- 数组扁平化
- 数组去重
- 类数组转化为数组
- Array.prototype.filter()
- Array.prototype.map()
- Array.prototype.forEach()
- Array.prototype.reduce()
- Function.prototype.call
- Function.prototype.apply()
- Function.prototype.bind()
- debounce
- throttle
- 函数柯里化
- 模拟new操作
- instanceof
- Object.assign
- 深拷贝
- promise
- Promise并行限制
- JSONP(JSON with Padding)
- AJAX
- event
- 图片懒加载
- 渲染大数据
- 获取当前页面html元素种类
- 将VirtualDom转换为真实DOM
- 字符串解析
数组扁平化
//32手写//01.数组扁平化let arr = [1, [2, [3, [4, 5]]], 6];// => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]let res;res = arr.flat(Infinity);res = JSON.stringify(arr).replace(/\[|\]/g, "").split(",");res = JSON.parse("[" + JSON.stringify(arr).replace(/\[|\]/g, "") + "]");const flatten = arr => {return arr.reduce((pre, cur) => {return pre.concat(Array.isArray(cur) ? flatten(cur) : cur);}, []);};res = flatten(res);const result = [];const f2 = arr => {for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {Array.isArray(arr[i]) ? f2(arr[i]) : result.push(arr[i]);}return result;};res = f2(arr);console.log(res);
数组去重
// 02.数组去重arr = [1, 1, "1", 17, true, true, false, false, "true", "a", {}, {}];// => [1, '1', 17, true, false, 'true', 'a', {}, {}]res = [...new Set(arr)];const unique = arr => {return arr.filter((item, idx) => {return arr.indexOf(item) === idx;});};res = unique(arr);console.log(res);
类数组转化为数组
// 03.类数组转化为数组// const div = document.querySelector('div')const div = [1, 1]; //一般是 arguments 或是 dom 操作方法返回的数据res = Array.from(div);res = Array.prototype.slice.call(div);res = [...div];res = Array.prototype.concat.call(div);console.log(res);
Array.prototype.filter()
//04.Array.prototype.filter()Array.prototype.fakeFilter = function(callback,thisArg){if(this == undefined)throw new TypeError('this is null or undefined');if(typeof callback !== "function")throw new TypeError(callback+'is not a function');const res = [];const O = Object(this)const len = O.length >>> 0for(let i = 0;i<len;i++){if(i in O){if(callback.call(thisArg,O[i],i,O)){res.push(O[i])}}}return res}const arr =[-1,-1,11,1,1]console.log(arr.fakeFilter((item)=>{return item > 0}))
Array.prototype.map()
//05.Array.prototype.map()Array.prototype.myMap = function(callback,thisArg){if(this == undefined)throw new TypeError('this is null or undefined');if(typeof callback !== "function")throw new TypeError(callback+'is not a function');const res = []const O = Object(this)const len = O.length>>>0for(let i =0;i<len;i++){if( i in O){res[i] = callback.call(thisArg,O[i],i,this)}}return res}function arrDouble(i){return i*2}res = arr.myMap(arrDouble)console.log(res);
Array.prototype.forEach()
//06.Array.prototype.forEach()Array.prototype.myForEach = function(callback,thisArg){if(this == undefined)throw new TypeError('this is null or undefined');if(typeof callback !== "function")throw new TypeError(callback+'is not a function');const O = Object(this)const len = O.length>>>0let k =0while(k < len){if(k in O){callback.call(thisArg,O[k],k,this)}k++}}function clog(i){console.log(i)}res.myForEach(clog)// console.log(res)
Array.prototype.reduce()
//07.Array.prototype.reduce()Array.prototype.myReduce = function(callback,initValue){if (this == undefined) throw new TypeError("this is null or undefined");if (typeof callback !== "function")throw new TypeError(callback + "is not a function");const O = Object(this)const len = O.length >>> 0let accumulator = initValuelet k = 0if(accumulator === undefined){while(k < len && !(k in O))k++//找到数组的第一个有效值if(k >= len)throw new TypeError('Reduce of empty array with no initial Value')accumulator = O[k++]}while(k<len){if(k in O)accumulator = callback.call(undefined,accumulator,O[k],k,O)k++}return accumulator}const arr = [1,1,1,,4,5]function add(a,b){return a+b}let res = arr.myReduce(add)// console.log(res)
Function.prototype.call
//08.Function.prototype.callFunction.prototype.myCall = function (context = window, ...args) {if (typeof this !== 'function') throw new TypeError('Type Error')const fn = Symbol('fn')context[fn] = thisconst res = context[fn](...args)delete context[fn]return res}const a = {name: 'aaa',sayName: function () {console.log(this.name)},}const b = {name: 'bbb',}// a.sayName.myCall(b) //bbbfunction Parent(name) {this.name = namethis.showName = function () {console.log(this.name)}}function Child(name) {Parent.myCall(this, name)}const c = new Child('ccc')// c.showName() //ccc
Function.prototype.apply()
//09.Function.prototype.apply()//与call不同的是 函数接收的参数是数组Function.prototype.myApply = function (context = window, args) {if (typeof this !== 'function') throw new TypeError('Type Error')const fn = Symbol('fn')context[fn] = thisif (args) {const res = context[fn](...args)} else {const res = context[fn]()}delete context[fn]return res}// a.sayName.myApply(b) //bbbfunction C2(name) {Parent.myApply(this, [name])}const c2 = new C2('c222')// c2.showName() //c222
Function.prototype.bind()
//10.Function.prototype.bindFunction.prototype.myBind = function (context, ...args) {if (typeof this !== 'function') throw new TypeError('Type Error')const fnToBind = thisconst fuBound = function () {return fnToBind.apply(context, [...args, ...arguments])}return fuBound}const boy = {age: 18,getAge() {return this.age},}const getX = boy.getAge.myBind(boy)// console.log(getX())//18function add(a, b) {return a + b}// console.log(add.myBind(null, 10)(12, 1)) //22
深拷贝和浅拷贝最根本的区别在于是否真正获取一个对象的复制实体,而不是引用。 假设B复制了A,修改A的时候,看B是否发生变化:
如果B跟着也变了,说明是浅拷贝,拿人手短!(修改堆内存中的同一个值)
如果B没有改变,说明是深拷贝,自食其力!(修改堆内存中的不同的值) 浅拷贝(shallowCopy)只是增加了一个指针指向已存在的内存地址,
深拷贝(deepCopy)是增加了一个指针并且申请了一个新的内存,使这个增加的指针指向这个新的内存,
debounce
//11 debounceconst myDebounce = (fn, time) => {let timeout = nullreturn function () {clearTimeout(timeout)timeout = setTimeout(() => {fn.apply(this, arguments)}, time)}}
throttle
//12. throttleconst myThrottle = (fn, time) => {let flag = truereturn function () {if (!flag) returnflag = falsesetTimeout(() => {fn.apply(this, arguments)flag = true}, time)}}
函数柯里化
//13.函数柯里化//实现add(1)(2)(3)(4)=10; 、 add(1)(1,2,3)(2)=9;//直接简单add版本function add2() {const _args = [...arguments]function inner() {_args.push(...arguments)return inner}inner.toString = function () {return _args.reduce((sum, cur) => sum + cur)}return inner}const resAdd = add2(1)(2)(3)(4)// console.log(resAdd == 10) //true// console.log(resAdd === 10) //false// //实际上得到的 resAdd 是一个函数//参数定长柯里化function myCurry(fn) {//获取原函数的参数长度const argLen = fn.length//保留预置参数const presetArgs = [].slice.call(arguments, 1) //去掉传入的第一个参数(fn)// console.log(presetArgs)//返回新函数return function () {// const restArgs = [].slice.call(arguments) //和下面的写法一样效果const restArgs = [...arguments]// console.log(restArgs)const allArgs = [...presetArgs, ...restArgs]// console.log(allArgs)if (allArgs.length >= argLen) {//如果参数够了,就执行原函数// console.log(this)// console.log(allArgs)// console.log(fn.apply(this, [1, 2, 3]))return fn.apply(null, allArgs)} else {//否则继续柯里化return myCurry.call(null, fn, ...allArgs)}}}function add(a, b, c) {return a + b + c}// 把函数传进去就可以了const addCurry = myCurry(add)// console.log(addCurry)// console.log(addCurry(1)(2)(3))// console.log(addCurry(1)(2, 3))// console.log(addCurry(1, 2, 4))// console.log(addCurry(1, 2)(3))//参数不定长柯里化function myCurry2(fn) {const preset = [].slice.call(arguments, 1)function curried() {const rest = [].slice.call(arguments)const all = [...preset, rest]//新函数执行后仍然返回一个结果函数。return myCurry2.call(null, fn, ...all)}//结果函数可以被Javascript引擎解析 ==> 重写toStringcurried.toString = function () {return fn.apply(null, preset)}return curried}function dynamicAdd() {return [...arguments].reduce((prev, curr) => {return prev + curr}, 0)}const addPro = myCurry2(dynamicAdd) //经 curry处理,得到一个新函数,这一点不变。console.log(typeof addPro)// addPro(1)(2)(3)(4) // 10// addPro(1, 2)(3, 4)(5, 6) // 21
模拟new操作
//模拟new操作function myNew(someConstructor, ...args) {if (typeof someConstructor !== 'function') throw new TypeError('Type Error')//以 someConstructor 为原型创建一个对象const obj = Object.create(someConstructor.prototype)//执行构造函数并将this绑定到新创建的对象上const res = someConstructor.apply(obj, args)//判断构造函数执行返回的结果是否是引用数据类型//若是则返回构造函数返回的结果//若不是则返回创建的对象const isObj = typeof res === 'object' && res !== nullconst isFuc = typeof res === 'function'return isObj || isFuc ? res : obj}function Otest() {this.a = 'a'}const o1 = myNew(Otest)// console.log(o1.a) //a
instanceof
//15. instanceof//左侧是对象,右侧是函数const myInstanceof = (left, right) => {//基本数据类型 falseif (typeof left !== 'object' || left === null) return falselet proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(left)while (true) {if (proto === null) return falseif (proto === right.prototype) return trueproto = Object.getPrototypeOf(proto)}}function grandpa() {}function father() {}father.prototype = new grandpa()function son() {}son.prototype = new father()let xiaoming = new son()// console.log(myInstanceof(xiaoming, son)) //true// console.log(myInstanceof(xiaoming, father)) //true// console.log(myInstanceof(xiaoming, grandpa)) //true
//16. 原型继承——寄生组合继承function Parent() {this.name = 'parent'}function Child() {Parent.call(this)this.type = 'children'}Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype)Child.prototype.constructor = Childconst c = new Child()// console.log(c.name) //parent// console.log(c.type) //children// console.log(c instanceof Parent) //true//17. Object.is/* 主要解决:1. +0 === -0 //true2. NaN === NaN //false*/const myIs = (x, y) => {if (x === y) {return x !== 0 || y !== 0 || 1 / x === 1 / y} else {return x !== x && y !== y}}// console.log(myIs(+0,-0))//false// console.log(myIs(NaN,NaN))//true
Object.assign
深拷贝
//19. 深拷贝const myCloneDeep = (target, hash = new WeakMap()) => {//对于传入参数进行处理if (typeof target !== 'object' || target === null)return target//哈希表中存在则直接返回if (hash.has(target)) return hash.get(target)const cloneTarget = Array.isArray(target) ? [] : {}hash.set(target, cloneTarget)//针对Symbol属性const symKeys = Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(target)if (symKeys.length) {symKeys.forEach((symKey) => {if (typeof target[symKey] === 'object' &&target[symKey] !== null) {cloneTarget[symKey] = myCloneDeep(target[symKey])} else {cloneTarget[symKey] = target[symKey]}})}for (const i in target) {if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(target, i)) {cloneTarget[i] =typeof target[i] === 'object' && target[i] !== null? myCloneDeep(target[i], hash): target[i]}}return cloneTarget}const obj = {a: 1,}const obj2 = myCloneDeep(obj)// console.log(obj2) //{a:1}// obj2.a = 2// console.log(obj) //{a:1}// console.log(obj2) //{a:2,b:2}
promise
Promise.all()会等待所有Promise完成,Promise.race()只会执行一个Promise。
//20.promise// 模拟实现Promise// Promise利用三大手段解决回调地狱:// 1. 回调函数延迟绑定// 2. 返回值穿透// 3. 错误冒泡const PENDING = 'PENDING'const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED'const REJECTED = 'REJECTED'class myPromise {constructor(exector) {//初始化状态this.status = PENDING//将成功、失败结果放在 this 上,便于then、catch 访问this.value = undefinedthis.reason = undefined//成功态回调函数队列this.onFulfilledCallbacks = []//失败态回调函数队列this.onRejectedCallback = []const resolve = (value) => {//只有进行中状态才能更改状态if (this.status === PENDING) {this.status = FULFILLEDthis.value = value//成功态函数依次执行this.onFulfilledCallbacks.forEach((fn) =>fn(this.value),)}}const reject = (reason) => {if (this.status === PENDING) {this.status = REJECTEDthis.reason = reason//失败态的函数依次执行this.onRejectedCallback.forEach((fn) =>fn(this.reason),)}}try {//立即执行executor//把内部的resolve和reject 传入executor,用户可调用resolve和rejectexector(resolve, reject)} catch (e) {//exrcutor 执行出错,将错误内容reject抛出去reject(e)}}then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {onFulfilled =typeof onFulfilled === 'function'? onFulfilled: (value) => valueonRejected =typeof onRejected === 'function'? onRejected: (reason) => {throw new Error(reason instanceof Error? reason.message: reason,)}//保存thisconst self = thisreturn new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {if (self.status === PENDING) {self.onFulfilledCallbacks.push(() => {//try捕获错误try {//模拟微任务setTimeout(() => {const result = onFulfilled(self.value)//分两种情况://1.回调函数返回值是 Promise 执行then操作//2.如果不是Promise,调用新Promise的resolve函数result instanceof myPromise? result.then(resolve, reject): resolve(result)})} catch (e) {reject(e)}})self.onRejectedCallback.push(() => {try {setTimeout(() => {const result = onRejected(self.reason)result instanceof myPromise? result.then(resolve, reject): resolve(result)})} catch (e) {reject(e)}})} else if (self.status === FULFILLED) {try {setTimeout(() => {const result = onFulfilled(self.value)result instanceof myPromise? result.then(resolve, reject): resolve(result)})} catch (e) {reject(e)}} else if (self.status === REJECTED) {try {setTimeout(() => {const result = onRejected(self.reason)result instanceof myPromise? result.then(resolve, reject): resolve(result)})} catch (e) {reject(e)}}})}catch(onRejected) {return this.then(null, onRejected)}static resolve(value) {if (value instanceof myPromise) {//如果是Promise实例,则直接返回return value} else {//如果不是,则返回一个新的 Promise对象,状态为FULFILLEDreturn new myPromise((resolve, reject) =>resolve(value),)}}static reject(reason) {return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {reject(reason)})}//Promise.all是支持链式调用的,本质上就是返回了一个Promise实例,通过resolve和reject来改变实例状态。static all(promiseArr) {return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {const len = promiseArr.lengthconst values = new Array(len)//记录已经成功执行的promise个数let count = 0for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {//Promise.resolve()处理,确保每一个都是promise实例myPromise.resolve(promiseArr[i]).then((val) => {values[i] = valcount++//如果全部执行完,返回promise状态就可以改变if (count === len) resolve(values)},(err) => reject(err),)}})}//Promise.race(iterable) 方法返回一个 promise//一旦迭代器中的某个promise解决或拒绝//返回的 promise就会解决或拒绝。static race(promiseArr) {return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {promiseArr.forEach((p) => {Promise.resolve(p).then((val) => resolve(val),(err) => reject(err),)})})}}
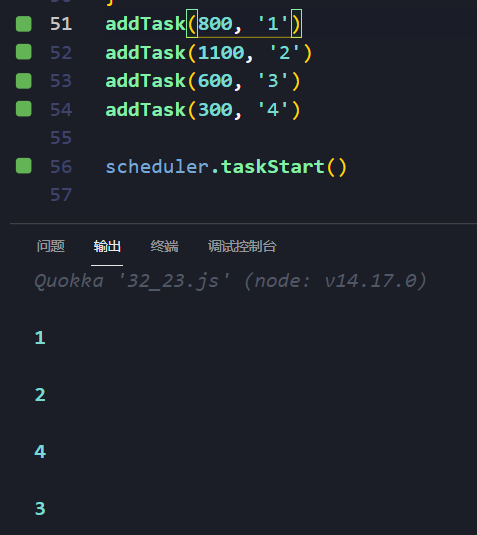
Promise并行限制
//23. Promise并行限制class Scheduler {constructor() {this.queue = []//最大并行个数this.maxCount = 2this.runCount = 0}//往队列中插入Promise Creator函数add(promiseCreator) {this.queue.push(promiseCreator)}//每次从队列中取出Promise Creator并执行//此Promise执行完成之后//应该递归调用request函数来执行下一个Promiserequest() {if (!this.queue ||!this.queue.length ||this.runCount >= this.maxCount) {return}this.runCount++this.queue.shift()().then(() => {this.runCount--this.request()})}//启动函数,将队列中的两个Promise启动起来taskStart() {for (let i = 0; i < this.maxCount; i++) {this.request()}}}//testconst timeout = (time) =>new Promise((resolve) => {setTimeout(resolve, time)})const scheduler = new Scheduler()const addTask = (time, order) => {scheduler.add(() =>timeout(time).then(() => console.log(order)),)}addTask(800, '1')addTask(1100, '2')addTask(600, '3')addTask(300, '4')scheduler.taskStart()
JSONP(JSON with Padding)
//24. JSONP(JSON with Padding)//jsonp的核心原理是利用script标签没有同源限制的方式,可以发送跨域的get请求(只能发送get请求)。const jsonp = ({ url, params, callbackName }) => {//script标签中的src属性将请求参数和当前请求的回调函数名拼接在链接上。最终由服务端接收到请求之后拼接成前端可执行的字符串的形式返回。这个结果字符串最终会在前端的script标签中解析并执行。const generateUrl = () => {let dataSrc = ''for (let key in params) {if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(params, key)) {dataSrc += `${key}=${params[key]}&`}}dataSrc += `callback=${callbackName}`return `${url}?${dataSrc}`}return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {const scriptEle = document.createElement('script')scriptEle.src = generateUrl()document.body.appendChild(scriptEle)window[callbackName] = (data) => {resolve(data)document.removeChild(scriptEle)}})}/* btn.addEventListener('click', () => {jsonp({url: 'http://localhost:3000/xxx',params: {name: 'xx',age: 18,},callback: 'show',}).then((data) => {console.log(data)})}) */
AJAX
//25.AJAX// xhr 具有一个 open 方法,这个方法的作用类似于初始化,并不会发起真正的请求// open 方法具有 5 个参数,但是常用的是前 3 个// method: 请求方式 —— get / post// url:请求的地址// async:是否异步请求,默认为 true(异步)//xhr.open(method, url, async)// send 方法发送请求,并接受一个可选参数// 当请求方式为 post 时,可以将请求体的参数传入// 当请求方式为 get 时,可以不传或传入 null// 不管是 get 还是 post,参数都需要通过 encodeURIComponent 编码后拼接//xhr.send(data)//注意:XMLHttpRequest不是node内置的,需要安装//npm install xmlhttprequest// const XMLHttpRequest =// require('xmlhttprequest').XMLHttpRequest//或者安装quokka browser插件jsdom-quokka-plugin可以在vscode中调试const ajax = function (options) {const url = options.urlconst method = options.method.toLowerCase() || 'get'const async = options.async != false //默认为trueconst data = options.data//兼容IEconst xhr = XMLHttpRequest? new XMLHttpRequest(): new ActiveXObject('Mscrosoft.XMLHttp')if (options.timeout && options.timeout > 0) {xhr.timeout = options.timeout}return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {//处理超时xhr.onTimeout = () => reject && reject('请求超时')xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {if (xhr.readyState !== 4) return// HTTP 状态在 200-300 之间表示请求成功// HTTP 状态为 304 表示请求内容未发生改变,可直接从缓存中读取if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) ||xhr.status === 304) {resolve && resolve(xhr.responseText)} else {reject && reject(new Error(xhr.responseText))}}xhr.onerror = (err) => reject && reject(err)let paramArr = []let encodeDataif (data instanceof Object) {for (let key in data) {//通过encodeURIComponent编码后再拼接参数paramArr.push(`${encodeURIComponent(key)}=${encodeURIComponent(data[key],)}`,)}encodeData = paramArr.join('&')}//看要不要处理urlif (method === 'get') {//检测url中是否存在?以及其下标const index = url.indexOf('?')if (index === -1) url += '?'else if (index !== url.length - 1) url += '&'//拼接url += encodeData}//初始化请求xhr.open(method, url, async)if (method === 'get') xhr.send(null)else {//post方法,设置请求头xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type','application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8',)xhr.send(encodeData)}})}//testajax({url: 'http://xxx',method: 'get',async: true,timeout: 1000,data: {k1: 111,k2: 211,},}).then((res) => console.log('请求成功: ' + res),(err) => console.log('请求失败: ' + err),)
event
- on(eventName, func): 监听 eventName事件, 事件触发的时候调用 func函数
- emit(eventName, arg1, arg2, arg3,arg4…) : 触发eventName 事件, 并且把参数 arg1, arg2, arg3,arg4…传给事件处理函数
- off(eventName, func) : 停止监听某个事件
addListener是emitter.on(eventName, listener) 的别名。
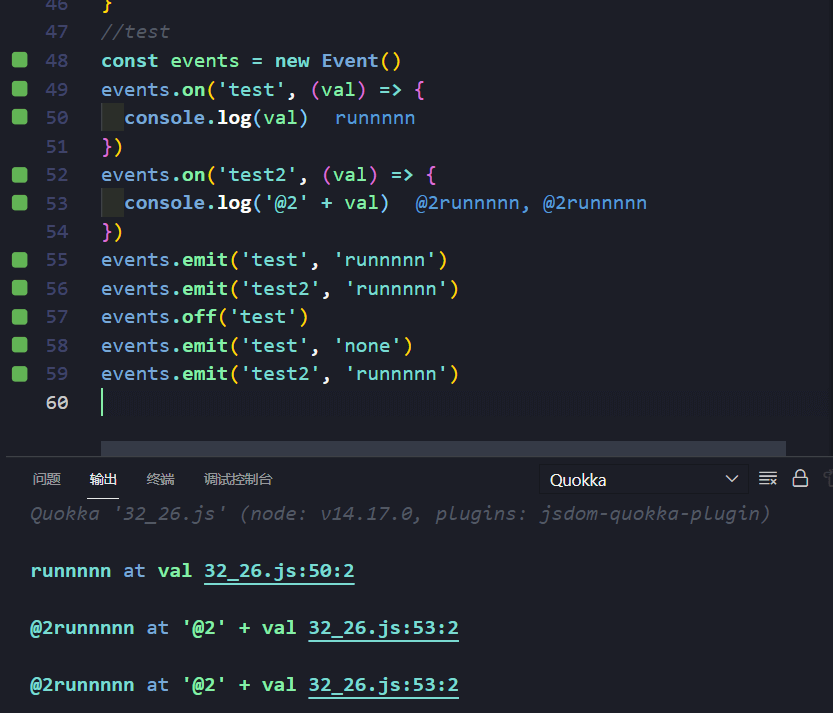
//26.event模块//events只对外暴露一个对象,就是EventEmitter,EventEmitter作用只有2个,分别是:事件的发射和事件的监听。class Event {constructor() {//储存事件的数据结构——字典this.cache = new Map()}//绑定on(type, func) {//出于查找方便和节省空间将同一类型事件放到一个模拟队列的数组中let fns = (this.cache[type] = this.cache[type] || [])if (fns.indexOf(func) === -1) {fns.push(func)}return this}//触发emit(type, data) {let fns = this.cache[type]if (Array.isArray(fns)) {fns.forEach((fn) => {fn(data)})}return this}//解绑off(type, func) {let fns = this.cache[type]if (Array.isArray(fns)) {if (func) {let index = fns.indexOf(func)if (index !== -1) {fns.splice(index, 1)}} else {//没指定就清空fns.length = 0}}return this}}//testconst events = new Event()events.on('test', (val) => {console.log(val)})events.on('test2', (val) => {console.log('@2' + val)})events.emit('test', 'runnnnn')events.emit('test2', 'runnnnn')events.off('test')events.emit('test', 'none')events.emit('test2', 'runnnnn')
图片懒加载
//27. 图片懒加载//先设置一个临时的 data-src 属性进行src的占位const lazyLoad = () => {const imgs = document.querySelectorAll('img')const len = imgs.length//窗口高度const viewH = document.documentElement.clientHeight//滚动条高度const scrollH =//这两者有个特点:同时只有一个值生效,另一个始终为0document.documentElement.scrollTop +document.body.scrollTopfor (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {const offsetH = imgs[i].offsetTopif (offsetH < viewH + scrollH) {const src = imgs[i].dataset.srcimgs[i].src = src}}}//使用lazyLoad() //首屏加载window.addEventListener('scroll', lazyLoad)//还可以配合节流一起使用//28. 滚动加载window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {const { clientHeight, scrollTop, scrollHeight } =document.documentElement//检测到滚动页面接近页面底部if (clientHeight + scrollTop >= scrollHeight + 50) {//加载后面的部分窗口}})
渲染大数据
//29.较大的数据量需要渲染时//合理使用createDocumentFragment和requestAnimationFrame,将操作切分为一小段一小段执行。setTimeout(() => {//插入十万条数据const total = 100000//一次插入的数据const once = 20//插入数据需要的次数const loopCount = Math.ceil(total / once)let countOfRender = 0const ul = document.querySelector('ul')//添加数据const add = () => {//在虚拟节点对象上操作const fragment = document.createDocumentFragment()for (let i = 0; i < once; i++) {const li = document.createElement('li')li.innerText = Math.floor(Math.random * total)fragment.appendChild(li)}//插入的实际操作ul.appendChild(fragment)countOfRender++loop()}//刷新const loop = () => {if (countOfRender < loopCount) {//window.requestAnimationFrame() 告诉浏览器——你希望执行一个动画,并且要求浏览器在下次重绘之前调用指定的回调函数更新动画。该方法需要传入一个回调函数作为参数,该回调函数会在浏览器下一次重绘之前执行window.requestAnimationFrame(add)}}loop()}, 0)
获取当前页面html元素种类
//30 当前页面html元素种类const printSpeciesOfHtml = () => {return [...new Set(),[...document.querySelectorAll('*')].map((el) => el.tagName,),].length}
将VirtualDom转换为真实DOM
//31.将VirtualDom 转化为真实DOM结构// vnode结构:// {// tag,// attrs,// children,// }//Virtual DOM => DOMconst render = (vnode, container) => {container.appendChild(_render(vnode))}const _render = (vnode) => {//如果是数字类型就转化为字符串if (typeof vnode === 'number ') {vnode = String(vnode)}//字符串类型则直接作为文本节点if (typeof vnode == 'string') {return document.createTextNode(vnode)}//else就是//普通DOMconst dom = document.createElement(vnode.tag)if (vnode.attrs) {//遍历属性Object.keys(vnode.attrs).forEach((key) => {const value = vnode.attrs[key]dom.setAttribute(key, value)})}//子数组进行递归操作vnode.children.forEach((child) => render(child, dom))return dom}
字符串解析
//32.字符串解析问题const a = {z: 123,q: '123',}//实现函数使得将str字符串中的{}内的变量替换,如果属性不存在保持原样(比如{a.d})//类似于模版字符串,但有一点出入,实际上原理大差不差const parseStr = (str, obj) => {let res = ''//标志位,标志前面是否有{let flag = falselet startfor (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {if (str[i] === '{') {flag = truestart = i + 1continue}if (!flag) res += str[i]else {if (str[i] === '}') {flag = falseres += match(str.slice(start, i), obj)}}}return res}//对象匹配操作const match = (str, obj) => {const keys = str.split('.').slice(1)let index = 0let o = objwhile (index < keys.length) {const key = keys[index]if (!o[jey]) return `{${str}}`else o = o[key]index++}return o}