参考链接
第 15 章 HQL: Hibernate 查询语言
廖雪峰-查询数据(分类比较明确)
边学边练习-sqlzoo/参考答案
在线sql
关键知识点:
1、基础查询: 别名,
2、限制语法:where , order by,
3、分组:group by …having,
4、连接查询
基础语法
HQL对关键字不区分大小写
--distinct表示去重--condition: and、or、between、in、not in、--order by 全局排序,sort by 本机排序--limit--join--union all 合并多个select查询结果查询语法:select [all | distinct] select_expr, select_expr, ...from table_reference[where where_condition][group by col_list][order by col_list][cluster by col_list| [distribute by col_list] [sort by col_list]][limit [offset,] rows]-------------------
// 1,简单的查询,Employee为实体名而不是数据库中的表名(面向对象特性)hql = "FROM Employee";hql = "FROM Employee AS e"; // 使用别名hql = "FROM Employee e"; // 使用别名,as关键字可省略// 只查询一个列,返回的集合的元素类型就是这个属性的类型hql = "SELECT e.name FROM Employee e";// 查询多个列,返回的集合的元素类型是Object数组hql = "SELECT e.id,e.name FROM Employee e";
查询限制or表达式
array_contains(数组, value) 用于 判断 数组中是否还有value 如果存在返回true
使用nvl()函数 nvl(属性名, 默认值) 当属性为null 会使用默认值
coalesce函数也可以实现判空的功能 coalesce(属性名,参数1,参数2)
参数1 为不为null输出的内容 参数2 为null 输出的内容
like 与 rlike
(1)like的内容 不是正则 ,而是通配符。像mysql中的”like”,但是建议使用高级函数” instr “效率更高。
(2)rlike的内容可以是正则,正则的写法与java一样。需要转义,例如’\m’需要使用’\m’
where .. between ... and ...is null / is not nullin/not in: t.name in ('haha','hehe')#函数:max\min\count总数\sum\avghaving 针对分组数据进行筛选 Group By ... Havingselect e.deptno,avg(e.sal) avgsal from emp e group by e.deptno having avgsal>2000;<>不等
// 2,带上过滤条件的(可以使用别名):WhereFROM Employee WHERE id<10;FROM Employee e WHERE e.id<1;FROM Employee e WHERE e.id<10 AND e.id>5;from User user where user.age = 20;from User user where user.age between 20 and 30;from User user where user.age in (20, 30);from User user where user.name is null;from User user where user.name like '% zx % ';from User user where (user.age % 2) = 1;from User user where user.age = 20 and user.name like '% zx % ';
模糊查询
字符串模式匹配:关键词like[表达式] 开启模糊查询,
通配符%表示任意个字符,
_表示一个字符,
[]表示括号内所列字符中的一个,
[^ ]:表示不在括号所列之内的单个字符,要求所匹配对象为指定字符以外的任一个字符
把u_name为“张三”,“张猫三”、“三脚猫”,“唐三藏”等等有“三”的记录全找出来。SELECT * FROM [user] WHERE u_name LIKE '%三%'既有“三”又有“猫”的记录SELECT * FROM [user] WHERE u_name LIKE '%三%' AND u_name LIKE '%猫%'SELECT * FROM [user] WHERE u_name LIKE '_三_'只找出“唐三藏”这样u_name为三个字且中间一个字是“三”的;SELECT * FROM [user] WHERE u_name LIKE '[张李王]三'将找出“张三”、“李三”、“王三”(而不是“张李王三”);SELECT * FROM [user] WHERE u_name LIKE '[^张李王]三'将找出不姓“张”、“李”、“王”的“赵三”、“孙三”等;
regexp_extract函数
regexpextract(string subject, string **_pattern, int index**)
高级查询
分组
group by
各个部门工资select e.deptno,avg(e.sal) from emp e group by e.deptno;
join
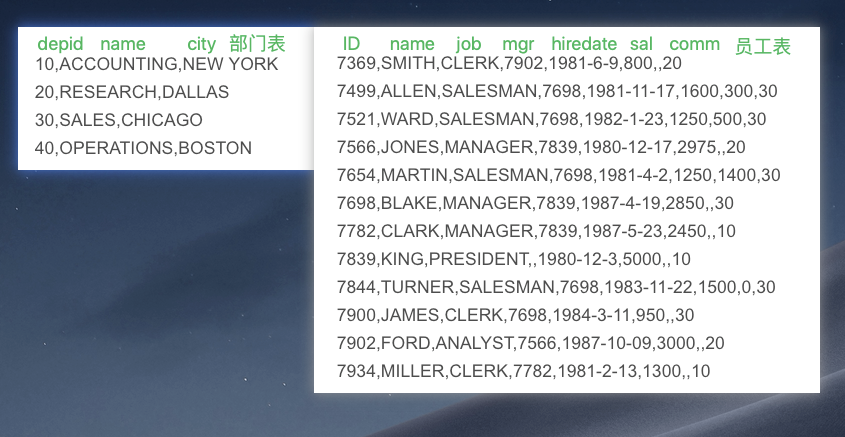
两个表进行连接,例如有两个表m n ,m表中的一条记录和n表中的一条记录组成一条记录
两张表,一个部门表、一个员工表;部门表和员工表可以通过depid连接;现在将两个表合成一个表|depid|depname|empno|empname|select d.deptno,d.dname e.empno,e.ename from emp ejoin dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;[join on 等值连接][left join 以join左边的表为准 如果右边的数据不在则补空 ]比如左边表为部门表,右边表为员工表;若以左边为主,即部门表是列全的,允许没有员工的部门存在在结果表中|depid|depname|empno|empname|1 a 001 xiaohuang2 b 002 xiaohei3 c null nullselect d.deptno,d.dname, e.empno,e.ename from dept dleft join emp e on e.deptno = d.deptno;[
case..when
[case ... when (condition)then xxxelse xxxend]select id,#对字段a进行赋值,如果当前满足when的条件 则a为1 否则a为0case when array_contains(id_courses, courses[0]) then 1 else 0 end as a,case when array_contains(id_courses, courses[1]) then 1 else 0 end as b,case when array_contains(id_courses, courses[2]) then 1 else 0 end as c,case when array_contains(id_courses, courses[3]) then 1 else 0 end as d,case when array_contains(id_courses, courses[4]) then 1 else 0 end as e,case when array_contains(id_courses, courses[5]) then 1 else 0 end as ffrom id_courses;
union
UNION ALL
•用来合并多个select的查询结果,需要保证select中字段须一致
•select_statement UNION ALL select_statement UNION ALL select_statement
子查询
对于支持子查询的数据库,Hibernate 支持在查询中使用子查询。一个子查询必须被圆括号包围起来(经常是 SQL 聚集函数的圆括号)。甚至相互关联的子查询(引用到外部查询中的别名的子查询)也是允许的。
子查询只可以在 select 或者 where 子句中出现
from Cat as fatcatwhere fatcat.weight >(select avg(cat.weight) from DomesticCat cat)from DomesticCat as catwhere cat.name = some (select name.nickName from Name as name)from Cat as catwhere not exists (from Cat as mate where mate.mate = cat)
复杂数据类型
数组

map