前言
进程:内存运行的程序。
线程:进程中的一个执行单元。
创建多线程的方式
本质都是调用自己写的run方法。
1继承thread抽象类
Thread thread = new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("线程创建的第一种方式:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());}};thread.start();
2实现Runnable接口
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("线程创建的第二种方式:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());}});thread2.start();
3实现Callable接口
可以有返回值,可以抛出异常
public class TestCallAble implements Callable<String> {/*** Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.** @return computed result* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result*/@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {return "123";}}# 调用Future<String> submit = executorService.submit(new TestCallAble());System.out.println(submit.get());
lambda简写
改进实现runnable接口的形式
jdk8 lambda简写:
new Thread(()->{System.out.println(123);}).start();
完整版
new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i);}}}).start();
线程池
- Executors创建线程池
阿里巴巴不推荐
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);service.submit(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("新线程执行");}});
有什么线程池?new SingleThreadExecutor:创建一个单线程的线程池new FixedThreadPool:创建固定大小的线程池new CachedThreadPool:创建一个可缓存的线程池,最大空闲时间默认为1分钟,超过就会被删除。new ScheduledThreadPool:创建一个大小无限的线程池,可以延迟、定时循环执行任务。
- 线程池启动策略
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10,20,60L,TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
线程池创建添加任务时:如果当前线程数量小于corePoolSize,则马上创建线程运行任务。如果大于等于core Pool Size,任务放入队列。如果队列满了,线程总数小于最大值,创建线程运行任务。如何,线程总数等于,则报错。
线程安全
多个线程同时对一个数据进行写操作,会出现安全问题。
同步代码块
所有线程都要使用同一把锁,比如: “”
synchronized(同步锁){# 需要同步操作的代码}# 强制处于waiting状态同步锁.waiting();# 唤醒处于waiting状态的线程来抢锁:同步锁.notify();
同步方法
对于非static方法,同步锁就是this。 对于static方法,我们使用当前方法所在类的字节码对象(类名.class)
public synchronized void method(){可能会产生线程安全问题的代码}
锁机制
同理:一定要使用同一把锁!!!
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);service.submit(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {lock.lock();System.out.println(123);lock.unlock();}});
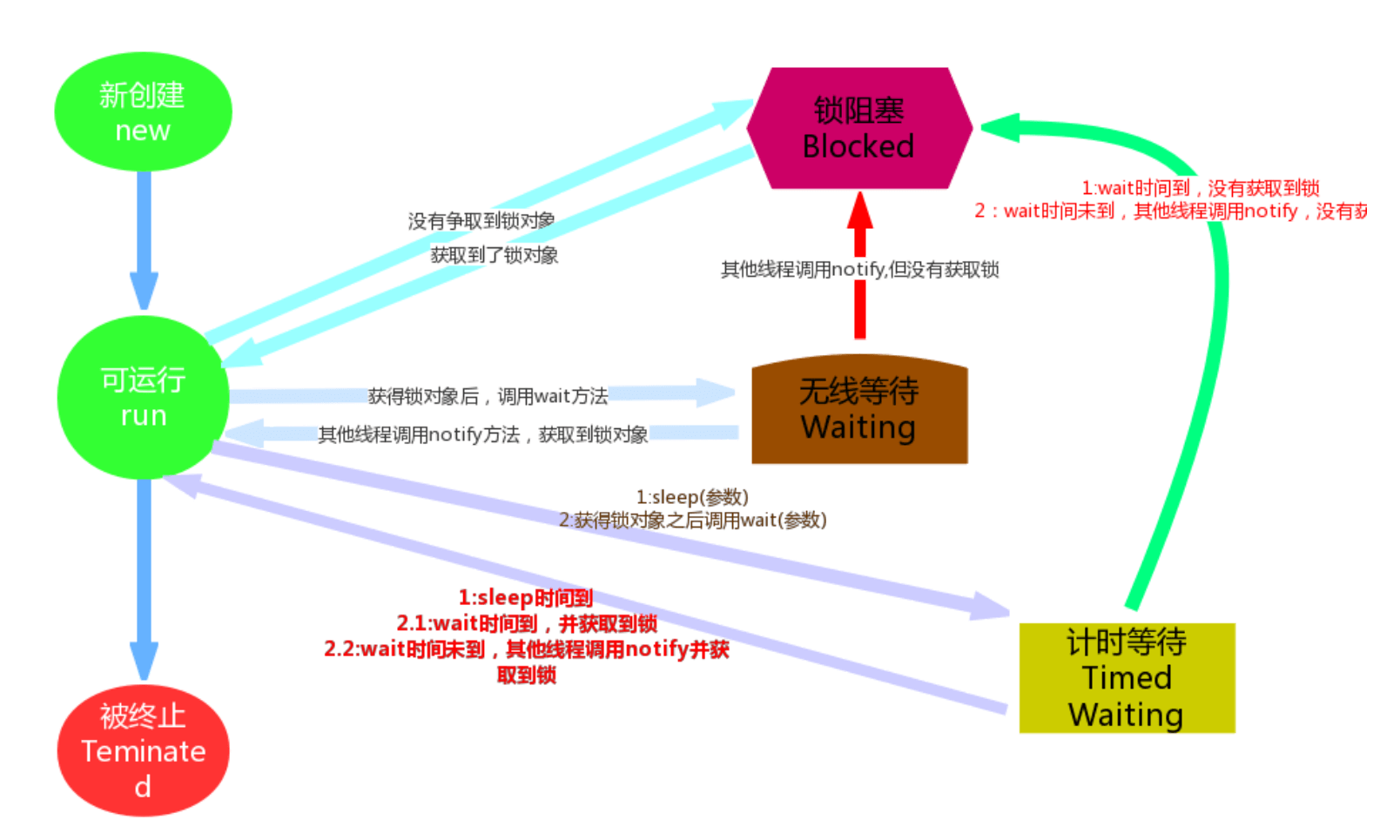
线程状态
多线程处理数据
多线程执行任务,并获取返回的结果,按照返回结果的顺序依次处理。
参考:https://my.oschina.net/hongliangsun/blog/1546370
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;import java.util.concurrent.CompletionService;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorCompletionService;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;import java.util.concurrent.Future;public class ExecutorCallableTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个线程池ExecutorService pools = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletionService<Integer> s = new ExecutorCompletionService<Integer>(pools);//创建多个有返回值的任务, 要用lambda表达式。for(int i = 0 ; i <= 10 ; i++){s.submit(()-> new Integer(id) );}for(int i = 0 ; i <= 10 ; i++){try {System.out.println(s.take().get());} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}pools.shutdown();}}任务[1]开始执行任务[4]开始执行任务[5]开始执行任务[6]开始执行任务[0]开始执行任务[2]开始执行任务[9]开始执行任务[8]开始执行任务[7]开始执行41任务[10]开始执行560298710任务[3]开始执行3
限制线程访问数
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;public class SemaphoreDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();// 最多10个线程同时访问final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(10);// 20个线程同时启动for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {final int index = i;exec.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {// 获取许可semaphore.acquire();// 调用资源callRomote(index);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {// 访问完后,释放semaphore.release();//availablePermits()指的是当前库中有多少个许可可以被使用System.out.println("availablePermits => " + semaphore.availablePermits());}}});}// 退出线程池exec.shutdown();}/*** 被调用资源** @param arg*/public static void callRomote(int arg) {System.out.println("arg: " + arg);try {Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 6000));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
CompletableFuture
参考:https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/1252599548343744/1306581182447650
jdk8新功能
回调函数
针对Future做了改进,可以传入回调对象,当异步任务完成或者发生异常时,自动调用回调对象的回调方法
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 创建异步执行任务:CompletableFuture<Double> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(Main::fetchPrice);// 如果执行成功:cf.thenAccept((result) -> {System.out.println("price: " + result);});// 如果执行异常:cf.exceptionally((e) -> {e.printStackTrace();return null;});// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:Thread.sleep(200);}static Double fetchPrice() {try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if (Math.random() < 0.3) {throw new RuntimeException("fetch price failed!");}return 5 + Math.random() * 20;}}
并行执行
功能: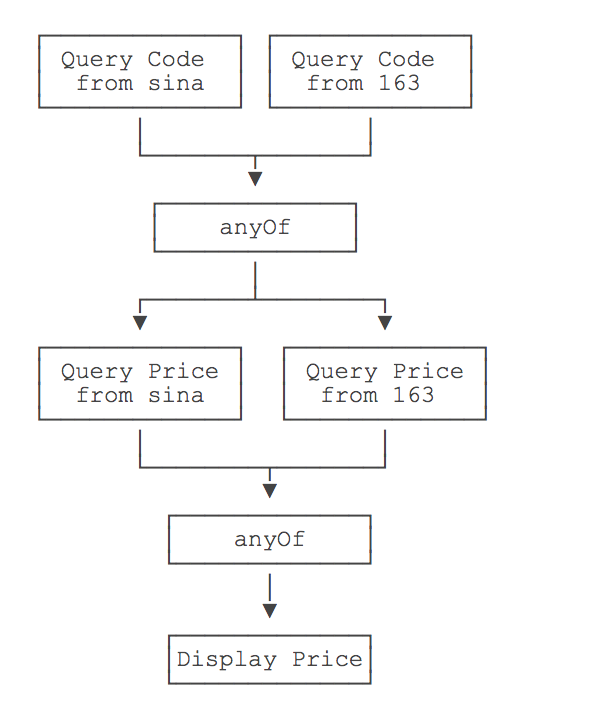
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 两个CompletableFuture执行异步查询:CompletableFuture<String> cfQueryFromSina = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return queryCode("中国石油", "https://finance.sina.com.cn/code/");});CompletableFuture<String> cfQueryFrom163 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return queryCode("中国石油", "https://money.163.com/code/");});// 用anyOf合并为一个新的CompletableFuture:CompletableFuture<Object> cfQuery = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cfQueryFromSina, cfQueryFrom163);// 两个CompletableFuture执行异步查询:CompletableFuture<Double> cfFetchFromSina = cfQuery.thenApplyAsync((code) -> {return fetchPrice((String) code, "https://finance.sina.com.cn/price/");});CompletableFuture<Double> cfFetchFrom163 = cfQuery.thenApplyAsync((code) -> {return fetchPrice((String) code, "https://money.163.com/price/");});// 用anyOf合并为一个新的CompletableFuture:CompletableFuture<Object> cfFetch = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cfFetchFromSina, cfFetchFrom163);// 最终结果:cfFetch.thenAccept((result) -> {System.out.println("price: " + result);});// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:Thread.sleep(200);}static String queryCode(String name, String url) {System.out.println("query code from " + url + "...");try {Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 100));} catch (InterruptedException e) {}return "601857";}static Double fetchPrice(String code, String url) {System.out.println("query price from " + url + "...");try {Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 100));} catch (InterruptedException e) {}return 5 + Math.random() * 20;}}
等待完成
// 开始 等待所有任务执行完成CompletableFuture<Void> all = CompletableFuture.allOf(cf1, cf2);System.out.println("start block");all.join();System.out.println("block finish, consume time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));

