虚拟化技术
虚拟化基础
本章重点
- 什么是虚拟化?虚拟化的作用?
- 虚拟化的原理?
- 虚拟化分类?怎么区分?各有啥优缺点?
- 硬件为虚拟化提供了哪些支持?
引言
美国环境保护署 (EPA)报告的一组有趣的统计数据发现,实际上服务器只有5%的时间是在工作的。在其他时间,服务器都处于“休眠”状态。
什么是虚拟化
背景:随着计算机硬件技术的发展,物理资源的容量越来越大而价格越来越低,在既有的计算元件架构下,物理资源不可避免地产生了闲置和浪费。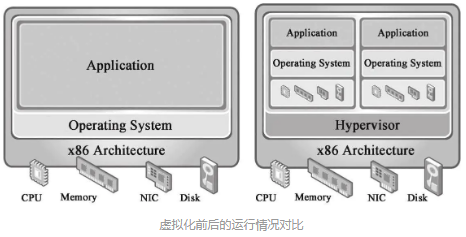
所以有了虚拟化,虚拟化目的:为了充分利用计算机资源(硬件资源和软件资源)
虚拟化方式:在之前的操作系统层在加一个虚拟层,然后同时可运行多个操作系统。
虚拟化是构建云基础架构不可或缺的关键技术之一。虚拟化在资源的有效利用、动态调配和高可靠性方面有着巨大的优势。
个人理解: 虚拟化其实就是集群的相反工作。一个是为了多台设备并行运算。一个是为了1台设备多用户使用。
虚拟化原理
虚拟化技术引入一个新的虚拟化层,对下管理真实的物理资源,对上提供虚拟的系统资源。
在X86平台虚拟化技术中,新引入的虚拟化层通常称为虚拟机监控器(VirtualMachine Monitor,VMM),也叫做Hypervisor。
虚拟机监控器运行的环境,也就是真实的物理平台,称之为宿主机(Host)。而虚拟出来的平台通常称为客户机(Guest),里面运行的系统对应地也称为客户机操作系统。
虚拟化的原理:在OS中加入一个虚拟化层(VMM),虚拟化层可以对下层(HostOS)硬件资源(物理CPU、内存、磁盘、网卡、显卡等)进行封装、隔离,抽象为另一种形式的逻辑资源,再提供给上层(GuestOS)使用。所以你可以理解VMM其实就是联系HostOS和GuestOS的一个中间件,当然虚拟化可以将一份资源抽象为多份,也可以将多份资源抽象为一份。
虚拟化的分类
软件虚拟化和硬件虚拟化
- 软件虚拟化:就是纯软件实现VMM层,比如qemu(不启用硬件虚拟化辅助时),可以通过纯软件测试各个平台,二进制指令被软件翻译成宿主机二进制指令。
软件虚拟化优点:不依赖平台和硬件支持。 缺点: 性能极差。 - 硬件虚拟化:为了提高虚拟化效率,硬件上做了虚拟化支持,比如Intel VT-x等为了VMM提供权限访问,EPT拓展页表等。 比如Intel VT-d 为IO设备直接透传到虚拟机中做了支持等。
硬件支持虚拟化优点:性能好。缺点:依赖平台和硬件支持。
半虚拟化和全虚拟化
虚拟化的最好体验是:
- 客户机完全不知道自己运行在虚拟化环境中,还以为自己运行在原生环境里。
- 完全不需要VMM介入客户机的运行过程
全虚拟化(Full Virtualization)和准虚拟化(para-virtualization)的区别:
- FV: 不需要对GuestOS操作系统软件的源代码做任何的修改,就可以运行在这样的VMM中。
- PV: 需要对GuestOS的内核代码做一定的修改,才能够将GuestOS运行在半虚拟化的VMM中。
可以看到PV没有达到“客户机完全不知道自己运行在虚拟化环境中”的体验,主要是为了 提升性能和 简化VMM复杂度。 因为intel-VT等技术未支持,只能用软件来实现虚拟化技术,比较复杂。 比如:virtio,属于比较早期的虚拟化技术,
但FV在硬件虚拟化支持之后,性能远超了PV。
Bare-metal虚拟化和Host OS虚拟化方式
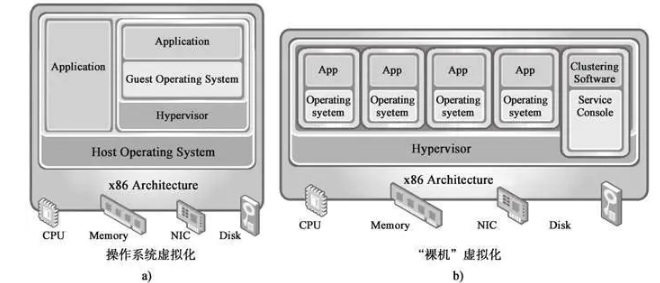
- Host OS类型将Hypervisor虚拟化层安装在传统的操作系统中,虚拟化软件以应用程序进程形式运行在Windows和Linux等主机操作系统中。在Hypervisor虚拟化环境下,部署在物理服务器上的系统称为Host OS,而部署在Hypervisor上的虚拟机操作系统称为Guest OS。
- Bare-metal类型的Hypervisor虚拟化环境中无须完整的Host OS,直接将Hypervisor部署在裸机上并将裸机服务器的硬件资源虚拟化,也可以将Hypervisor理解为仅对硬件资源进行虚拟和调度的薄操作系统,其并不提供常规Host OS的功能
。
Host OS虚拟化我们比较常见的就是:virmware/virtualbox
硬件虚拟化支持
Inte Virtualization支持概述
2005年以后,Intel和AMV等分别在在虚拟化上加入了硬件支持
参考文献: 英特尔VT具体包括分别针对处理器、芯片组、网络的VT-X、VT-D和VT-C技术。
- 处理器:英特尔虚拟化技术(英特尔VT-x),包括英特尔虚拟化灵活迁移技术(Intel VT FlexMigration)、英特尔VT FlexPriority、英特尔VT 扩展页表(Extended Page Tables)
- 芯片组:英特尔支持直接 I/O 访问的 VT虚拟化技术(英特尔VT-d)
- 网络:支持连接的英特尔虚拟化技术(英特尔VT-c),包括虚拟机设备队列(VMDq)、 虚拟机直接互连(VMDc)
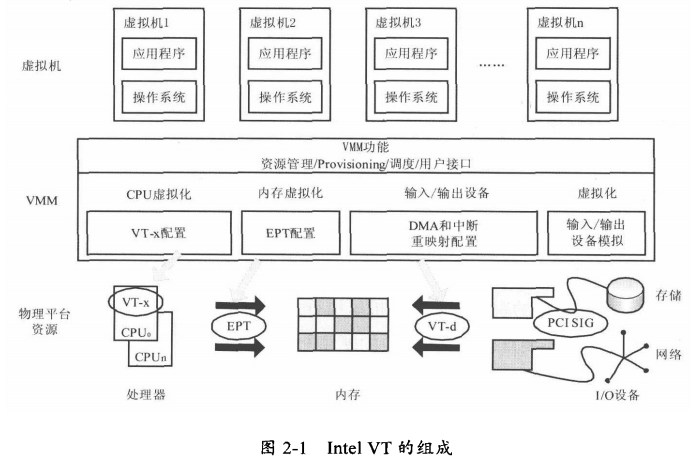
- VT-x (Intel Virtualization Technology),x其实是X86平台,是虚拟化支持的基础
- VT-d (Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O),其实就是后边说的IO设备独占
- VT-c (Virtualization Technology for Connectivity),也就是后边说的IO设备共享,主要用在网卡
VT 是 Virtualization Technology 的缩写
VT-x 其实就是 Intel Virtualization Technology 至于为什么后边有个 x 呢?是因为英特尔在起名字的时候,将x86平台上的VT技术,称之为VT-x;在Itanium平台上的VT技术,称之为VT-i。 VT-x 是 Intel CPU 的硬件虚拟化技术,提供内存以及虚拟机的硬件隔离,这也是平常我们想在 intel 平台上做虚拟化最基本需要支持的技术。 VT-x不仅需要处理器的支持,也需要主板、BOIS的支持
VT-d 英文全程为 Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O 其中,d代表Directed VT-d 的 Intel 官方中文名称是 定向 I/O 虚拟化技术 这个技术就是俗称的虚拟化直通技术,就是允许宿主机将某些硬件资源(比如硬盘、显卡、网卡)的管辖权直接移交给虚拟机,此时宿主机将不能再使用此硬件,虚拟机会以直通独占的方式使用它们. 这种直通的技术带来的好处就是,虚拟机中使用该硬件的性能损耗是极小的, 改善了 I/O 设备在虚拟化环境中的性能并且隔离更加彻底提高了系统的安全性
VT-c 英文全程为 Virtualization Technology for Connectivity VT-c 主要是针对提高网络 I/O提供的虚拟化技术,它可以在一个物理网卡上,建立针对虚拟机的设备队列,最大限度的提高 I/O 吞吐率。
网上文章千篇一律的都只是官方的介绍一下 VMDq 和 VMDc ,甚至搞不清 VT-d 和 VT-c 到底有什么区别,其实这个很简单 一个数据包的处理,传统方式是由虚拟机管理系统(CPU处理)来分配这个数据包到底给到哪台虚拟机,现在是由网卡的硬件直接来处理,所以减少了处理延迟,提高了效率.类似VT-d
VT-c和 VT-d 有什么区别? VT-d 是可以将一个物理网卡直通给一个虚拟机。 VT-c 就很厉害了,可以将一个物理网卡分成十份,分别直通给10个虚拟机,并且这十份都是隔离互不影响的,注意,这里我用了直通两个字,也就是分割成十份这个操作是不经过虚拟机管理系统的(也就是不经过CPU),所以 I/O 性能很高,并且减少CPU的负载
CPU虚拟化支持-主要是特权访问
Intel在处理器级别提供了对虚拟化技术的支持,被称为VMX(virtual-machineextensions)。
有两种VMX操作模式:VMX根操作(root operation)与VMX非根操作(non-root operation)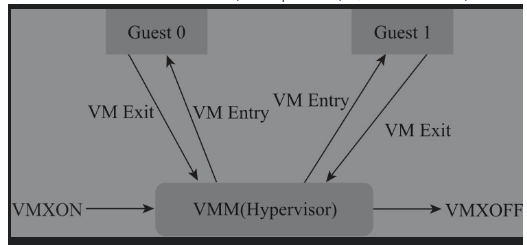
Intel CPU和ARMv8一样,分为RING0-RING3四种特权模式,所以需要专用指令来切换到更高特权模式。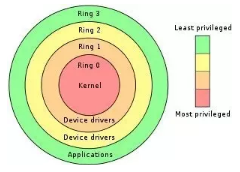
好像也只用到RING0和RING3,区分特权模式和非特权模式而已。
内存拓展页表支持
内存虚拟化就是要将客户机虚拟地址(GVA)转化为最终能够访问的宿主机上的物理地址(HPA)-如下图,虚拟机监控器就需要维护从客户机虚拟地址到宿主机物理地址之间的一个映射关系,在没有硬件提供的内存虚拟化之前,这个维护映射关系的页表叫作影子页表(Shadow Page Table)
- 1)客户机虚拟地址,GVA(Guest Virtual Address
- 2)客户机物理地址,GPA(Guest Physical Address)
- 3)宿主机虚拟地址,HVA(Host Virtual Address)
- 4)宿主机物理地址,HPA(Host Physical Address)
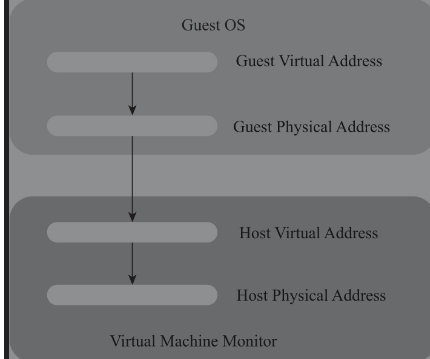
这样不可避免的大大影响了性能,所以:
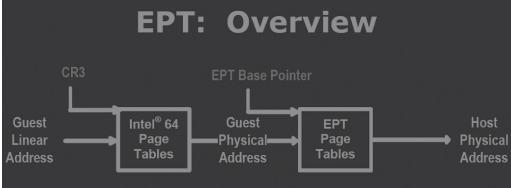
Intel CPU在硬件设计上就引入了EPT(Extended Page Tables,扩展页表),从而将客户机虚拟地址到宿主机物理地址的转换通过硬件来实现。
IO虚拟化-Intel VT-d和Intel VT-x
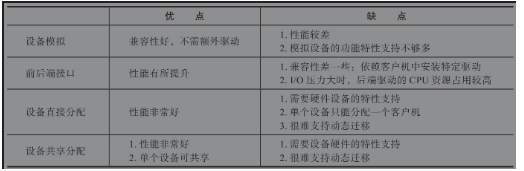
一般情况下VMM支持I/O虚拟化可以通过以下四种方式实现:
- 设备模拟(纯软件模拟)。即VMM的软件模拟一个现有的I/O设备,老毛病:兼容性好,性能和功能较差。
- 前后端驱动接口-纯软件模拟,在第一种基础上引入新的I/O操作接口,这些接口针对I/O虚拟化进行一定的优化,这样虽然能够解决一定的性能问题,但是兼容性问题又出现了,因为需要使用新的操作接口。
这个可以看看后边的virtio半虚拟化。 - 硬件分配,直接将I/O设备分配给某个VM(Virtual Machine),这样只有指定的VM能够使用该I/O设备,并且I/O设备的驱动位于VM中,并且VM能够直接对I/O设备进行操作,这样性能和兼容性都能达到最佳,但是一个I/O设备只能给一个VM使用。
这就是Intel VT-d技术 - I/O设备分享,这是硬件分配方式的一种扩展,主要还是需要I/O设备本身需要支持一定的功能,如能够同时提供多个功能接口,比如PCIe设备的SR-IOV功能,即PCIe设备本身能够将一个物理PCIe设备,变成多个逻辑设备,这多个逻辑设备共享该PCIe设备上的物理资源,并且可以独立地分配给不同的VM。
这就是Intel VT-c技术
Intel VT-d和VT-c
Intel VT-d为虚拟机监控器提供了几个重要的能力:I/O设备分配、DMA重定向、中断重定向、中断投递等.
但硬件分配同一时间只能给一台设备使用,所以出现了I/O设备分享,比如SR-IOV功能。
KVM(Kernel-based Virtual Machine)原理
KVM是基于内核的虚拟机,是采用硬件虚拟化技术的全虚拟化,属于bare-metal虚拟化==解决方案。
它以内核模块的形式加载之后,就将Linux内核变成了一个Hypervisor,但硬件管理等还是通过Linuxkernel来完成的。
KVM对硬件最低的依赖是CPU的硬件虚拟化支持,比如:Intel的VT技术和AMD的AMD-V技术,而其他的内存和I/O的硬件虚拟化支持,会让整个KVM虚拟化下的性能得到更多的提升。
KVM组成部分
==KVM内核部分+QEMU(应用)组成 ==
- KVM内核模块,它属于标准Linux内核的一部分,是一个专门提供虚拟化功能的模块,主要负责CPU和内存的虚拟化,包括:客户机的创建、虚拟内存的分配、CPU执行模式的切换、vCPU寄存器的访问、vCPU的执行。
- QEMU用户态工具,它是一个普通的Linux进程,为客户机提供设备模拟的功能,包括模拟BIOS、PCI/PCIE总线、磁盘、网卡、显卡、声卡、键盘、鼠标等。同时它通过ioctl系统调用与内核态的KVM模块进行交互
注:- Qemu默认采用纯软件方式,如果要使能KVM进行支持,则带参数 -enable-kvm
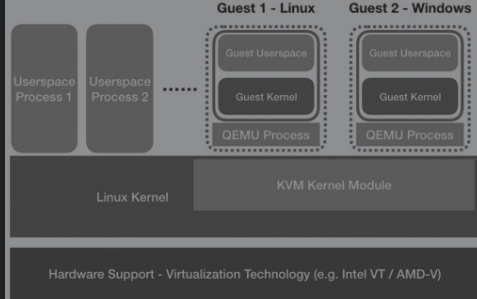
KVM内核部分也分为两个模块:
[baiy@server_202 linux-5.7.14]$ lsmod | grep kvmkvm_intel 174250 0kvm 570658 1 kvm_intel # 处理器架构相关的部分irqbypass 13503 1 kvm # 处理器架构无关的部分ls -al /dev/kvm # 也应该创建了kvm设备节点kvm-ok命令进行测试
KVM的主要功能是初始化CPU硬件,打开虚拟化模式,然后将虚拟客户机运行在虚拟机模式下,并对虚拟客户机的运行提供一定的支持。
构建KVM环境
包括:硬件系统的配置、宿主机(Host)操作系统的安装、KVM的编译与安装、QEMU的编译与安装、客户机(Guest)的安装,直到最后启动你的第一个KVM客户机.
详细构建步骤:https://abelsu7.top/2019/04/16/kvm-in-action-1/
KVM环境快速确定
baiy@baiy-ThinkPad-E470c:~$ grep -E 'svm|vmx' /proc/cpuinfo # 确定硬件CPU支持虚拟化flags : ..... vmx .....(base) baiy@inno:bin$ lsmod | grep kvm # 确定安装了kvm驱动模块kvm_intel 253952 6kvm 655360 1 kvm_intel(base) baiy@inno:bin$ ls -al /dev/kvm # 确定安装kvm驱动模块2crw-rw---- 1 root kvm 10, 232 9月 4 13:34 /dev/kvm(base) baiy@inno:bin$ kvm-ok # 初步验证kvm环境OKINFO: /dev/kvm existsKVM acceleration can be used
硬件配置
BIOS中Security->Virtualization选项使能:
- Intel(R)Virtualization Techology // VT-x
- Intel (R) VT-d Feature // VT-d
验证是否支持硬件虚拟化
# Intel系列CPU支持虚拟化的标志为“vmx”,AMD系列CPU的标志为“svm”baiy@baiy-ThinkPad-E470c:~$ grep -E 'svm|vmx' /proc/cpuinfoflags : ..... vmx .....baiy@inno-NUC8i3BEH:qemu-5.1.0-rc3$ lsmod | grep kvm # intelkvm_intel 253952 0kvm 655360 1 kvm_intelinno@inno-MS-7B89:~/workspace/qemu-kvm$ lsmod | grep kvm # amdkvm 651264 0irqbypass 16384 1 kvm
Ubuntu环境安装
KVM and Libvirt on Ubuntu20.04
安装命令:
sudo apt-get install -y bridge-utils qemu-kvm virtinst libvirt-daemon virt-manager libsdl2-dev libcurl4-openssl-dev libusbredirhost-dev libpixman-1-dev
安装完成测试:
baiy@inno-NUC8i3BEH:vaapi$ sudo kvm-okINFO: /dev/kvm existsKVM acceleration can be used
编译和安装KVM
如果没有 “/dev/kvm”的话,可能需要更换vmlinux和kvm驱动(因为Ubuntu新版本包含这部分,所以暂时跳过)
# 以下两种方式都可以git clone https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/virt/kvm/kvm.gitgit clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/virt/kvm/kvm.git
详情参考:https://abelsu7.top/2019/04/16/kvm-in-action-1/ (目前主流系统都已支持KVM,不在详细列举)
编译QEMU
Qemu命令相关
注: qemu-kvm和qemu-system-xxx
在老版本中有单独的qemu-kvm模块存在,结合qemu一起做虚拟机工作。 在后续新版本中,已经将qemu-kvm模块完全合并到qemu中去。 因此当需要使用kvm特性时候,只需要qemu-system-x86_64 启动命令中增加参数 –enable-kvm参数使能即可
git clone git://git.qemu.org/qemu.git
之前使用qemu测试嵌入式设备,回顾下.
sudo apt-get install libpixman-1-dev # 需要依赖 pixmanmkdir qemu-x86-64-bin && realpath qemu-x86-64-bin/首先:配置, target为自己的架构,prefix为安装路径./configure --prefix=/home/inno/workspace/qemu-kvm/qemu-system-x86 \--enable-kvm \--enable-libusb \--enable-usb-redir \--enable-debug \--enable-debug-info \--enable-curl \--enable-sdl \--enable-vhost-net \--enable-spice \--enable-vnc \--enable-opengl \--target-list=x86_64-softmmu然后:编译和安装make && make install可以看生成结果baiy@baiy-ThinkPad-E470c:qemu$ ls qemu-x86-64-bin/bin/qemu-system-x86_64qemu-x86-64-bin/bin/qemu-system-x86_64
创建CentOS
因为一直玩Ubuntu,也弄个CentOS KDE环境玩玩
wget http://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/7/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7-x86_64-LiveKDE-2003.iso# 创建一个40G的磁盘空间-根据实际使用动态拓展空间# 玩过VMware都知道:根据实际使用大小来动态拓空间,本身不占空间qemu-img create -f raw centOS7.img 40Gbaiy$:virt$ qemu-img create -f raw centOS7.img 40GFormatting 'centOS7.img', fmt=raw size=42949672960baiy$:virt$ ls -alh centOS7.img-rw-r--r-- 1 baiy baiy 40G 8月 26 06:19 centOS7.imgbaiy$:virt$ du -h centOS7.img0 centOS7.img# 创建一个40G的磁盘空间-根据实际使用动态拓展空间qemu-img create -f raw -o preallocation=full centOS7.img 40G
这里使用raw格式,也支持其他格式
使用QEMU加载CentOS
sudo qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -m 4G -smp 4 -boot once=d -cdrom CentOS-7-x86_64-LiveKDE-2003.iso centOS7.img-m 4G是给客户机分配8G内存,-smp 4是指定客户机为对称多处理器结构并分配4个CPU,-boot once=d是指定系统的启动顺序为首次光驱,以后再使用默认启动项,-cdrom**是分配客户机的光驱
第一次用和装虚拟机一样,后边执行:
sudo qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -m 4G -smp 4 ./centOS7.img
ctrl+alt+1 虚拟机模式
ctrl+alt+2 qemu调试模式, 可通过 info xxx查看虚拟机状态
qemu加载裸的X86内核
make x86_64_defconfigmake make menuconfig # 没啥要配置的make
目前文件系统肯定还有问题,不过能跑起来,后期再看吧
sudo qemu-system-x86_64 -smp 4 -m size=10G --enable-kvm -kernel ./arch/x86/boot/bzImage -hda qemu_rootfs.img -append "root=/dev/sda rootfstype=ext4 rw rdinit=/linuxrc"
https://www.cnblogs.com/dion-90/articles/8522718.html
附录
附录1 qemu安装配置
qemu配置
| header 1 | header 2 |
|---|---|
| —target-list | 对客户机架构的支持 |
baiy@inno-NUC8i3BEH:qemu-5.1.0-rc3$ ./configure --helpUsage: configure [options]Options: [defaults in brackets after descriptions]Standard options:--help print this message--prefix=PREFIX install in PREFIX [/usr/local]--interp-prefix=PREFIX where to find shared libraries, etc.use %M for cpu name [/usr/gnemul/qemu-%M]--target-list=LIST set target list (default: build everything)Available targets: aarch64-softmmu alpha-softmmuarm-softmmu avr-softmmu cris-softmmu hppa-softmmui386-softmmu lm32-softmmu m68k-softmmumicroblaze-softmmu microblazeel-softmmu mips-softmmumips64-softmmu mips64el-softmmu mipsel-softmmumoxie-softmmu nios2-softmmu or1k-softmmu ppc-softmmuppc64-softmmu riscv32-softmmu riscv64-softmmurx-softmmu s390x-softmmu sh4-softmmu sh4eb-softmmusparc-softmmu sparc64-softmmu tricore-softmmuunicore32-softmmu x86_64-softmmu xtensa-softmmuxtensaeb-softmmu aarch64-linux-useraarch64_be-linux-user alpha-linux-userarm-linux-user armeb-linux-user cris-linux-userhppa-linux-user i386-linux-user m68k-linux-usermicroblaze-linux-user microblazeel-linux-usermips-linux-user mips64-linux-usermips64el-linux-user mipsel-linux-usermipsn32-linux-user mipsn32el-linux-usernios2-linux-user or1k-linux-user ppc-linux-userppc64-linux-user ppc64abi32-linux-userppc64le-linux-user riscv32-linux-userriscv64-linux-user s390x-linux-user sh4-linux-usersh4eb-linux-user sparc-linux-usersparc32plus-linux-user sparc64-linux-usertilegx-linux-user x86_64-linux-userxtensa-linux-user xtensaeb-linux-user--target-list-exclude=LIST exclude a set of targets from the default target-listAdvanced options (experts only):--cross-prefix=PREFIX use PREFIX for compile tools []--cc=CC use C compiler CC [cc]--iasl=IASL use ACPI compiler IASL [iasl]--host-cc=CC use C compiler CC [cc] for code run atbuild time--cxx=CXX use C++ compiler CXX [c++]--objcc=OBJCC use Objective-C compiler OBJCC [cc]--extra-cflags=CFLAGS append extra C compiler flags QEMU_CFLAGS--extra-cxxflags=CXXFLAGS append extra C++ compiler flags QEMU_CXXFLAGS--extra-ldflags=LDFLAGS append extra linker flags LDFLAGS--cross-cc-ARCH=CC use compiler when building ARCH guest test cases--cross-cc-flags-ARCH= use compiler flags when building ARCH guest tests--make=MAKE use specified make [make]--install=INSTALL use specified install [install]--python=PYTHON use specified python [/usr/bin/python3]--sphinx-build=SPHINX use specified sphinx-build []--smbd=SMBD use specified smbd [/usr/sbin/smbd]--with-git=GIT use specified git [git]--static enable static build [no]--mandir=PATH install man pages in PATH--datadir=PATH install firmware in PATH/qemu--docdir=PATH install documentation in PATH/qemu--bindir=PATH install binaries in PATH--libdir=PATH install libraries in PATH--libexecdir=PATH install helper binaries in PATH--sysconfdir=PATH install config in PATH/qemu--localstatedir=PATH install local state in PATH (set at runtime on win32)--firmwarepath=PATH search PATH for firmware files--efi-aarch64=PATH PATH of efi file to use for aarch64 VMs.--with-confsuffix=SUFFIX suffix for QEMU data inside datadir/libdir/sysconfdir [/qemu]--with-pkgversion=VERS use specified string as sub-version of the package--enable-debug enable common debug build options--enable-sanitizers enable default sanitizers--enable-tsan enable thread sanitizer--disable-strip disable stripping binaries--disable-werror disable compilation abort on warning--disable-stack-protector disable compiler-provided stack protection--audio-drv-list=LIST set audio drivers list:Available drivers: oss alsa sdl pa--block-drv-whitelist=L Same as --block-drv-rw-whitelist=L--block-drv-rw-whitelist=Lset block driver read-write whitelist(affects only QEMU, not qemu-img)--block-drv-ro-whitelist=Lset block driver read-only whitelist(affects only QEMU, not qemu-img)--enable-trace-backends=B Set trace backendAvailable backends: dtrace ftrace log simple syslog ust--with-trace-file=NAME Full PATH,NAME of file to store tracesDefault:trace-<pid>--disable-slirp disable SLIRP userspace network connectivity--enable-tcg-interpreter enable TCG with bytecode interpreter (TCI)--enable-malloc-trim enable libc malloc_trim() for memory optimization--oss-lib path to OSS library--cpu=CPU Build for host CPU [x86_64]--with-coroutine=BACKEND coroutine backend. Supported options:ucontext, sigaltstack, windows--enable-gcov enable test coverage analysis with gcov--gcov=GCOV use specified gcov [gcov]--disable-blobs disable installing provided firmware blobs--with-vss-sdk=SDK-path enable Windows VSS support in QEMU Guest Agent--with-win-sdk=SDK-path path to Windows Platform SDK (to build VSS .tlb)--tls-priority default TLS protocol/cipher priority string--enable-gprof QEMU profiling with gprof--enable-profiler profiler support--enable-debug-stack-usagetrack the maximum stack usage of stacks created by qemu_alloc_stack--enable-pluginsenable plugins via shared library loading--disable-containers don't use containers for cross-building--gdb=GDB-path gdb to use for gdbstub tests [/usr/bin/gdb]Optional features, enabled with --enable-FEATURE anddisabled with --disable-FEATURE, default is enabled if available:system all system emulation targetsuser supported user emulation targetslinux-user all linux usermode emulation targetsbsd-user all BSD usermode emulation targetsdocs build documentationguest-agent build the QEMU Guest Agentguest-agent-msi build guest agent Windows MSI installation packagepie Position Independent Executablesmodules modules support (non-Windows)module-upgrades try to load modules from alternate paths for upgradesdebug-tcg TCG debugging (default is disabled)debug-info debugging informationsparse sparse checkersafe-stack SafeStack Stack Smash Protection. Depends onclang/llvm >= 3.7 and requires coroutine backend ucontext.gnutls GNUTLS cryptography supportnettle nettle cryptography supportgcrypt libgcrypt cryptography supportauth-pam PAM access controlsdl SDL UIsdl-image SDL Image support for iconsgtk gtk UIvte vte support for the gtk UIcurses curses UIiconv font glyph conversion supportvnc VNC UI supportvnc-sasl SASL encryption for VNC servervnc-jpeg JPEG lossy compression for VNC servervnc-png PNG compression for VNC servercocoa Cocoa UI (Mac OS X only)virtfs VirtFSmpath Multipath persistent reservation passthroughxen xen backend driver supportxen-pci-passthrough PCI passthrough support for Xenbrlapi BrlAPI (Braile)curl curl connectivitymembarrier membarrier system call (for Linux 4.14+ or Windows)fdt fdt device treekvm KVM acceleration supporthax HAX acceleration supporthvf Hypervisor.framework acceleration supportwhpx Windows Hypervisor Platform acceleration supportrdma Enable RDMA-based migrationpvrdma Enable PVRDMA supportvde support for vde networknetmap support for netmap networklinux-aio Linux AIO supportlinux-io-uring Linux io_uring supportcap-ng libcap-ng supportattr attr and xattr supportvhost-net vhost-net kernel acceleration supportvhost-vsock virtio sockets device supportvhost-scsi vhost-scsi kernel target supportvhost-crypto vhost-user-crypto backend supportvhost-kernel vhost kernel backend supportvhost-user vhost-user backend supportvhost-vdpa vhost-vdpa kernel backend supportspice spicerbd rados block device (rbd)libiscsi iscsi supportlibnfs nfs supportsmartcard smartcard support (libcacard)libusb libusb (for usb passthrough)live-block-migration Block migration in the main migration streamusb-redir usb network redirection supportlzo support of lzo compression librarysnappy support of snappy compression librarybzip2 support of bzip2 compression library(for reading bzip2-compressed dmg images)lzfse support of lzfse compression library(for reading lzfse-compressed dmg images)zstd support for zstd compression library(for migration compression and qcow2 cluster compression)seccomp seccomp supportcoroutine-pool coroutine freelist (better performance)glusterfs GlusterFS backendtpm TPM supportlibssh ssh block device supportnuma libnuma supportlibxml2 for Parallels image formattcmalloc tcmalloc supportjemalloc jemalloc supportavx2 AVX2 optimization supportavx512f AVX512F optimization supportreplication replication supportopengl opengl supportvirglrenderer virgl rendering supportxfsctl xfsctl supportqom-cast-debug cast debugging supporttools build qemu-io, qemu-nbd and qemu-img toolsbochs bochs image format supportcloop cloop image format supportdmg dmg image format supportqcow1 qcow v1 image format supportvdi vdi image format supportvvfat vvfat image format supportqed qed image format supportparallels parallels image format supportsheepdog sheepdog block driver supportcrypto-afalg Linux AF_ALG crypto backend drivercapstone capstone disassembler supportdebug-mutex mutex debugging supportlibpmem libpmem supportxkbcommon xkbcommon supportrng-none dummy RNG, avoid using /dev/(u)random and getrandom()libdaxctl libdaxctl support
附录2:x86平台qemu安装
安装命令
./configure --prefix=/home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dstmake && make install
相关配置和日志
baiy@inno-NUC8i3BEH:qemu-5.1.0-rc3$ ./configure --prefix=/home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst --target-list=x86_64-softmmuInstall prefix /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dstBIOS directory /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst/share/qemufirmware path /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst/share/qemu-firmwarebinary directory /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst/binlibrary directory /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst/libmodule directory /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst/lib/qemulibexec directory /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst/libexecinclude directory /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst/includeconfig directory /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst/etclocal state directory /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst/varManual directory /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/x86-qemu-dst/share/manELF interp prefix /usr/gnemul/qemu-%MBuild directory /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/qemu-5.1.0-rc3Source path /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/qemu-5.1.0-rc3GIT binary gitGIT submodulesC compiler ccHost C compiler ccC++ compiler c++Objective-C compiler ccARFLAGS rvCFLAGS -O2 -U_FORTIFY_SOURCE -D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -gQEMU_CFLAGS -I/usr/include/pixman-1 -pthread -I/usr/include/glib-2.0 -I/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/glib-2.0/include -fPIE -DPIE -m64 -mcx16 -D_GNU_SOURCE -D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64 -D_LARGEFILE_SOURCE -Wstrict-prototypes -Wredundant-decls -Wall -Wundef -Wwrite-strings -Wmissing-prototypes -fno-strict-aliasing -fno-common -fwrapv -std=gnu99 -Wold-style-declaration -Wold-style-definition -Wtype-limits -Wformat-security -Wformat-y2k -Winit-self -Wignored-qualifiers -Wempty-body -Wnested-externs -Wendif-labels -Wexpansion-to-defined -Wno-missing-include-dirs -Wno-shift-negative-value -Wno-psabi -fstack-protector-strong -I/usr/include/libpng16 -I$(SRC_PATH)/capstone/includeQEMU_LDFLAGS -Wl,--warn-common -Wl,-z,relro -Wl,-z,now -pie -m64 -fstack-protector-strongmake makeinstall installpython /usr/bin/python3 -B (3.6.9)genisoimage /usr/bin/genisoimageefi_aarch64 /home/baiy/workspace/linux-learn/qemu-kvm/qemu-5.1.0-rc3/pc-bios/edk2-aarch64-code.fdpython_yaml yesslirp support internalsmbd /usr/sbin/smbdmodule support noalt path mod load nohost CPU x86_64host big endian notarget list x86_64-softmmugprof enabled nosparse enabled nostrip binaries yesprofiler nostatic build nosafe stack noSDL support yes (2.0.8)SDL image support noGTK support noGTK GL support noVTE support noTLS priority NORMALGNUTLS support nolibgcrypt nonettle nolibtasn1 noPAM noiconv support yescurses support novirgl support nocurl support yesmingw32 support noAudio drivers pa ossBlock whitelist (rw)Block whitelist (ro)VirtFS support yesMultipath support noVNC support yesVNC SASL support noVNC JPEG support yesVNC PNG support yesxen support nobrlapi support noDocumentation noPIE yesvde support nonetmap support noLinux AIO support noLinux io_uring support noATTR/XATTR support yesInstall blobs yesKVM support yes # 默认支持KVMHAX support noHVF support noWHPX support noTCG support yesTCG debug enabled noTCG interpreter nomalloc trim support yesRDMA support noPVRDMA support nofdt support nomembarrier nopreadv support yesfdatasync yesmadvise yesposix_madvise yesposix_memalign yeslibcap-ng support yesvhost-net support yesvhost-crypto support yesvhost-scsi support yesvhost-vsock support yesvhost-user support yesvhost-user-fs support yesvhost-vdpa support yesTrace backends logspice support norbd support noxfsctl support nosmartcard support nolibusb nousb net redir noOpenGL support noOpenGL dmabufs nolibiscsi support nolibnfs support nobuild guest agent yesQGA VSS support noQGA w32 disk info noQGA MSI support noseccomp support nocoroutine backend ucontextcoroutine pool yesdebug stack usage nomutex debugging nocrypto afalg noGlusterFS support nogcov gcovgcov enabled noTPM support yeslibssh support noQOM debugging yesLive block migration yeslzo support nosnappy support nobzip2 support nolzfse support nozstd support noNUMA host support nolibxml2 notcmalloc support nojemalloc support noavx2 optimization yesavx512f optimization noreplication support yesbochs support yescloop support yesdmg support yesqcow v1 support yesvdi support yesvvfat support yesqed support yesparallels support yessheepdog support yescapstone internallibpmem support nolibdaxctl support nolibudev yesdefault devices yesplugin support nofuzzing support nogdb /usr/bin/gdbrng-none noLinux keyring yescross containers noNOTE: guest cross-compilers enabled: cc

