- 分享主题:Transfer Learning, Domain Generalization, CV, Explicit Feature Distribution Alignment, Adversarial
- 论文标题:Multi-adversarial Discriminative Deep Domain Generalization for Face Presentation Attack Detection
- 论文链接:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/Shao_Multi-Adversarial_Discriminative_Deep_Domain_Generalization_for_Face_Presentation_Attack_Detection_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf
1.Summary
This is a paper about face anti-spoofing. Suppose there are some face image datasets. These face datasets are labeled. The label is whether it is a living face, rather than non-living faces such as printed pictures and photos on mobile phones. Now we need to transfer the knowledge from these datasets to an unknown dataset. Because the picture differences between different datasets are relatively large, transfer will become more difficult. In order to solve this problem, this paper proposes a model called MADDG. This model uses domain adversarial method to improve the transfer effect. Different from previous methods, MADDG first pretrains a model (composed of feature extractor and classifier) for each domain. Then a discriminator is set for each domain to judge whether the features of the hidden layer come from the feature extractor of the pretrained model or the feature generator in the adversarial structure, so as to learn the shared feature space of different domains. In addition to using transfer learning to optimize the model, MADDG also uses dual-force triple-mining constraint and face depth information to improve the effect of the model. In order to deepen my understanding of this paper, I can read some papers on transfer learning of multiple domains in the way of domain adversarial method.2.你对于论文的思考
这是一篇关于人脸反欺诈的文章,为了将一些带标签的数据集中的知识迁移到未知的数据集上,文中用了迁移学习的方法,并使用了域对抗的方法来实现迁移学习,与以往的域对抗方法不同,比如MMD-AAE(设置一个先验概率分布,将所有的源域拉近这个先验概率分布),本文中的模型MADDG先是为所有源域预训练了一个模型(由Feature Extractor和Classifier组成),然后为每一个源域设置了一个判别器,然后在对抗的时候,判别器就判别中间的隐藏层特征是来自预训练模型的Feature Extractor,还是来自对抗结构中的生成器Feature Generator,以此来学习不同domain的共享特征空间,在最后的 实验中,效果好于MMD-AAE。之前的域对抗方法基本只适用于领域自适应或者是只有一个源域和一个目标的普通迁移学习,而MADDG适用于多源域的领域泛化,为多源域的领域泛化提供了新的思路。3. 其他
3.1 解决的问题
本文解决的是人脸欺诈问题,如下图所示,绿框的是活体人脸,而红框的是一些打印出来的图片或者电子设备上的照片,左侧是一些已知的带标签(标签为是否是活体人脸)的数据集,现在需要利用这些数据集,把知识迁移到右边的未知的数据集上。
3.2 MADDG模型

3.2.1 Multi-adversarial Deep Domain Generalization
域对抗部分:Pretrain Multiple Source Feature Extractors
为每一个domain预训练一个模型(由Feature Extractor和Classifier组成),损失函数如下:
Multi-adversarial Deep Domain Generalization
每一个domain设置一个Discriminator,然后在对抗的时候,Discriminator就判别中间的隐藏层特征Z是来自预训练模型的Feature Extractor,还是来自对抗结构中的生成器Feature Generator,损失函数如下:
3.2.2 Dual-force Triplet-mining Constraint
每一个domain都有两类图片,活体人脸或者非活体人脸,把活体人脸看作正样本,把非活体人脸看作负样本,进而每次可以从中取出三张图片,包含两个正样本和一个负样本,可以把其中一个正样本看作是锚,这一步的目标有两个:(1)拉近同一个domain中的锚与正样本之间的距离,拉远同一个domain中的锚与负样本之间的距离;(2)拉近不同domain中的锚与正样本之间的距离,拉远不同domain中的锚与负样本之间的距离。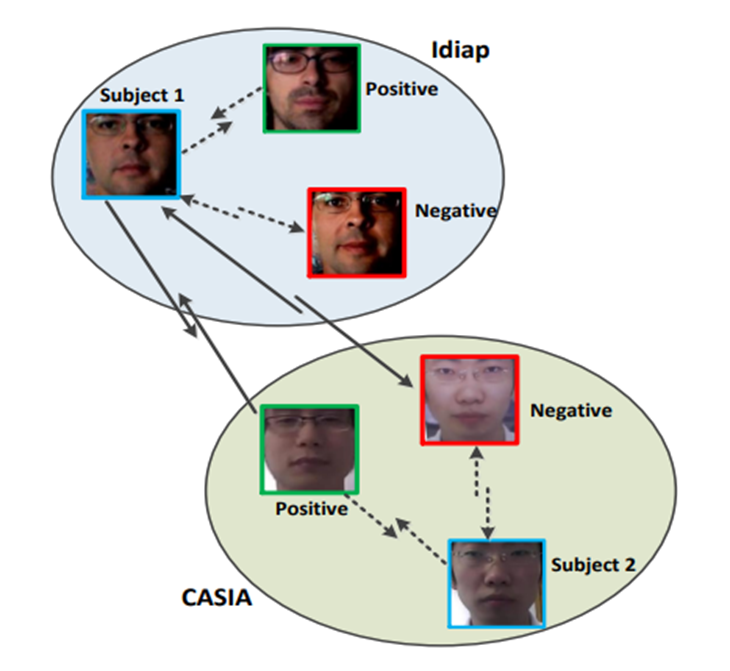
损失函数如下:
3.2.3Auxiliary Face Depth Information
这一部分是利用人脸的深度信息来进行监督学习,因为非活体人脸是打印的图片或者电子设备中的照片,因此看起来没什么立体感,也就是人脸的深度很小,在这里,把照片中各处的人脸深度都看作0,也就是没有人脸深度,而对于活体人脸利用PRNet网络来估计真实人脸的深度图,作为真实人脸的辅助监督信息。损失函数如下:
3.2.4 总体训练
总体损失函数: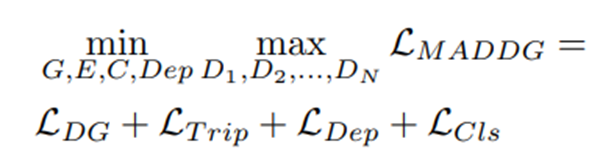
因为模型比较复杂,于是分为以下两个阶段交叉训练:
(1)训练Feature Generator、Discriminator、Feature Embedder、 Classifier,
(2)训练Feature Generator、Depth Estimator,
重复交叉训练,直到收敛。3.3 实验
数据集:人脸活体检测数据集:CASIA 、Idiap 、 MSU、Oulu
(1)对比其它活体检测方法
(2)对比domain generalization中的其它活体检测方法
(3)消融实验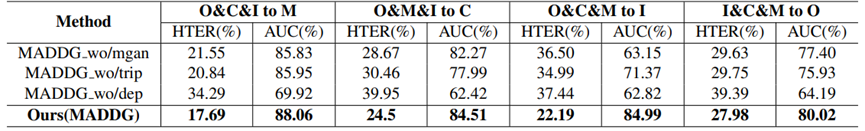
(4)减少源域的域数量
实验指标HTER(half total error rate):
HTER =
其中FAR是假人脸被判断成真人脸的比率,FRR是真人脸被判断成假人脸的比率。

