power Management version 2Flags: PMEClk- DSI+ D1- D2- AuxCurrent=0mA PME(D0-,D1-,D2-,D3hot-,D3cold-)Status: D0 NoSoftRst- PME-Enable- DSel=0 DScale=0 PME-Capabilities: [100 v1] Process Address Space ID (PASID)PASIDCap: Exec- Priv-, Max PASID Width: 14PASIDCtl: Enable- Exec- Priv-Capabilities: [200 v1] Address Translation Service (ATS)ATSCap: Invalidate Queue Depth: 00ATSCtl: Enable-, Smallest Translation Unit: 00Capabilities: [300 v1] Page Request Interface (PRI)PRICtl: Enable- Reset-PRISta: RF- UPRGI- Stopped+Page Request Capacity: 00008000, Page Request Allocation: 00000000Kernel driver in use: i915Kernel modules: i915
lspci -t 的解析(重点,也可通过sysfs进行查看,更直观)
以下边为例,来详解一个lspci 的树形结构
# 其实真没有下边这个直观(base) baiy@inno-MS-7B89:~$ tree /sys/bus/pci/devices//sys/bus/pci/devices/├── 0000:00:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:00.0├── 0000:00:00.2 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:00.2├── 0000:00:01.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.0├── 0000:00:01.1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.1├── 0000:00:01.3 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.3├── 0000:00:02.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0├── 0000:00:03.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:03.0├── 0000:00:03.1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:03.1├── 0000:00:04.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:04.0├── 0000:00:05.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:05.0├── 0000:00:07.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0├── 0000:00:07.1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.1├── 0000:00:08.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.0├── 0000:00:08.1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.1├── 0000:00:08.2 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.2├── 0000:00:08.3 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.3├── 0000:00:14.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:14.0├── 0000:00:14.3 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:14.3├── 0000:00:18.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:18.0├── 0000:00:18.1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:18.1├── 0000:00:18.2 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:18.2├── 0000:00:18.3 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:18.3├── 0000:00:18.4 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:18.4├── 0000:00:18.5 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:18.5├── 0000:00:18.6 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:18.6├── 0000:00:18.7 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:18.7├── 0000:01:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.1/0000:01:00.0├── 0000:03:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.3/0000:03:00.0├── 0000:03:00.1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.3/0000:03:00.1├── 0000:03:00.2 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.3/0000:03:00.2├── 0000:20:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.3/0000:03:00.2/0000:20:00.0├── 0000:20:01.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.3/0000:03:00.2/0000:20:01.0├── 0000:20:04.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.3/0000:03:00.2/0000:20:04.0├── 0000:22:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.3/0000:03:00.2/0000:20:01.0/0000:22:00.0├── 0000:26:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:03.1/0000:26:00.0├── 0000:26:00.1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:03.1/0000:26:00.1├── 0000:27:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.1/0000:27:00.0├── 0000:28:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.1/0000:28:00.0├── 0000:28:00.1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.1/0000:28:00.1├── 0000:28:00.3 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.1/0000:28:00.3├── 0000:28:00.4 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.1/0000:28:00.4├── 0000:30:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.2/0000:30:00.0└── 0000:31:00.0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.3/0000:31:00.0(base) baiy@inno-MS-7B89:~$ lspci00:00.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148000:00.2 IOMMU: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148100:01.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148200:01.1 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148300:01.3 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148300:02.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148200:03.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148200:03.1 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148300:04.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148200:05.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148200:07.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148200:07.1 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148400:08.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148200:08.1 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148400:08.2 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148400:08.3 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148400:14.0 SMBus: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] FCH SMBus Controller (rev 61)00:14.3 ISA bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] FCH LPC Bridge (rev 51)00:18.0 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 144000:18.1 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 144100:18.2 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 144200:18.3 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 144300:18.4 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 144400:18.5 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 144500:18.6 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 144600:18.7 Host bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 144701:00.0 Non-Volatile memory controller: Sandisk Corp Device 500603:00.0 USB controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 43d5 (rev 01)03:00.1 SATA controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 43c8 (rev 01)03:00.2 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 43c6 (rev 01)20:00.0 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 43c7 (rev 01)20:01.0 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 43c7 (rev 01)20:04.0 PCI bridge: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 43c7 (rev 01)22:00.0 Ethernet controller: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller (rev 15)26:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation Device 1f82 (rev a1)26:00.1 Audio device: NVIDIA Corporation Device 10fa (rev a1)27:00.0 Non-Essential Instrumentation [1300]: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148a28:00.0 Non-Essential Instrumentation [1300]: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148528:00.1 Encryption controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148628:00.3 USB controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 149c28:00.4 Audio device: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] Device 148730:00.0 SATA controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] FCH SATA Controller [AHCI mode] (rev 51)31:00.0 SATA controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD] FCH SATA Controller [AHCI mode] (rev 51)(base) baiy@inno-MS-7B89:~$ lspci -t-[0000:00]-+-00.0+-00.2+-01.0+-01.1-[01]----00.0+-01.3-[03-25]--+-00.0| +-00.1| \-00.2-[20-25]--+-00.0-[21]--| +-01.0-[22]----00.0| \-04.0-[25]--+-02.0+-03.0+-03.1-[26]--+-00.0| \-00.1+-04.0+-05.0+-07.0+-07.1-[27]----00.0+-08.0+-08.1-[28]--+-00.0| +-00.1| +-00.3| \-00.4+-08.2-[30]----00.0+-08.3-[31]----00.0+-14.0+-14.3+-18.0+-18.1+-18.2+-18.3+-18.4+-18.5+-18.6\-18.7
setpci 修改配置空间
可以用来修改配置空间
参考: setpci
sudo setpci -s 00:02.0 F4.B=FFsetpci 是修改设备属性的命令。-s 表示接下来输入的是设备的地址。00:02.0 VGA设备地址(<总线>:<接口>.<功能>)。F4 要修改的属性的地址,这里应该表示“亮度”。.B 修改的长度(B应该是字节(Byte),还有w(应该是Word,两个字节)、L(应该是Long,4个字节))。=FF 要修改的值(可以改)(base) baiy@inno-MS-7B89:Linux-kernel-test$ sudo setpci -s 26:00.0 04.W=0407(base) baiy@inno-MS-7B89:Linux-kernel-test$ lspci -s 26:00.0 -xxxvvv26:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation Device 1f82 (rev a1) (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])Subsystem: Micro-Star International Co., Ltd. [MSI] Device 8d92Control: I/O+ Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx+Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR+ <PERR- INTx-Latency: 0, Cache Line Size: 64 bytesInterrupt: pin A routed to IRQ 94Region 0: Memory at f6000000 (32-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=16M]Region 1: Memory at e0000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=256M]Region 3: Memory at f0000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=32M]Region 5: I/O ports at e000 [size=128]Expansion ROM at 000c0000 [disabled] [size=128K]Capabilities: <access denied>Kernel driver in use: nouveauKernel modules: nvidiafb, nouveau00: de 10 82 1f 07 04 10 40 a1 00 00 03 10 00 80 0010: 00 00 00 f6 0c 00 00 e0 00 00 00 00 0c 00 00 f020: 00 00 00 00 01 e0 00 00 00 00 00 00 62 14 92 8d30: 00 00 00 f7 60 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0a 01 00 00
实战应用
在我测试时,遇到过一个任务:HotReset 一个设备,怎么办?
通过前边,我们知道: 7.5.1.3.13 Bridge Control Register (Offset 3Eh) 中的 Secondary Bus Reset 位 写1 可以使用Host Rset(PCI总线,
使用RST#信号复位, PCIE设备使用TS1和TS2序列对下游设备进行Host Rset)
那么只需要lspci -t 找到设备所在的switch上,使用setpci命令将Secondary Bus Reset进行复位即可。
附录:提供两个查看PCI得工具
1. Mindshare Arbor
Mindshare是一家专业的第三方硬件系统培训公司,主要方向为PCI Express、M-PCIe、NVMe、USB、ARM Architecture、DDRx/LPDDRx、Intel Haswell/Broadell、Intel Mobile Platform and SoC、x86 Architecture、HyperTransport、PCI/PCI-X、SAS Storage、SATA Storage、ISA System、InfiniBand Network Architecture、x86 Firmware:UEFI and BIOS和OpenCL等内容。
该公司还出版过多本相关内容的书籍:https://www.mindshare.com/Books/Books_*_eBooks
Arbor是该公司开发的一款调试软件,主要用于PCI/PCI-X/PCIe/Hyper Transport系统的分析与调试。支持主流的Windows和Linux系统:https://www.mindshare.com/software/?section=132B0BA21710
用户可以在以上链接免费下载该软件,并有14天的免费试用期,试用期结束后,调试分析功能将被锁定,但是PCI/PCIe Configuration Space查阅功能仍然可以正常使用。该功能实际上就是把PCI/PCIe Spec的相关内容做成了一个软件,方便设计者快速地查找Configuration Space中的每个寄存器的意义和使用方法,如下图所示: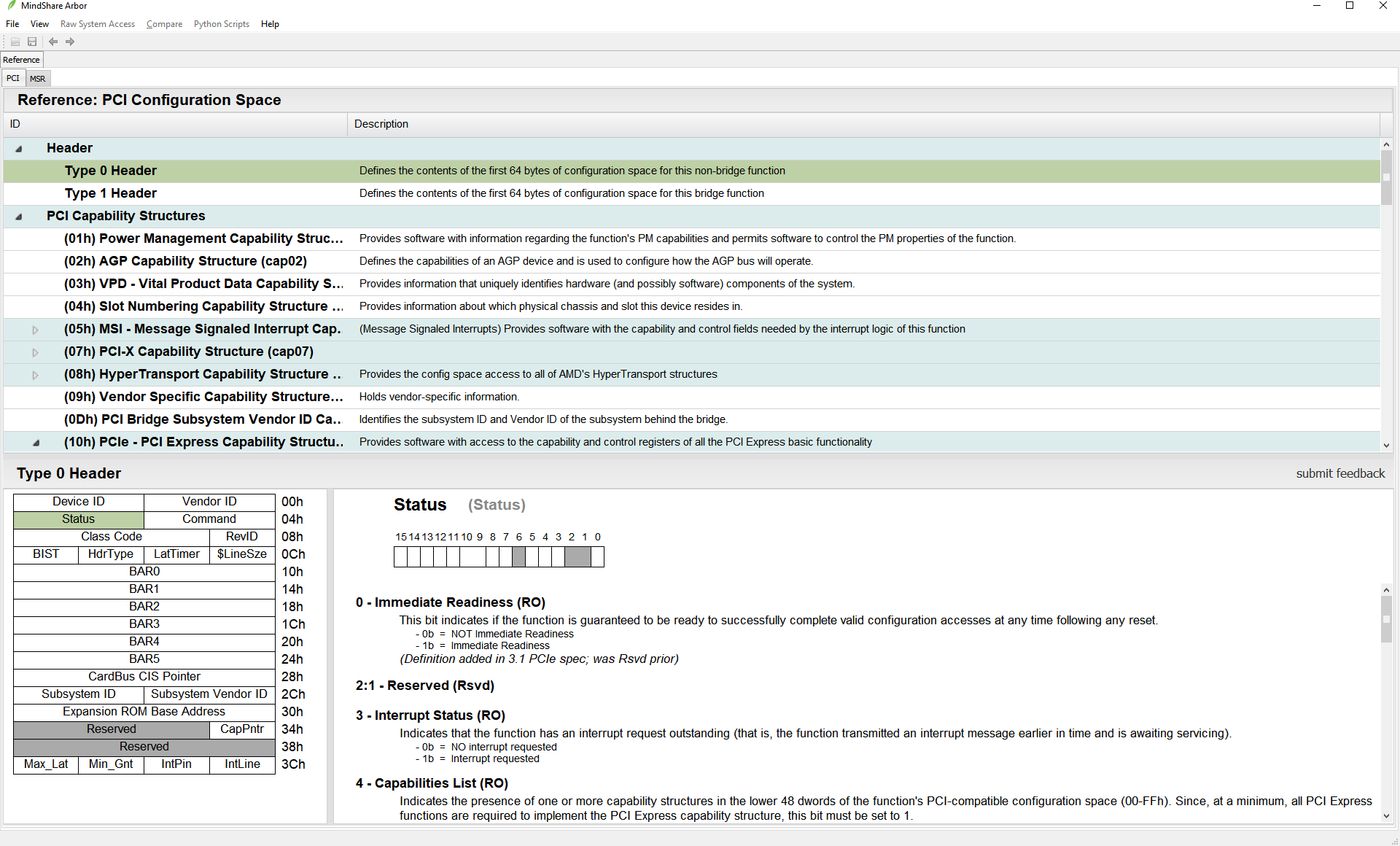
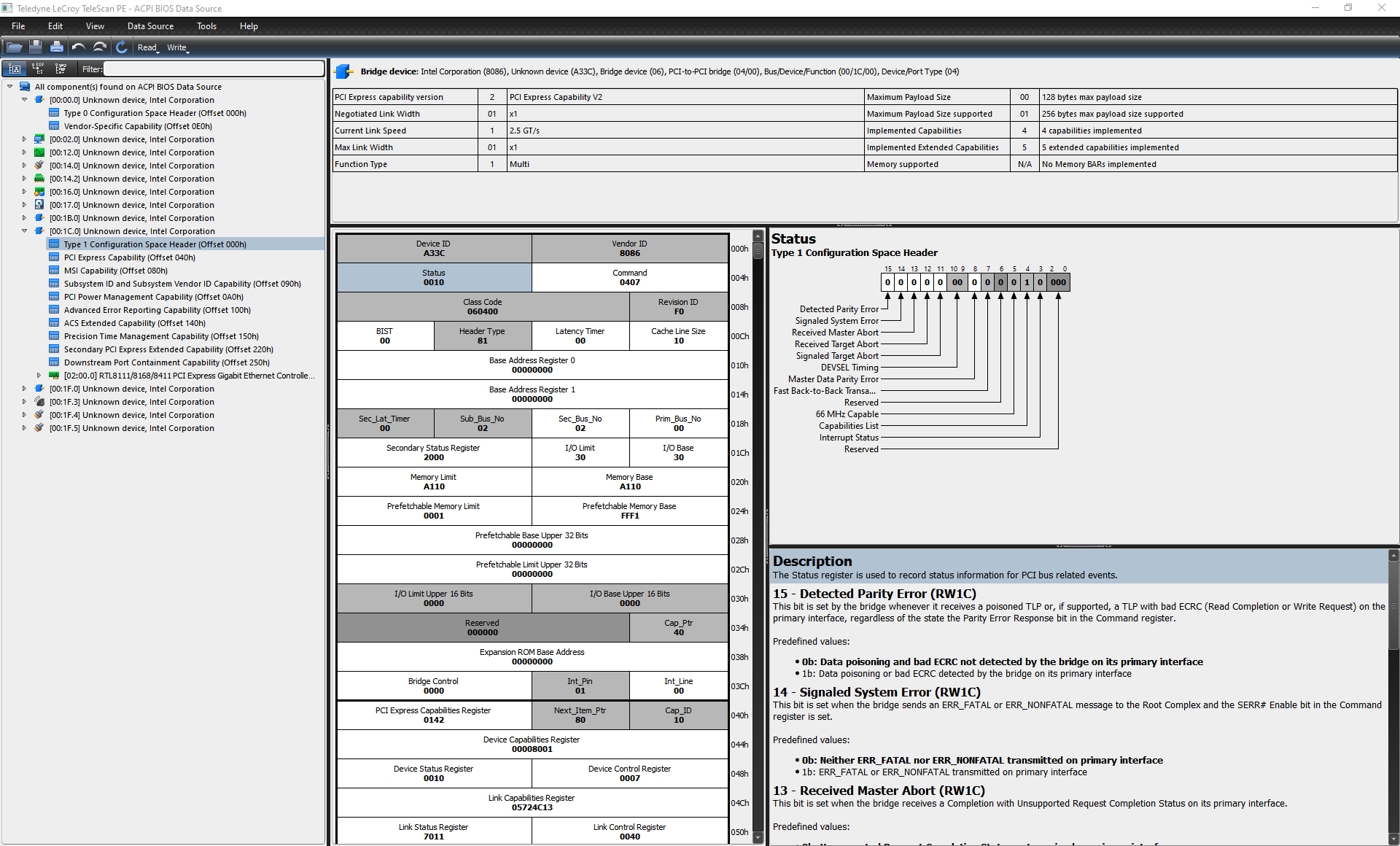
2. Teledyne LeCroy TeleScan PE**
Teledyne LeCroy TeleScan PE是与LeCroy的PCIe协议分析仪配套的软件套件中的一部分,和Arbor一样,该软件也同时支持主流的Windows和Linux系统。大家可以在LeCroy的官网上免费下载,并免费使用:
https://teledynelecroy.com/protocolanalyzer/pci-express/telescan-pe-software/resources/analysis-software
TeleScan PE刚好提供了Arbor需要付费才能使用的那部分功能:用户可以通过TeleScan PE来扫描系统中的PCI/PCIe设备,并提供了读写其配置空间中的寄存器的功能。TeleScan PE软件的用户界面截图如下图所示: