- 分享主题:Transfer Learning, Domain Generalization, NLP, Explicit Feature Distribution Alignment, Adversarial
- 论文标题:Unseen Target Stance Detection with Adversarial Domain Generalization
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2010/2010.05471.pdf
1.Summary
This is a paper on stance detection. Stance detection is to give a Target and a Sentence. It is necessary to judge whether sense is favor, against or neutral in the Target. When a new Target appears, there is little data that can be used for model training. This paper assumes that the target domain has no known data, so some other datasets in the past need to be used to help model training. Therefore, this paper uses the adversarial method to realize the transfer learning. In order to prove the effectiveness of migration, this paper also sets up different models. In order to deepen my understanding of this paper, I can learn some NLP knowledge.2.你对于论文的思考
这是一篇立场检测的文章,当一个新的Target出现时,没有数据来给模型训练,因此,这篇文章第一次把迁移学习引入了立场检测。文中假设目标域没有数据,因此是一个多源域的对抗迁移学习,为了证明迁移效果的有效性,文章设置了不同的模型来对比效果。3. 其他
3.1 解决的问题
本文解决的是立场检测的问题,给定一个Target和一个Sentence,需要判断Sentence在Target的场景下是favor、against还是neutral,本文并不是独立的对Sentence和Target分别进行编码,而是糅合两者,并利用attention根据不同的Target给Sentence中的每一个词一个权重。此外,当一个新的Target出现时,可以用于模型训练的数据很少,因此文中假设目标域是没有已知数据的,并利用对抗迁移学习的方法把以前的一些数据集中的知识迁移到未知的目标域中。3.2 模型
如下图所示,模型采取了域对抗的形式。生成器部分是利用BiLSTM对Target和Sentence进行编码,然后利用attention对Sentence中的不同单词提取权重;标签预测器包含MLP和一个softmax分类器;域判别器是一个softmax分类器。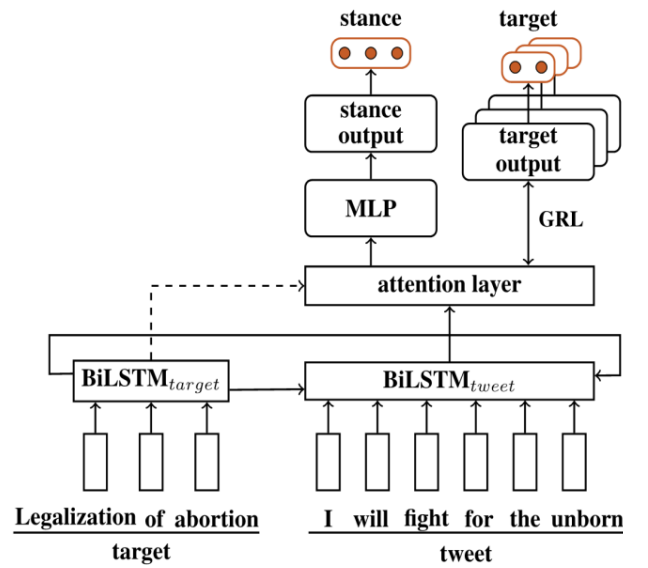
3.2.1 生成器
Target是直接用BiLSTM进行编码,而Sentence则是要如下面的式子suoshi所示,利用Target的编码进行编码。
正向: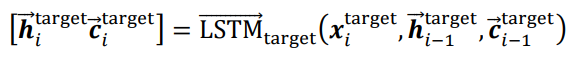
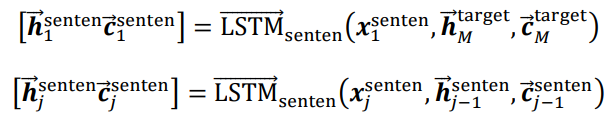
反向: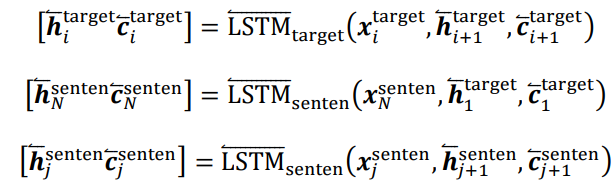
Sentence最终的编码结果: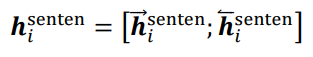
编码完成后,利用attention对Sentence中的不同单词提取权重:
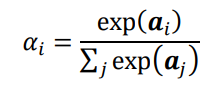
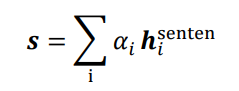
3.2.2 标签预测器

3.2.3 域判别器
对生成器的结果进行域对抗: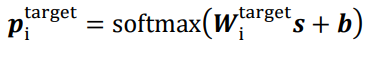
3.2.4 损失函数
域判别器: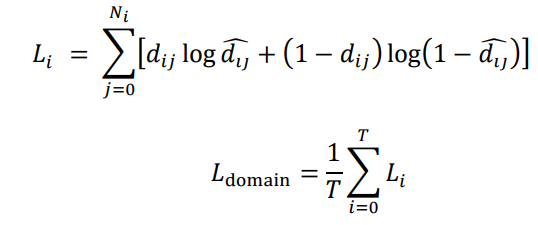
生成器、标签预测器: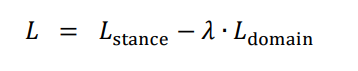
3.2.5 对照组
(1)对Target和Sentence单独编码,concatenate之后进行与对抗已经标签预测,这个模型是为了验证生成器编码(不单独编码比单独编码有效)的有效性而设置的。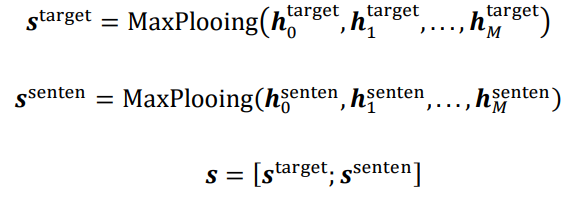
(2)对生成器的结果进行域对抗,但是在标签预测的时候,会如下面的式子所示加入未进行过域对抗的Target和Sentence的编码s,这个模型是为了验证域对抗的有效性而设置的(最后实验结果是只使用域对抗后的编码会更有效,以此验证域对抗的有效性)。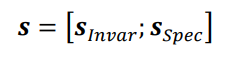
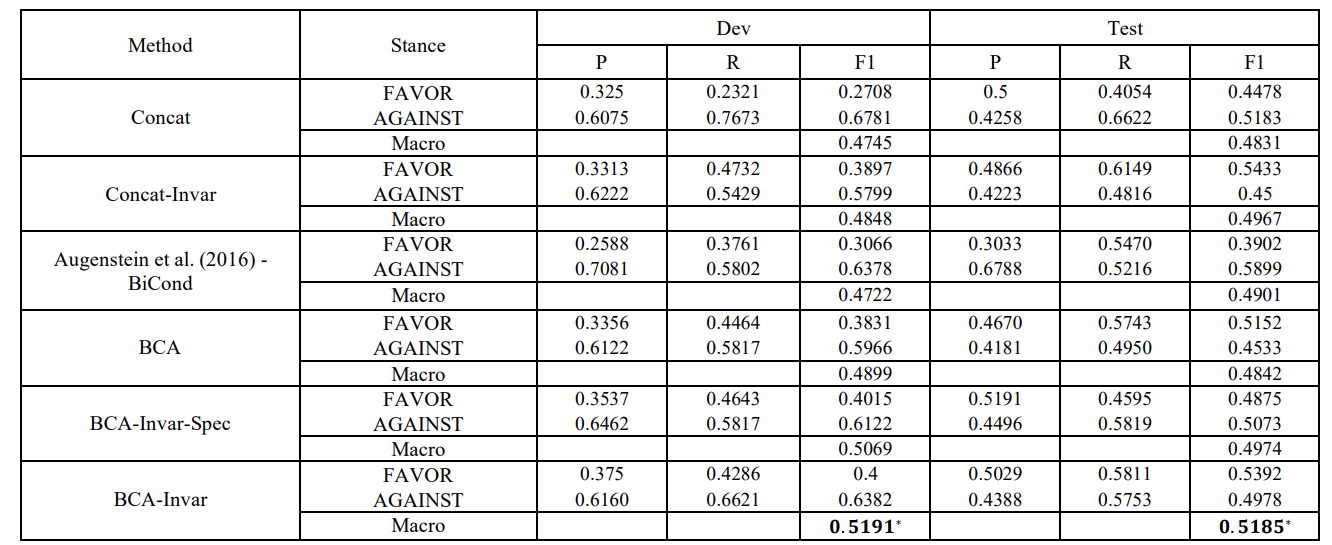
3.3 实验
实验结果表明了域对抗的有效性,使用了域对抗的模型比未使用的好,并且也比在标签预测器输入中额外添加了未经过域对抗的编码的模型好。同时也表明了在生成器中对Target和Sentence不单独编码比单独编码效果好。