题目
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 get 和 写入数据 put 。
获取数据 get(key) - 如果密钥 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取密钥的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。
写入数据 put(key, value) - 如果密钥不存在,则写入其数据值。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最近最少使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶:
你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
示例:
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* 缓存容量 */ );cache.put(1, 1);cache.put(2, 2);cache.get(1); // 返回 1cache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得密钥 2 作废cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)cache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得密钥 1 作废cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)cache.get(3); // 返回 3cache.get(4); // 返回 4
来源:力扣(LeetCode)链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lru-cache
解析
LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制: Least Recently Used的缩写,即最近最少使用,选择最近最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。该算法赋予每个页面一个访问字段,用来记录一个页面自上次被访问以来所经历的时间 t,当须淘汰一个页面时,选择现有页面中其 t 值最大的,即最近最少使用的页面予以淘汰。
根据算法特点,第一快速,使用哈希;第二页面最久没被使用,表示数据要按照时间有序,使用链表结构。两者兼顾的数据结构—哈希链表。
方法1:Java的LinkHashMap实现LRU
class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer>{private int capacity;public LRUCache(int capacity) {super(capacity, 0.75F, true);this.capacity = capacity;}public int get(int key) {return super.getOrDefault(key, -1);}public void put(int key, int value) {super.put(key, value);}@Overrideprotected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) {return size() > capacity;}}/*** LRUCache 对象会以如下语句构造和调用:* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);* int param_1 = obj.get(key);* obj.put(key,value);*/
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:对于 put 和 get 操作复杂度是 O(1),因为有序字典中的所有操作: get/in/set/move_to_end/popitem(get/containsKey/put/remove) 都可以在常数时间内完成。
空间复杂度:O(capacity),因为空间只用于有序字典存储最多 capacity + 1 个元素。
方法2:哈希表+双向链表
这个问题可以用哈希表,辅以双向链表记录键值对的信息。所以可以在 O(1) 时间内完成 put 和 get 操作,同时也支持 O(1) 删除第一个添加的节点。
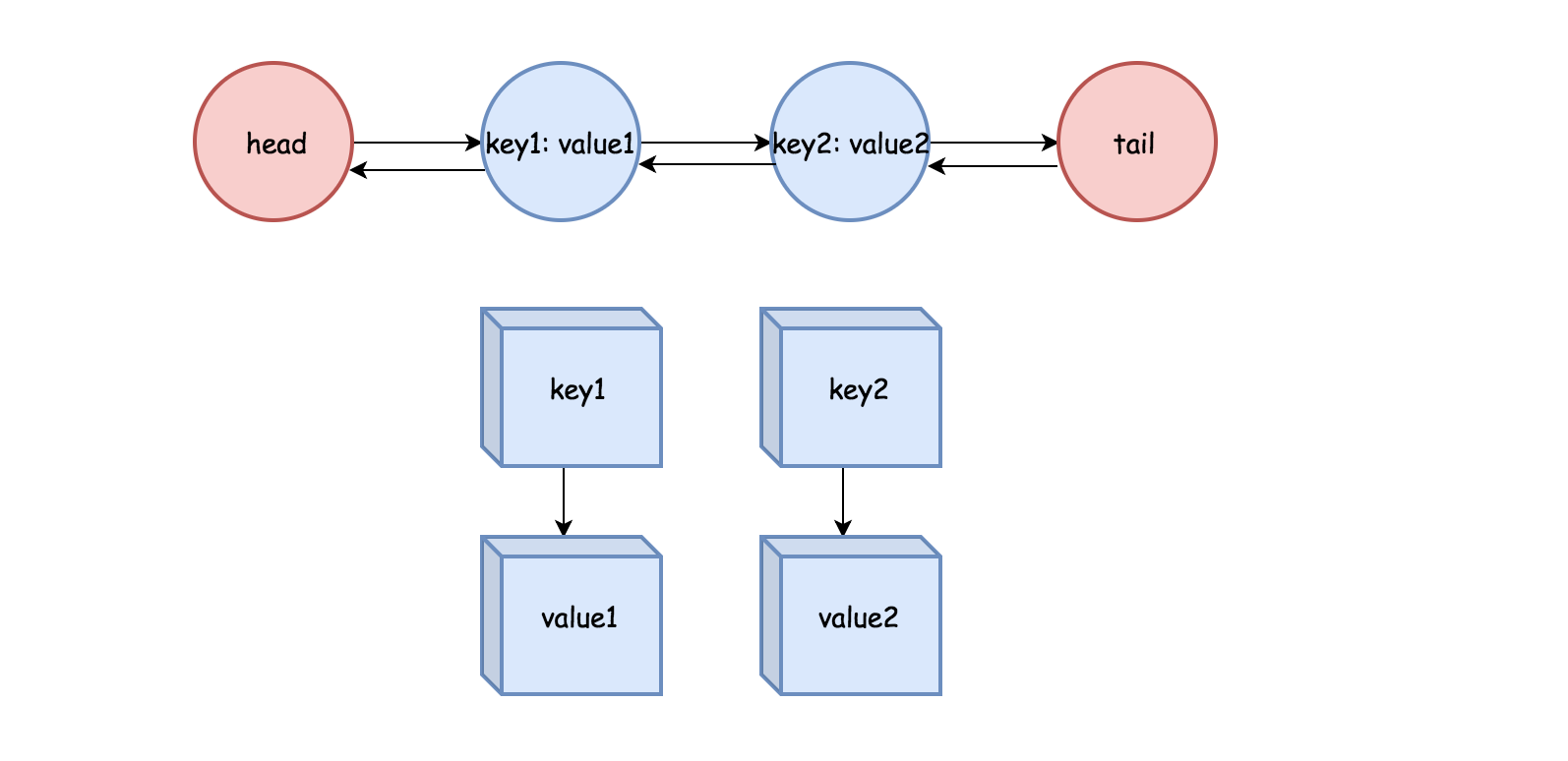
为什么使用双向链表?
使用双向链表的一个好处是不需要额外信息删除一个节点,同时可以在常数时间内从头部或尾部插入删除节点。
一个需要注意的是,在双向链表实现中,这里使用一个伪头部和伪尾部标记界限,这样在更新的时候就不需要检查是否是 null 节点。
import java.util.Hashtable;public class LRUCache {class DLinkedNode {int key;int value;DLinkedNode prev;DLinkedNode next;}private void addNode(DLinkedNode node) {/*** Always add the new node right after head.*/node.prev = head;node.next = head.next;head.next.prev = node;head.next = node;}private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node){/*** Remove an existing node from the linked list.*/DLinkedNode prev = node.prev;DLinkedNode next = node.next;prev.next = next;next.prev = prev;}private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node){/*** Move certain node in between to the head.*/removeNode(node);addNode(node);}private DLinkedNode popTail() {/*** Pop the current tail.*/DLinkedNode res = tail.prev;removeNode(res);return res;}private Hashtable<Integer, DLinkedNode> cache =new Hashtable<Integer, DLinkedNode>();private int size;private int capacity;private DLinkedNode head, tail;public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.size = 0;this.capacity = capacity;head = new DLinkedNode();// head.prev = null;tail = new DLinkedNode();// tail.next = null;head.next = tail;tail.prev = head;}public int get(int key) {DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);if (node == null) return -1;// move the accessed node to the head;moveToHead(node);return node.value;}public void put(int key, int value) {DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);if(node == null) {DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode();newNode.key = key;newNode.value = value;cache.put(key, newNode);addNode(newNode);++size;if(size > capacity) {// pop the tailDLinkedNode tail = popTail();cache.remove(tail.key);--size;}} else {// update the value.node.value = value;moveToHead(node);}}}/*** LRUCache 对象会以如下语句构造和调用:* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);* int param_1 = obj.get(key);* obj.put(key,value);*/
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:对于 put 和 get 都是O(1)。
空间复杂度:O(capacity),因为哈希表和双向链表最多存储 capacity + 1 个元素。
总结
学习使用哈希表和链表,明确双向链表的适用场景。

