自google在2018年提出的Bert后,预训练模型成为了NLP领域的马前卒,目前也有提供可直接使用的预训练Model,接下来笔者将更新一套复用性极高的基于Bert预训练模型的文本分类代码详解,分为三篇文章对整套代码详细解读,本篇将详解数据读取部分。
源码下载地址:(链接):(https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pvJmbaLU9fldm9eBjvKKcg)
提取码:2021
(一) 数据读取
代码中对数据的读取在data_loader.py文件下,接下来对每个class和function进行解读,并理清其逻辑关系。
文件内的class和function如下图所示: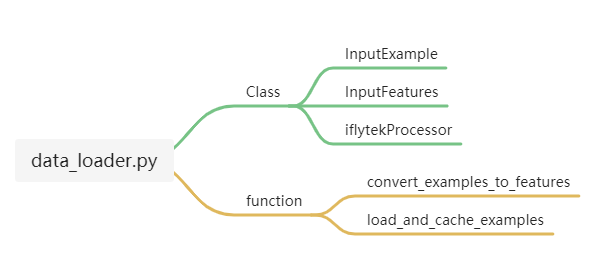
简单解释:
InputExample:样本对象,为每一个样本创建对象,可以根据任务重写内部方法。
InputFeatures:特征对象,为每一个特征创建对象,可以根据任务重写内部方法。
iflytekProcessor:处理对象,对文件数据进行处理,返回InputExample类,这个类不是固定名称的,可以根据具体的task自己修改对应的读取方法。在此处以iflytek为例将Processor命名为iflytekProcessor。
convert_examples_to_features:转换函数,将InputExample类转化为InputFeatures类,输入InputExample类返回InputFeatures类
load_and_cache_examples:缓存函数,缓存convert_examples_to_features生成的InputExample类到本地,每次训练不用都加载一边。
逻辑:![[13]高复用Bert模型文本分类代码详解 - 图2](/uploads/projects/armor-novr7@work/093f9122ac22eee8ace348a002761d3d.jpeg)
InputExample
这个类很简单,在初始化方法中定义了输入样本的几个属性:
guid: 示例的唯一id。
words: 示例句子。
label: 示例的标签。
无需进行修改,如果是做文本匹配还可以添加另一个words,如self.wordspair = wordspair,具体根据任务来。
class InputExample(object):"""A single training/test example for simple sequence classification.Args:guid: Unique id for the example.words: list. The words of the sequence.label: (Optional) string. The label of the example."""def __init__(self, guid, words, label=None, ):self.guid = guidself.words = wordsself.label = labeldef __repr__(self):return str(self.to_json_string())def to_dict(self):"""Serializes this instance to a Python dictionary."""output = copy.deepcopy(self.__dict__)return outputdef to_json_string(self):"""Serializes this instance to a JSON string."""return json.dumps(self.to_dict(), indent=2, sort_keys=True) + "\n"
InputFeatures
这个类主要描述是bert的输入形式,input_ids、attention_mask、token_type_ids在加一个label_id
如果也是使用bert模型那么无需进行修改,当然需要根据对应的预训练模型的输入方式进行修改。
class InputFeatures(object):"""A single set of features of data."""def __init__(self, input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids, label_id):self.input_ids = input_idsself.attention_mask = attention_maskself.token_type_ids = token_type_idsself.label_id = label_iddef __repr__(self):return str(self.to_json_string())def to_dict(self):"""Serializes this instance to a Python dictionary."""output = copy.deepcopy(self.__dict__)return outputdef to_json_string(self):"""Serializes this instance to a JSON string."""return json.dumps(self.to_dict(), indent=2, sort_keys=True) + "\n"
iflytekProcessor
class iflytekProcessor(object):"""Processor for the JointBERT data set """def __init__(self, args):self.args = argsself.labels = get_labels(args)self.input_text_file = 'data.csv'@classmethoddef _read_file(cls, input_file, quotechar=None):"""Reads a tab separated value file."""df = pd.read_csv(input_file)return dfdef _create_examples(self, datas, set_type):"""Creates examples for the training and dev sets."""examples = []for i, rows in datas.iterrows():try:guid = "%s-%s" % (set_type, i)# 1. input_textwords = rows["text"]# 2. intentlabel = rows["labels"]except :print(rows)examples.append(InputExample(guid=guid, words=words, label=label))return examplesdef get_examples(self, mode):"""Args:mode: train, dev, test"""data_path = os.path.join(self.args.data_dir, self.args.task, mode)logger.info("LOOKING AT {}".format(data_path))return self._create_examples(datas=self._read_file(os.path.join(data_path, self.input_text_file)),set_type=mode)
convert_examples_to_features
主要根据bert的编码方式对examples进行编码,转换为input_ids、attention_maskmax_seq_len、token_type_ids的形式,生成features
def convert_examples_to_features(examples, max_seq_len, tokenizer,cls_token_segment_id=0,pad_token_segment_id=0,sequence_a_segment_id=0,mask_padding_with_zero=True):# Setting based on the current model typecls_token = tokenizer.cls_tokensep_token = tokenizer.sep_tokenunk_token = tokenizer.unk_tokenpad_token_id = tokenizer.pad_token_idfeatures = []for (ex_index, example) in enumerate(examples):if ex_index % 5000 == 0:logger.info("Writing example %d of %d" % (ex_index, len(examples)))# Tokenize word by word (for NER)tokens = []for word in example.words:word_tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(word)if not word_tokens:word_tokens = [unk_token] # For handling the bad-encoded wordtokens.extend(word_tokens)# Account for [CLS] and [SEP]special_tokens_count = 2if len(tokens) > max_seq_len - special_tokens_count:tokens = tokens[:(max_seq_len - special_tokens_count)]# Add [SEP] tokentokens += [sep_token]token_type_ids = [sequence_a_segment_id] * len(tokens)# Add [CLS] tokentokens = [cls_token] + tokenstoken_type_ids = [cls_token_segment_id] + token_type_idsinput_ids = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)# The mask has 1 for real tokens and 0 for padding tokens. Only real# tokens are attended to.attention_mask = [1 if mask_padding_with_zero else 0] * len(input_ids)# Zero-pad up to the sequence length.padding_length = max_seq_len - len(input_ids)input_ids = input_ids + ([pad_token_id] * padding_length)attention_mask = attention_mask + ([0 if mask_padding_with_zero else 1] * padding_length)token_type_ids = token_type_ids + ([pad_token_segment_id] * padding_length)assert len(input_ids) == max_seq_len, "Error with input length {} vs {}".format(len(input_ids), max_seq_len)assert len(attention_mask) == max_seq_len, "Error with attention mask length {} vs {}".format(len(attention_mask), max_seq_len)assert len(token_type_ids) == max_seq_len, "Error with token type length {} vs {}".format(len(token_type_ids), max_seq_len)label_id = int(example.label)if ex_index < 5:logger.info("*** Example ***")logger.info("guid: %s" % example.guid)logger.info("tokens: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in tokens]))logger.info("input_ids: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in input_ids]))logger.info("attention_mask: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in attention_mask]))logger.info("token_type_ids: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in token_type_ids]))logger.info("label: %s (id = %d)" % (example.label, label_id))features.append(InputFeatures(input_ids=input_ids,attention_mask=attention_mask,token_type_ids=token_type_ids,label_id=label_id,))return features
load_and_cache_examples
加载和缓存函数,顾名思义做了读取和保存两件事
1.先根据参数生成以cached_数据集模式_数据集名称_MaxLen命名的缓存名cached_features_file
2.判断是否有当前路径下的缓存文件是否存在,若存在则直接读取保存文件,不存在则加载处理。
- 首先,使用
processors获得examples。 - 然后,通过
convert_examples_to_features获得features并保存缓存数据。
3.将features数据转换为张量并使用TensorDataset构建数据集
def load_and_cache_examples(args, tokenizer, mode):processor = processors[args.task](args)# Load data features from cache or dataset filecached_features_file = os.path.join(args.data_dir,'cached_{}_{}_{}_{}'.format(mode,args.task,list(filter(None, args.model_name_or_path.split("/"))).pop(),args.max_seq_len))print(cached_features_file)if os.path.exists(cached_features_file) and False:logger.info("Loading features from cached file %s", cached_features_file)features = torch.load(cached_features_file)else:# Load data features from dataset filelogger.info("Creating features from dataset file at %s", args.data_dir)if mode == "train":examples = processor.get_examples("train")elif mode == "dev":examples = processor.get_examples("dev")elif mode == "test":examples = processor.get_examples("test")else:raise Exception("For mode, Only train, dev, test is available")# Use cross entropy ignore index as padding label id so that only real label ids contribute to the loss laterfeatures = convert_examples_to_features(examples,args.max_seq_len,tokenizer,)logger.info("Saving features into cached file %s", cached_features_file)torch.save(features, cached_features_file)# Convert to Tensors and build datasetall_input_ids = torch.tensor([f.input_ids for f in features],dtype=torch.long)all_attention_mask = torch.tensor([f.attention_mask for f in features],dtype=torch.long)all_token_type_ids = torch.tensor([f.token_type_ids for f in features],dtype=torch.long)all_label_ids = torch.tensor([f.label_id for f in features],dtype=torch.long)dataset = TensorDataset(all_input_ids, all_attention_mask,all_token_type_ids, all_label_ids)return dataset
输出展示
![[13]高复用Bert模型文本分类代码详解 - 图3](/uploads/projects/armor-novr7@work/9e2dd30d61761c3413c8ef27e9cb907c.jpeg)
(二) 模型部分
源码
源码中模型被单独保存在model文件夹下,先来看一下module.py,里面放置有简单的全连接神经网络模型,作为分类器。
分类器的网络结构很简单,仅由两层构成。
分类器
class IntentClassifier(nn.Module): def init(self, inputdim, numlabels, dropout_rate=0.): super(IntentClassifier, self).__init() self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate) self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, num_labels)
def forward(self, x):x = self.dropout(x)return self.linear(x)
接下来看重点看bert模型代码```pythonimport torchimport torch.nn as nnfrom transformers import BertPreTrainedModel, BertModel, BertConfigfrom torchcrf import CRFfrom .module import IntentClassifierclass ClsBERT(BertPreTrainedModel):def __init__(self, config, args, label_lst):super(ClsBERT, self).__init__(config)self.args = argsself.num_labels = len(label_lst)self.bert = BertModel(config=config) # Load pretrained bertself.classifier = IntentClassifier(config.hidden_size, self.num_labels, args.dropout_rate)def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids, label_ids):outputs = self.bert(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask,token_type_ids=token_type_ids) # sequence_output, pooled_output, (hidden_states), (attentions)sequence_output = outputs[0]pooled_output = outputs[1] # [CLS]logits = self.classifier(pooled_output)outputs = ((logits),) + outputs[2:] # add hidden states and attention if they are here# 1. Intent Softmaxif label_ids is not None:if self.num_labels == 1:loss_fct = nn.MSELoss()loss = loss_fct(logits.view(-1), label_ids.view(-1))else:loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()loss = loss_fct(logits.view(-1, self.num_labels), label_ids.view(-1))outputs = (loss,) + outputsreturn outputs # (loss), logits, (hidden_states), (attentions)
重点在forward部分
outputs = self.bert(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask,token_type_ids=token_type_ids) # sequence_output, pooled_output, (hidden_states), (attentions)sequence_output = outputs[0] # sequence_output = outputs.last_hidden_statepooled_output = outputs[1] # [CLS] / pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output
一般使用transformers做bert finetune时,bert(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask,token_type_ids=token_type_ids)会返回两个值,一个是sequence_output,其shape大小为(batch_size,bert_hidden_size),另一个是pooled_output,这里的pooler_output指的是输出序列最后一个隐层,即CLS标签,其shape大小为(batch_size,bert_hidden_size)
- 可以通过
outputs[0]或者outputs.last_hidden_state取得sequence_output向量。 - 可以通过
outputs[1]或者outputs.pooler_output取得pooled_output向量。
一般对于分类任务取bert的最后层输出做平均池化接入线性层,代码中可以直接用outputs.pooler_output作为linear的输入,也可以使用outputs.last_hidden_state.mean(dim=1)作为linear的输入,自己测试后者要更好一点。
改进bert输出
我们知道bert模型有12层transformer层组成,如果我们要取出其中某一层的向量,或者做向量拼接该如何做呢?
我们查看BertModel(BertPreTrainedModel)的官方文档,里面对返回值outputs的解释如下:
Outputs: Tuple comprising various elements depending on the configuration (config) and inputs:
last_hidden_state: torch.FloatTensor of shape (batchsize, sequence_length, hidden_size)
Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.
pooler_output: torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, hidden_size)
Last layer hidden-state of the first token of the sequence (classification token)further processed by a Linear layer and a Tanh activation function. The Linear layer weights are trained from the next sentence prediction (classification)
objective during Bert pretraining. This output is usually _not a good summary of the semantic content of the input, you’re often better with averaging or pooling the sequence of hidden-states for the whole input sequence.
hidden_states: (optional, returned when config.output_hidden_states=True),list of torch.FloatTensor (one for the output of each layer + the output of the embeddings)of shape (batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size):
Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
attentions: (optional, returned when config.output_attentions=True),list of torch.FloatTensor (one for each layer) of shape (batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length):Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
根据官方文档我们可以看到有一个**hidden_states**层会返回所有layer的向量,其形状为(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size),但要输出这个list需要在初始化bert时配置config.output_hidden_states=True,才会返回**hidden_states**
我们重新修改一下代码,尝试取出bert的倒数第三层transformer的输出向量
class ClsBERT(BertPreTrainedModel):def __init__(self, config, args, label_lst):super(ClsBERT, self).__init__(config)self.args = argsself.num_labels = len(label_lst)self.bert = BertModel(config=config) # Load pretrained bertself.classifier = IntentClassifier(config.hidden_size, self.num_labels, args.dropout_rate)def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids, label_ids):"""添加 output_hidden_states = True"""outputs = self.bert(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask,token_type_ids=token_type_ids,output_hidden_states = True)"""修改pooled_outputshidden_states[-3] 表示倒数第三层输出mean(dim=1) 表示 平均池化输出向量 得到(batch_size,hidden_layers)"""pooled_output = outputs.hidden_states[-3].mean(dim=1)logits = self.classifier(pooled_output)outputs = ((logits),) + outputs[2:] # add hidden states and attention if they are here# 1. Intent Softmaxif label_ids is not None:if self.num_labels == 1:loss_fct = nn.MSELoss()loss = loss_fct(logits.view(-1), label_ids.view(-1))else:loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()loss = loss_fct(logits.view(-1, self.num_labels), label_ids.view(-1))outputs = (loss,) + outputsreturn outputs # (loss), logits, (hidden_states), (attentions)
既然可以取出每一层的向量,那么我们也可以完成不同层向量拼接,修改代码如下:
先创建一个空的tensor :torch.empty(0, dtype=torch.long).to(self.device)
使用循环和cat拼接向量
记得修改对应的linear的输入层数大小,要和pooled_output的hidden_size一致
class ClsBERT(BertPreTrainedModel):def __init__(self, config, args, label_lst):super(ClsBERT, self).__init__(config)self.args = argsself.num_labels = len(label_lst)self.bert = BertModel(config=config) # Load pretrained bertself.classifier = IntentClassifier(config.hidden_size, self.num_labels, args.dropout_rate)def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids, label_ids):"""添加 output_hidden_states = True"""outputs = self.bert(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask,token_type_ids=token_type_ids,output_hidden_states = True)"""修改pooled_outputstorch.empty(0, dtype=torch.long).to(self.device)hidden_states[-3] 表示倒数第三层输出mean(dim=1) 表示 平均池化输出向量 得到(batch_size,hidden_layers)"""pooled_output = torch.empty(0, dtype=torch.long).to(self.device)for layer in outputs.hidden_states[self.concatnum:]:pooled_output = torch.cat((pooled_output, layer.mean(dim=1)), dim=1)"""修改 end"""logits = self.classifier(pooled_output)outputs = ((logits),) + outputs[2:] # add hidden states and attention if they are here# 1. Intent Softmaxif label_ids is not None:if self.num_labels == 1:loss_fct = nn.MSELoss()loss = loss_fct(logits.view(-1), label_ids.view(-1))else:loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()loss = loss_fct(logits.view(-1, self.num_labels), label_ids.view(-1))outputs = (loss,) + outputsreturn outputs # (loss), logits, (hidden_states), (attentions)
到此为止,模型代码的讲解已经结束,并且我们还对bert模型的输出形式进行了讨论和改进
关于优化器、学习率、损失函数,将在下一篇文章模型训练代码中进行讲解。
(三) 训练
![[13]高复用Bert模型文本分类代码详解 - 图4](/uploads/projects/armor-novr7@work/6d1b6cfae7ea52bc109a91ec185871e3.jpeg)
import osimport loggingimport randomimport numpy as npimport torchimport pandas as pdfrom tqdm import tqdm, trangefrom torch.utils.data import DataLoader, RandomSampler, SequentialSamplerfrom transformers import BertConfig, AdamW, get_linear_schedule_with_warmupfrom adversarial_training import FGM,PGDfrom utils import MODEL_CLASSES, compute_metrics, get_labelslogger = logging.getLogger(__name__)class Trainer(object):def __init__(self, args, train_dataset=None, dev_dataset=None, test_dataset=None):self.args = argsself.train_dataset = train_datasetself.dev_dataset = dev_datasetself.test_dataset = test_datasetself.test_results = Noneself.label_lst = get_labels(args)# Use cross entropy ignore index as padding label id so that only real label ids contribute to the loss laterself.config_class, self.model_class, _ = MODEL_CLASSES[args.model_type]self.config = self.config_class.from_pretrained(args.model_name_or_path, finetuning_task=args.task)self.model = self.model_class.from_pretrained(args.model_name_or_path,config=self.config,args=args,label_lst=self.label_lst,)# GPU or CPUself.device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() and not args.no_cuda else "cpu"self.model.to(self.device)# for adversarial trainingself.adv_trainer = Noneif self.args.at_method:if self.args.at_method == "fgm":self.adv_trainer = FGM(self.model, epsilon=self.args.epsilon_for_at)elif self.args.at_method == "pgd":self.adv_trainer = PGD(self.model,epsilon=self.args.epsilon_for_at,alpha=self.args.alpha_for_at,)else:raise ValueError("un-supported adversarial training method: {} !!!".format(self.args.at_method))def train(self):train_sampler = RandomSampler(self.train_dataset)train_dataloader = DataLoader(self.train_dataset, sampler=train_sampler, batch_size=self.args.train_batch_size)if self.args.max_steps > 0:t_total = self.args.max_stepsself.args.num_train_epochs = self.args.max_steps // (len(train_dataloader) // self.args.gradient_accumulation_steps) + 1else:t_total = len(train_dataloader) // self.args.gradient_accumulation_steps * self.args.num_train_epochsfor n, p in self.model.named_parameters():print(n)# BERT部分参数,设置一个较低的学习率optimizer_grouped_parameters = []bert_params = list(self.model.bert.named_parameters())# Prepare optimizer and schedule (linear warmup and decay)no_decay = ['bias', 'LayerNorm.weight']optimizer_grouped_parameters += [{'params': [p for n, p in bert_params if not any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],'weight_decay': self.args.weight_decay,"lr": self.args.learning_rate,},{'params': [p for n, p in bert_params if any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],'weight_decay': 0.0,'lr': self.args.learning_rate,}]# 线性层参数linear_params = list(self.model.classifier.named_parameters())no_decay = ['bias', 'LayerNorm.weight']optimizer_grouped_parameters += [{'params': [p for n, p in linear_params if not any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],'weight_decay': self.args.weight_decay,"lr": self.args.linear_learning_rate,},{'params': [p for n, p in linear_params if any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],'weight_decay': 0.0,'lr': self.args.linear_learning_rate,}]optimizer = AdamW(optimizer_grouped_parameters, lr=self.args.learning_rate, eps=self.args.adam_epsilon)scheduler = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer, num_warmup_steps=self.args.warmup_steps, num_training_steps=t_total)# Train!logger.info("***** Running training *****")logger.info(" Num examples = %d", len(self.train_dataset))logger.info(" Num Epochs = %d", self.args.num_train_epochs)logger.info(" Total train batch size = %d", self.args.train_batch_size)logger.info(" Gradient Accumulation steps = %d", self.args.gradient_accumulation_steps)logger.info(" Total optimization steps = %d", t_total)logger.info(" Logging steps = %d", self.args.logging_steps)logger.info(" Save steps = %d", self.args.save_steps)wait = 0global_step = 0tr_loss = 0.0best_score = 0.0self.model.zero_grad()train_iterator = trange(int(self.args.num_train_epochs), desc="Epoch")for _ in train_iterator:epoch_iterator = tqdm(train_dataloader, desc="Iteration")for step, batch in enumerate(epoch_iterator):self.model.train()batch = tuple(t.to(self.device) for t in batch) # GPU or CPUinputs = {'input_ids': batch[0],'attention_mask': batch[1],'label_ids': batch[3],}if self.args.model_type != 'distilbert':inputs['token_type_ids'] = batch[2]outputs = self.model(**inputs)loss = outputs[0]if self.args.gradient_accumulation_steps > 1:loss = loss / self.args.gradient_accumulation_stepsloss.backward()"""# ad training start"""if self.args.at_method is not None:if random.uniform(0, 1) > self.args.probs_for_at:logger.info("not to do adv training at this step!")else:logger.info(" do adv training at this step!")if self.args.at_method == "fgm":self.adv_trainer.attack() # 这个时候embedding被修改了# optimizer.zero_grad() # 如果不想累加梯度,就把这里的注释取消outputs_at = self.model(**inputs)loss_at = outputs_at[0]loss_at.backward() # 反向传播,在正常的grad基础上,累加对抗训练的梯度self.adv_trainer.restore() # 恢复Embedding的参数elif self.args.at_method == "pgd":self.adv_trainer.backup_grad() # 保存正常的grad# 对抗训练for t in range(self.args.steps_for_at):# 在embedding上添加对抗扰动, first attack时备份param.dataself.adv_trainer.attack(is_first_attack=(t == 0))if t != self.args.steps_for_at - 1:optimizer.zero_grad()else:self.adv_trainer.restore_grad() # 恢复正常的gradoutputs_at = self.model(**inputs)loss_at = outputs_at[0]loss_at.backward() # 反向传播,并在正常的grad基础上,累加对抗训练的梯度self.adv_trainer.restore() # 恢复embedding参数"""# ad training end"""tr_loss += loss.item()if (step + 1) % self.args.gradient_accumulation_steps == 0:torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.model.parameters(), self.args.max_grad_norm)optimizer.step()scheduler.step() # Update learning rate scheduleself.model.zero_grad()global_step += 1if self.args.logging_steps > 0 and global_step % self.args.logging_steps == 0:results = self.evaluate("dev")if best_score < results["kappa"]:wait = 0best_score = results["kappa"]self.save_model()else:wait += 1print("eraly stop {}/{}".format(wait,self.args.wait_patient))if wait >= self.args.wait_patient:break# if self.args.save_steps > 0 and global_step % self.args.save_steps == 0:# self.save_model()if 0 < self.args.max_steps < global_step:epoch_iterator.close()breakif 0 < self.args.max_steps < global_step:train_iterator.close()breakreturn global_step, tr_loss / global_stepdef evaluate(self, mode):if mode == 'test':dataset = self.test_datasetelif mode == 'dev':dataset = self.dev_datasetelse:raise Exception("Only dev and test dataset available")eval_sampler = SequentialSampler(dataset)eval_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, sampler=eval_sampler, batch_size=self.args.eval_batch_size)# Eval!logger.info("***** Running evaluation on %s dataset *****", mode)logger.info(" Num examples = %d", len(dataset))logger.info(" Batch size = %d", self.args.eval_batch_size)eval_loss = 0.0nb_eval_steps = 0preds = Noneout_label_ids = Noneself.model.eval()for batch in tqdm(eval_dataloader, desc="Evaluating"):batch = tuple(t.to(self.device) for t in batch)with torch.no_grad():inputs = {'input_ids': batch[0],'attention_mask': batch[1],'label_ids': batch[3],}if self.args.model_type != 'distilbert':inputs['token_type_ids'] = batch[2]outputs = self.model(**inputs)tmp_eval_loss, logits = outputs[:2]eval_loss += tmp_eval_loss.mean().item()nb_eval_steps += 1# Intent predictionif preds is None:preds = logits.detach().cpu().numpy()out_label_ids = inputs['label_ids'].detach().cpu().numpy()else:preds = np.append(preds, logits.detach().cpu().numpy(), axis=0)out_label_ids = np.append(out_label_ids, inputs['label_ids'].detach().cpu().numpy(), axis=0)eval_loss = eval_loss / nb_eval_stepsresults = {"loss": round(eval_loss,7)}# Intent resultpreds = np.argmax(preds, axis=1)total_result = compute_metrics(preds, out_label_ids)results.update(total_result)if mode == 'test':self.test_results = resultsself.save_results()logger.info("***** Eval results *****")for key in sorted(results.keys()):logger.info(" %s = %s", key, str(results[key]))return resultsdef save_model(self):# Save model checkpoint (Overwrite)if not os.path.exists(self.args.model_dir):os.makedirs(self.args.model_dir)model_to_save = self.model.module if hasattr(self.model, 'module') else self.modelmodel_to_save.save_pretrained(self.args.model_dir)# Save training arguments together with the trained modeltorch.save(self.args, os.path.join(self.args.model_dir, 'training_args.bin'))logger.info("Saving model checkpoint to %s", self.args.model_dir)def load_model(self):# Check whether model existsif not os.path.exists(self.args.model_dir):raise Exception("Model doesn't exists! Train first!")try:self.model = self.model_class.from_pretrained(self.args.model_dir,args=self.args,label_lst=self.label_lst,)self.model.to(self.device)logger.info("***** Model Loaded *****")except:raise Exception("Some model files might be missing...")def save_results(self):if not os.path.exists(self.args.results_dir):os.makedirs(self.args.results_dir)var = [self.args.task, self.args.learning_rate, self.args.num_train_epochs, self.args.max_seq_len, self.args.seed]names = ['task', 'lr', 'epoch', 'max_len', 'seed']vars_dict = {k: v for k, v in zip(names, var)}results = dict(self.test_results, **vars_dict)keys = list(results.keys())values = list(results.values())file_name = 'results.csv'results_path = os.path.join(self.args.results_dir, file_name)if not os.path.exists(results_path):ori = []ori.append(values)df1 = pd.DataFrame(ori, columns=keys)df1.to_csv(results_path, index=False)else:df1 = pd.read_csv(results_path)new = pd.DataFrame(results, index=[1])df1 = df1.append(new, ignore_index=True)df1.to_csv(results_path, index=False)data_diagram = pd.read_csv(results_path)print('test_results', data_diagram)

