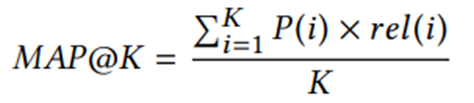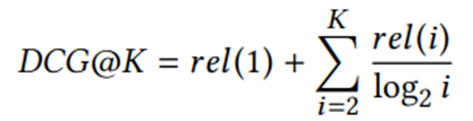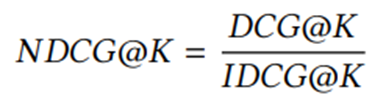- 分享主题:Transfer Learning, Domain Adaptation, Explicit Feature Distribution Alignment, Adversarial
- 论文标题:Where Will Dockless Shared Bikes be Stacked? — Parking Hotspots Detection in a New City
- 论文链接:https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3219819.3219920
1.Summary
This paper is about Parking Hotspots Detection. For some cities that have shared bicycles, the parking data of bicycles is relatively rich. According to those data, you can find the place where there are more bicycles parked at a certain time, so as to help the decision-making of bicycles scheduling. However, Some cities haven’t put on shared bikes before, so we can’t know where the parking hotspots are at a certain time. Parking hotspots are related to the features of cities. Parking hotspots in different cities may vary greatly, so it is difficult to transfer the model. In order to solve this problem, this paper proposes a model called ConvCDAN. It realizes transfer learning through adversarial method, so as to align the features of cities in source domain and target domain, that is, extract the features that can be transferred between them as much as possible. In order to deepen my understanding of this paper, I can read some papers related to transfer learning.2.你对于论文的思考
这是一篇关于停车热点检测的文章,与以往方法不同的是,这篇文章使用迁移学习的方法,利用域对抗的方式实现两个域的特征对齐,源域城市有着丰富的停车数据,而目标域城市并没有数据,如果光是把源域城市的模型拿过来给目标域城市用,那么可能效果会比较差,因为不同城市的城市特征可能差别会比较大,但是仍有一些特征是两个城市共有的,并且对最后的标签预测是有帮助的,本文提出的模型就是基于这一点进行域对抗,从而实现比较好的迁移效果。3. 其他
3.1 解决的问题
本文解决的是共享单车的停车热点检测问题,源于城市有每条道路的信息以及道路的热度(标签),而目标与城市只有每条道路的信息。虽然停车热点与具体的城市特征有关系,但是有一些特征可能是两个城市共有的,比如如下图所示,许多热点在空间上彼此接近,并且商业中心、交通枢纽和住宅区的道路更有可能成为热点,这些特点很可能是停车热点在不同城市共有的特点,因此可以利用迁移学习的方式提取这些特征,从而提升迁移效果。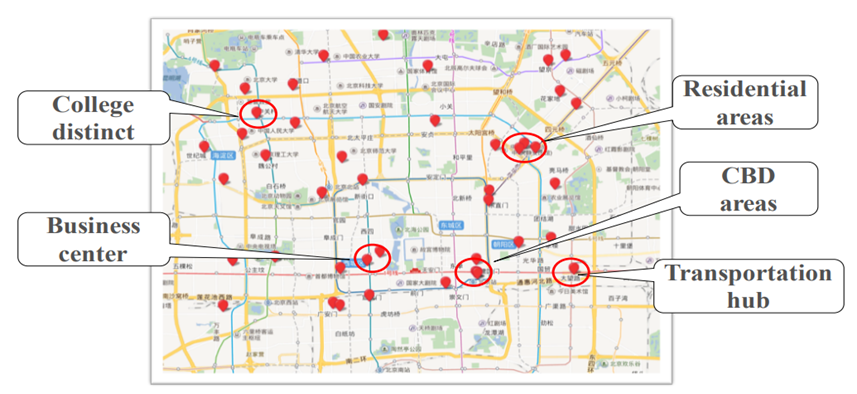
3.2 ConvCDAN模型
如下图所示,模型采用了域对抗的方式来进行特征对齐。
损失函数分为三部分:
(1)标签预测损失: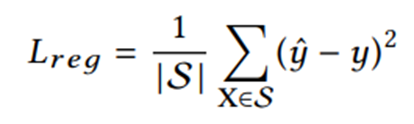
(2)域判别器损失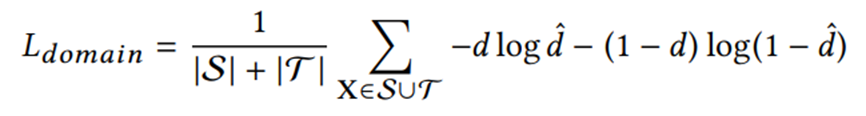
(3)排名损失(预测标签为道路热度,根据预测值排名,因为最终要得到热度最高的那几条道路,所以设计了这个损失函数,如果排名不准,便会产生损失):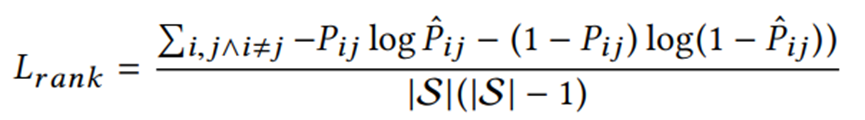
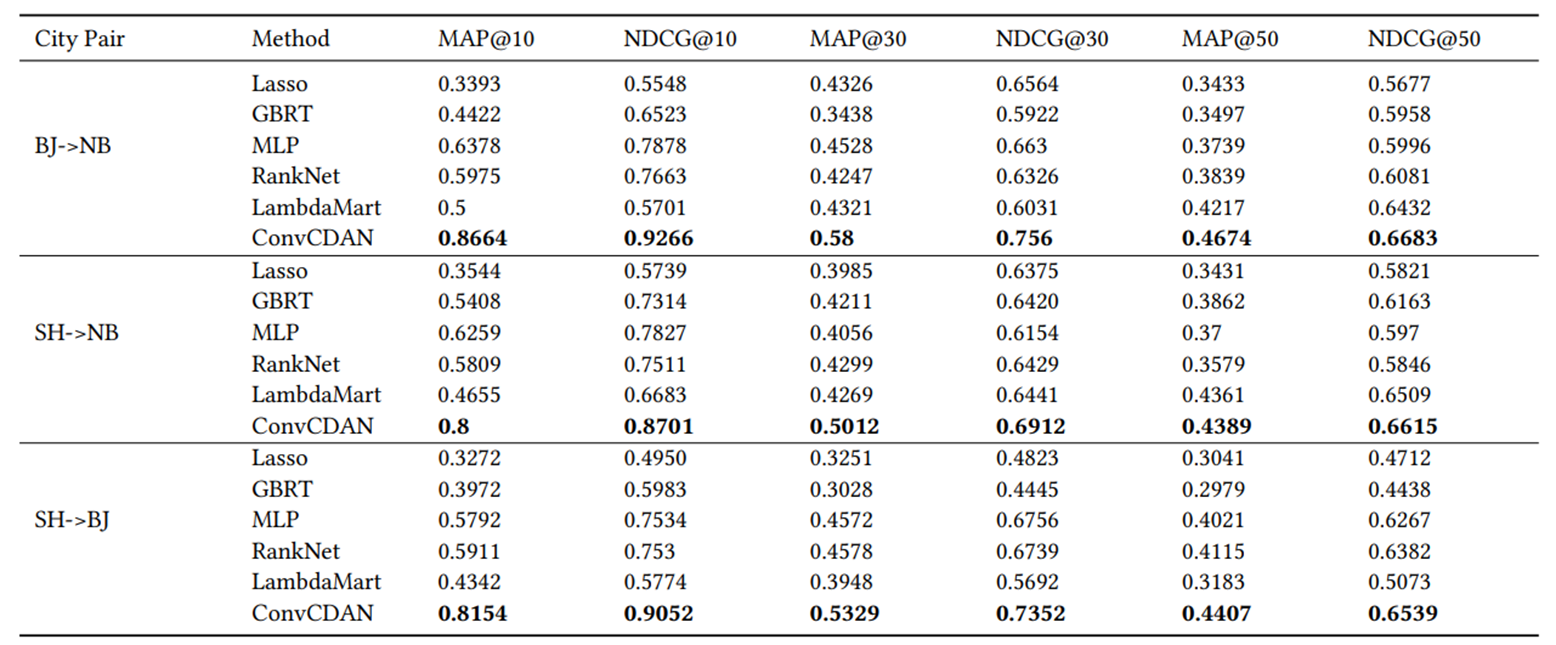
3.3 实验
数据集:上海、北京、宁波三个城市2017年7月1日到2017年7月31日的数据。