先讲原理,因为你不懂原理的话,很难去使用好git,原理很简单,git本质上就是个文件夹。
Git是什么
分布式文件版本控制系统(VCS)
解析:
- 分布式:同一套软件,可以部署到不同的电脑,不同电脑之间可以文件交互
- 文件版本控制系统:
- 版本就是某时间点的文件快照,快照就是文件某时间点的拷贝(类似相机瞬间拍照)
- 版本控制系统,就是管理一堆文件快照的系统
Git的本质是什么
根本上来讲 Git 是一个内容寻址(content-addressable)文件系统,并在此之上提供了一个版本控制系统的用户界面。
解析:
- 内容寻址文件系统:本质是一个文件夹(文件管理系统),内容寻址就是给每个文件生成一个“指纹”,通过指纹管理文件。Git 的核心部分是一个简单的键值对数据库(key-value data store)。 你可以向 Git 仓库中插入任意类型的内容,它会返回一个唯一的键,通过该键可以在任意时刻再次取回该内容。
- 文件指纹:哈希函数根据文件内容生成固定的哈希码值,Git使用的是SHA-1算法根据文件内容和一个头描述信息生成哈希码(长度40位:前两个字符用于命名子目录,余下的 38 个字符则用作文件名)。
- 可以看出,linus大神当年就是使用linux的文件系统改了一个VCS,用来管理linux的代码,取名为Git,机智。
- 用户界面:提供了一堆命令行,操作linux的文件管理命令或原语
Git解决问题的模型是什么
git解决了什么样的问题?
文件版本控制的问题,简单说就是记录代码文件修改过程。
为了解决这个问题,git定义了什么样模型?
四个区,五个状态
- 工作区 working
- 暂存区 stage
- 本地仓库 local repository
- 远程仓库 remote repository
被追踪的文件,在未进入和进入上述四个区之后分别有一个状态,所以一共有五个状态:
- 未修改 origin
- 已修改 modified
- 已暂存 staged
- 已提交 committed
- 已推送 pushed
解释:
- 三个概念:工作区,暂存区, 本地仓库
- 工作区就是你的工作目录,存放你的代码文件
- 暂存区用来临时保存你修改的文件
- 本地仓库保存你文件的所有修改记录和变动(用快照的形式)
- 远程仓库和本地仓库结构一样,同一套软件部署在不同机器而已
- 多个文件修改后,记为一次“提交”
- 多个“提交”形成一个“分支”,分支存在一个提交过程,表现为“分支线”
- 为了方便,某一次的提交可以简记为“标签”
评价:git提供的“分支”和“标签”极大的方便了代码开发,程序员可以灵活运用,达到各种管理代码文件的目的,其中对于分支的使用,还产生了很多种“工作流程 git flow”,其中以github和gitlab的两种流程最为著名。
该模型是linus当年给出的问题解决方案,一直延续到当下,还是很厉害的!
一图胜千言
git模型:
为了方便管理commit,git又引入了两种特殊的commit的引用,barch和tag,对于分支和标签以下特殊说明:
git模型对应的实现方式(本质):
git本质就是文件夹,内容寻址文件系统+一个版本控制控制界面

适当增加说明后:
git对文件有个颜色标识,看起来更方便:
以上所有图片是我自己画的:)
图片地址:https://www.processon.com/view/link/5f6ae4f31e0853769822efc5**
分支 branch
分支分为本地分支和远端分支
- 查看本地所有分支:
git branch - 查看远程所有分支:
git branch -r - 查看所有分支:
git branch -a - 创建分支:
git branch <branch name> - 删除分支:
git branch -d <branch name> - 修改分支名:
git branch -m old new - 切换分支:
git checkout <branch name> - 创建新分支并切换到新分支:
git checkout -b <branch name>该命令是以下两条命令的简写git branch <branch name>git checkout <branch name> - 合并分支:
git merge <branch name>这样会把某分支合并到当前分支 - 合并分支时如果有冲突,使用图形界面工具处理合并:
git mergetool - 推送分支
git push --set-upstream <remote> <branch> - 推送本地所有分支:以下三种方式均可
git push --all origingit push REMOTE --allgit push REMOTE '*:*'
- 拉取全部远程仓库分支:
- 同步所有远程分支:git branch -r | grep -v ‘->’ | while read remote; do git branch —track “${remote#origin/}” “$remote”; done
- 抓取取所有分支变动:
git fetch --all - 拉取所有分支并合并:
git pull --all
- 远程分支
- 查看所有远程分支:
git branch -r - 删除远程分支:
git push origin --delete <remote name>
- 查看所有远程分支:
git branch 帮助文档
git branch -husage: git branch [<options>] [-r | -a] [--merged | --no-merged]or: git branch [<options>] [-l] [-f] <branch-name> [<start-point>]or: git branch [<options>] [-r] (-d | -D) <branch-name>...or: git branch [<options>] (-m | -M) [<old-branch>] <new-branch>or: git branch [<options>] (-c | -C) [<old-branch>] <new-branch>or: git branch [<options>] [-r | -a] [--points-at]or: git branch [<options>] [-r | -a] [--format]Generic options-v, --verbose show hash and subject, give twice for upstream branch-q, --quiet suppress informational messages-t, --track set up tracking mode (see git-pull(1))-u, --set-upstream-to <upstream>change the upstream info--unset-upstream unset the upstream info--color[=<when>] use colored output-r, --remotes act on remote-tracking branches--contains <commit> print only branches that contain the commit--no-contains <commit>print only branches that don't contain the commit--abbrev[=<n>] use <n> digits to display SHA-1sSpecific git-branch actions:-a, --all list both remote-tracking and local branches-d, --delete delete fully merged branch-D delete branch (even if not merged)-m, --move move/rename a branch and its reflog-M move/rename a branch, even if target exists-c, --copy copy a branch and its reflog-C copy a branch, even if target exists-l, --list list branch names--show-current show current branch name--create-reflog create the branch's reflog--edit-description edit the description for the branch-f, --force force creation, move/rename, deletion--merged <commit> print only branches that are merged--no-merged <commit> print only branches that are not merged--column[=<style>] list branches in columns--sort <key> field name to sort on--points-at <object> print only branches of the object-i, --ignore-case sorting and filtering are case insensitive--format <format> format to use for the output
标签 tag
Git 支持两种标签:轻量标签(lightweight)与附注标签(annotated)
- 轻量标签很像一个不会改变的分支——它只是某个特定提交的引用
附注标签是存储在 Git 数据库中的一个完整对象, 它们是可以被校验的,其中包含打标签者的名字、电子邮件地址、日期时间, 此外还有一个标签信息,并且可以使用 GNU Privacy Guard (GPG)签名并验证。 通常会建议创建附注标签,这样你可以拥有以上所有信息。但是如果你只是想用一个临时的标签, 或者因为某些原因不想要保存这些信息,那么也可以用轻量标签。
列出标签:
git tag这个命令以字母顺序列出标签,但是它们显示的顺序并不重要。- 模糊查询某些标签:
git tag -l "v1.8.5*" - 创建附注标签:
git tag -a <tag name> -m "comment" - 创建轻量标签:
git tag <tag name> - 给以前的提交记录打标签:
git tag -a <tag name> <校验和或部分校验和> 示例:git tag -a v1.2 9fceb02 - 推送标签用以共享:git push origin
- 推送所有标签:
git push origin --tags - 删除标签:git tag -d
- 检出标签并根据这个标签创建一个新的分支:
git checkout -b <分支名> <标签名>
git tag 帮助文档
git tag -husage: git tag [-a | -s | -u <key-id>] [-f] [-m <msg> | -F <file>]<tagname> [<head>]or: git tag -d <tagname>...or: git tag -l [-n[<num>]] [--contains <commit>] [--no-contains <commit>] [--points-at <object>][--format=<format>] [--[no-]merged [<commit>]] [<pattern>...]or: git tag -v [--format=<format>] <tagname>...-l, --list list tag names-n[<n>] print <n> lines of each tag message-d, --delete delete tags-v, --verify verify tagsTag creation options-a, --annotate annotated tag, needs a message-m, --message <message>tag message-F, --file <file> read message from file-e, --edit force edit of tag message-s, --sign annotated and GPG-signed tag--cleanup <mode> how to strip spaces and #comments from message-u, --local-user <key-id>use another key to sign the tag-f, --force replace the tag if exists--create-reflog create a reflogTag listing options--column[=<style>] show tag list in columns--contains <commit> print only tags that contain the commit--no-contains <commit>print only tags that don't contain the commit--merged <commit> print only tags that are merged--no-merged <commit> print only tags that are not merged--sort <key> field name to sort on--points-at <object> print only tags of the object--format <format> format to use for the output--color[=<when>] respect format colors-i, --ignore-case sorting and filtering are case insensitive
Git怎么做的
一个Git仓库就是一个.git文件夹,如果你想备份或复制一个git仓库,拷贝这个.git文件夹就行了。
git init命令产生的.git文件夹内容如下:
configdescriptionHEADhooks/info/objects/refs/
description文件仅供 GitWeb 程序使用,我们无需关心。config文件包含项目特有的配置选项。info目录包含一个全局性排除(global exclude)文件, 用以放置那些不希望被记录在.gitignore文件中的忽略模式(ignored patterns)。hooks目录包含客户端或服务端的钩子脚本(hook scripts)。HEAD文件、(尚待创建的)index文件,和objects目录、refs目录。 它们都是 Git 的核心组成部分。objects目录存储所有数据内容;refs目录存储指向数据(分支、远程仓库和标签等)的提交对象的指针;HEAD文件指向目前被检出的分支;index文件保存暂存区信息。用objects文件夹构造键值数据库
我们说git本质是一个键值数据库,其实本质就是.git/objects文件夹,git通过SHA-1算法,把文件内容和头描述信息生成一个40位的校验和,前两位字母做文件夹名称,后38位做文件名。
故所有的文件都存在objects文件夹下,本质使用了操作系统的文件存储系统加SHA-1算法构造了一个键值数据库,绝妙的设计!
前两位字母做文件夹,两层目录结构便可以保存足够大量的文件。
但这个设计,没法保存原文件名和文件目录结构,linus用了这么一个办法,使用一个tree树结构文本表示文件目录和文件名,当然对于tree这种数据结构,只需要表示出一个叶子节点即可,一个节点就是一段文本,使用SHA-1算法也生成一个指纹,用作该节点的引用,这样子节点就可以用这个引用来表示了。
举个例子:
100644 blob a906cb2a4a904a152e80877d4088654daad0c859 README100644 blob 8f94139338f9404f26296befa88755fc2598c289 Rakefile040000 tree 99f1a6d12cb4b6f19c8655fca46c3ecf317074e0 lib
请注意,lib 子目录(所对应的那条树对象记录)并不是一个数据对象,而是一个指针,其指向的是另一个树对象:
100644 blob 47c6340d6459e05787f644c2447d2595f5d3a54b simplegit.rb
如下图: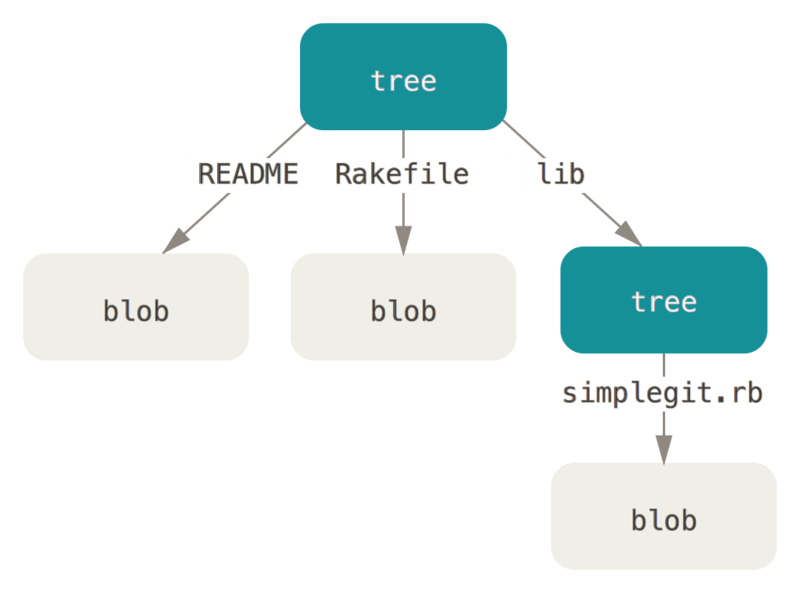
这样一个键值数据库就完成了,最主要的就是两种类型的文件,一是文件对象本身blob类型,另一种是目录结构和文件名的文本对象tree类型。从此可以看出linus对数据结构和文件系统使用能力,炉火纯青!
branch\tag\commit本质上都是ref
git把所有文件都保存为到objects文件夹,那么git的分支、提交、标签等数据又是怎么保存的呢?
分支,标签,提交 本质上都是 一个引用。
引用的本质就是那个40位长度的SHA-1校验和。
git的引用类型:
- 数据对象引用
- 树对象引用
- 提交对象 引用
- 标签对象引用
- 远程对象引用
.git 目录里有一个HEAD文件,用文本编辑器打开示例如下:
ref: refs/heads/master
HEAD文件保存的当前的分支,默认是master,而分支数据保存在.git/refs文件夹
refs文件里每个文件就是一个分支,如下:
\.git\refs 目录headsremotestags
每个文件里存着一个引用(40位的校验码),该引用最后提交的引用。
- Git 分支的本质:一个指向某一系列提交之首的引用
- 标签对象(tag object) 非常类似于一个提交对象——它包含一个标签创建者信息、一个日期、一段注释信息,以及一个指针。 主要的区别在于,标签对象通常指向一个提交对象,而不是一个树对象。 它像是一个永不移动的分支引用——永远指向同一个提交对象,只不过给这个提交对象加上一个更友好的名字罢了。

