树是计算机科学中经常用到的一种数据结构。
树是一种非线性的数据结构,以分层的方式存储数据。
树被用来存储具有层级关系的数据,比如文件系统中的文件;页面的DOM结构;
树还被用来存储有序列表。
二叉树
二叉树是一种特殊的树结构,它表示子节点不超过2个。二叉树具有诸多优点。相对于链表来说,二叉树在进行查找时速度非常快,而相对于数组来说,为二叉树添加或删除元素也非常快。
二叉树的子树有左右之分,其次序不能任意颠倒。
在实现二叉树时,采用的存储结构为链式存储结构,链式结构的意思是采用一个链表来存储一颗二叉树,二叉树中每一个节点用链表的一个节点来存储,在二叉树中,节点结构至少有三个域:数据域data,左指针域left,右指针域right,如下图所示: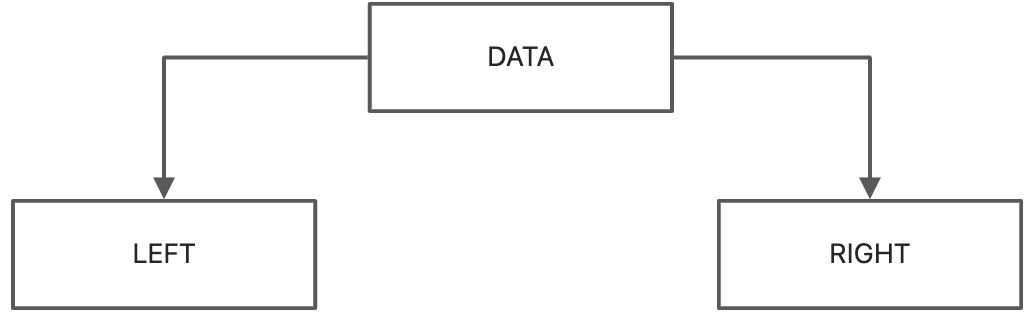
二叉树的Node节点结构
class Node{constructor(data, left, right){this.data = data;this.left = left;this.right = right;this.count = 1; // 比上图结构多了个属性,用于统计重复节点的数量}}
二叉排序树
二叉排序树或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质
- 如果存在左子节点,则左子节点值小于根节点的值
- 如果存在右子树,则右子树的所有节点大于根节点的值
- 左右子树也是二叉排序树
-
代码框架
class BSTree {constructor() {this.root = null;}// 删除一个节点_removeNode(node, data) {}// 删除给定的数据节点remove(data) {this.root = this._removeNode(this.root, data);}// 向二叉树中插入节点insert(data) {}// 寻找给定数据的节点find(data) {}// 获得最小值的节点getMinNode(node = this.root) { }// 获得最大值的节点getMaxNode(node = this.root) { }}
二叉树排序树基本操作
插入节点
插入操作可以分为两步:1.新建node节点。 2.找出合适位置插入
以data为值创建node节点let newNode = new Node(data, null, null);
接下来进行插入操作。使用parentNode记录当前节点的父节点,初始值为null。当前节点为currNode,初始时为该二叉树的根节点。
插入时,root为null,直接将currNode赋值给root即可。
- 如果newNode的值小于currNode的值,将newNode插入到currNode的左子树上。否则,插入到右子树上。
- 更新当前节点currNode所指的节点,直到当前节点不存在,说明找到了插入的位置。
insert(data) {let newNode = new Node(data, null, null);if (!this.root) {// 不存在根节点时,将新节点设置为根节点this.root = newNode;} else {let currNode = this.root;let parentNode = null;while (true) {// 做为暂时保存变量parentNode = currNode;// 插入的值,小于父节点的值,插入到左侧if (newNode.data < currNode.data) {// 更新currNode为左侧的子节点currNode = currNode.left;// 一直查找直到没有左节点时,将新节点newNode设置为parentNode的左节点if (!currNode) {parentNode.left = newNode;break;}} else if (newNode.data > currNode.data) {currNode = currNode.right;if (!currNode) {parentNode.right = newNode;break;}} else if (newNode.data == currNode.data) {this.count++;break;}}}}
获取最值
获取最小值
不断搜索排序二叉树的左子节点,直到左节点不存在,说明当前的节点就是最小节点getMinNode(node = this.root) {let curNode = node;while (curNode.left) {curNode = curNode.left;}return curNode;}
获取最大值
不断搜索排序二叉树的右子节点,直到右节点不存在,说明当前的节点就是最大节点getMaxNode(node = this.root) {let curNode = node;while (curNode.right) {curNode = curNode.right;}return curNode;}
查询节点
二叉树排序树中寻找给定的数据find(data) {let currNode = this.root;// 从根开始查找while (currNode) {if ((currNode.data = data)) {return currNode;} else if (currNode.data > data) {currNode = currNode.left;} else if (currNode.data < data) {currNode = currNode.right;}}return null;}
移除节点
删除节点:分为三种情况
- 待删除的节点是叶子节点。直接将节点删除。
- 待删除的节点有子节点,没有左子节点,或者没有右子节点。
- 待删除的节点没有左子节点时,返回该节点的右孩子节点,并删除该节点
- 待删除的节点没有右子节点时,返回该节点的左孩子节点,并删除该节点
- 待删除的节点的左右子节点均存在。
- 或者查找待删除节点左子树上的最大值
- 或者查找待删除节点右子树上的最小值
代码使用:查找其右子树上的最小值的方法。在找到待删除节点的右子树上的最小值后,创建临时节点,将临时节点上的值复制到待删除节点,然后再删除临时节点。
_removeNode(node, data) {// 根节点都为空,不能删除任何值if (node === null) {return null;}// 删除的节点是根节点if (data === node.data) {// {1}:删除的是叶子节点,没有子节点// 当待删除的节点时叶子节点时, 直接将待删除的节点置空返回if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {return null;}// 当待删除的节点没有左子节点时,返回该节点的右孩子节点,并删除该节点if (node.left === null) {return node.right;}if (node.right === null) {return node.left;}/* 最后一种情况待删除的节点的左右子节点均存在,有两种做法:要么查找待删除节点左子树上的最大值,要么查找其右子树上的最小值*/// 查找右节点的最小值let tempNode = this.getMinNode(node.right);node.data = tempNode.data; //右子树的最小值,替换要删除的值node.right = this._removeNode(node.right, tempNode.data);return node;}// 删除的节点在左节点else if (data < node.data) {node.left = this._removeNode(node.left, data);return node;} else {node.right = this._removeNode(node.right, data);return node;}}remove(data) {this._removeNode(this.root, data);}
测试代码
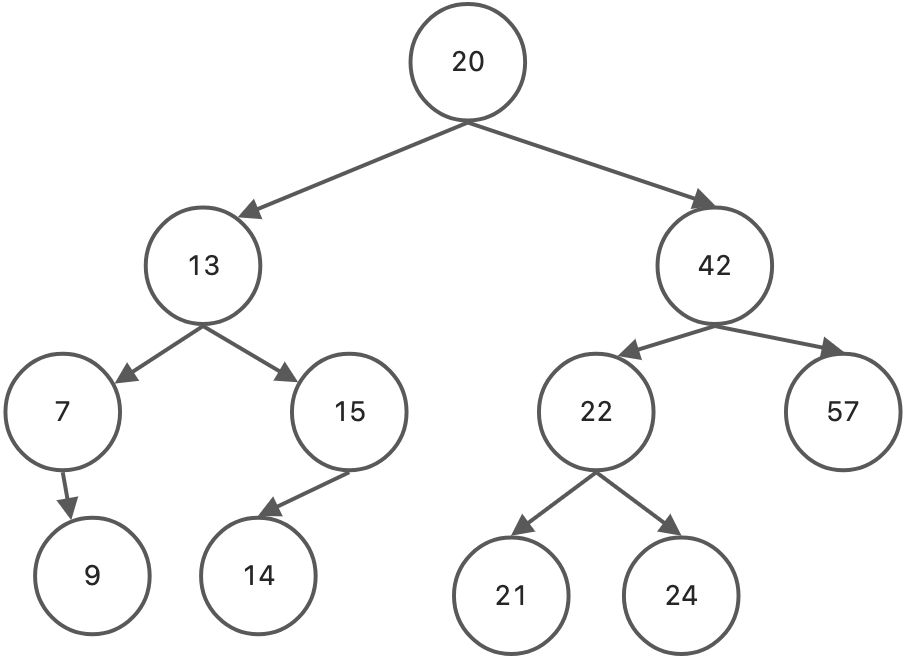
let myTree = new BSTree();myTree.insert(20);myTree.insert(13);myTree.insert(7);myTree.insert(9);myTree.insert(15);myTree.insert(14);myTree.insert(42);myTree.insert(22);myTree.insert(21);myTree.insert(24);myTree.insert(57);console.log(myTree.getMaxNode());//Node { data: 57, left: null, right: null, count: 1 }console.log(myTree.getMinNode()); //Node { data: 7, left: null, right: Node { data: 9, left: null, right: null, count: 1 },count: 1}myTree.remove(7);console.log(myTree.getMinNode()); //Node { data: 9, left: null, right: null, count: 1 }
二叉树排序树遍历操作
二叉树的遍历操作可以使用递归来完成。递归遍历会非常简单。
递归的方法往往表现的非常简洁,但是理解起来需要费一番功夫,所以本篇对二叉树的遍历还提供了非递归的方法。应当要注意的是,遍历操作适合所有的二叉树,而不仅仅是上一篇中实现的二叉排序树。
class BSTree {constructor() {this.root = null;}// 中序递归遍历inOrderRec(node = this.root) {}// 中序非递归遍历inOrderNonRec(node = this.root){}// 前序递归遍历preOrderRec(node = this.root) {}// 前序遍历非递归方法preOrderNonRec(node = this.root) {}// 后序遍历递归方法postOrderRec(node = this.root) {}// 后序遍历非递归的方法postOrderNonRec(node = this.root) {}// 层次遍历levelOrder(node = this.root) {}// 知道二叉树的先序和中序排列,重建二叉树preInCreate(preArr, inArr, pBeg, pEnd, iBeg, iEnd) {}}
层序遍历
首先实现最重要的一个变量方法,二叉树的很多操作都依赖该遍历实现。如:统计二叉树中叶子节点个数;获取二叉树的宽度;判断两颗二叉树是否相等;求二叉树的深度;
二叉树的层次遍历,即按照箭头所指的方向,按照20、13、42、7、15、22、57、9、14、21、24的层次顺序,对二叉树的各个节点进行访问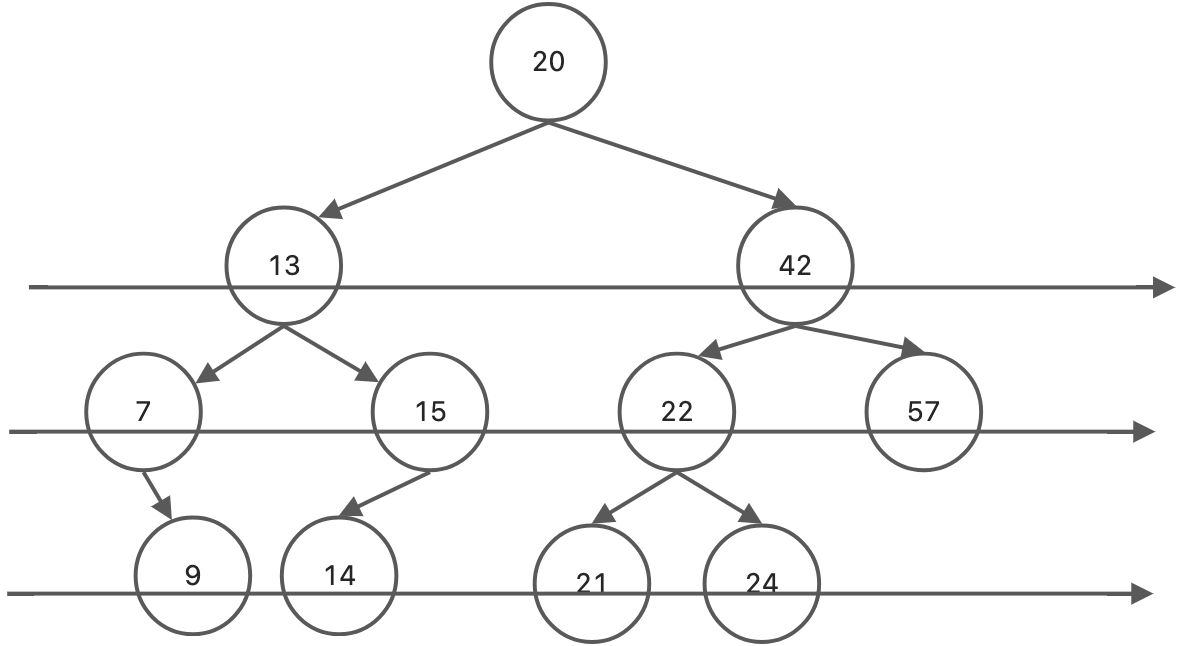
首先将二叉树的根节点入队列,然后出队,访问该节点,如果它的左子树不空,则将左子树的根节点入队。如果它的右子树不为空,则将右子树的根节点入队。然后出队,对出队节点进行访问,如此反复,直到队列为空。
levelOrder(node = this.root) {// 进行层次遍历,需要借助队列// 首先将二叉树的根节点入队列,然后出队,访问该节点,如果它的左子树不空,则将左子树的根节点入队。如果它的右子树不为空,则将右子树的根节点入队。let queue = [];let result = "";// 根节点入队列queue.push(node);while (queue.length > 0) {// 获取队列的开头node = queue.shift();// 记录二叉树节点的值result += `->${node.data} `;if (node.left) {// 左子节点入队queue.push(node.left);}if (node.right) {// 右子节点入队queue.push(node.right);}}return result.substring(2);}
测试
let myTree = new BSTree();myTree.insert(20);myTree.insert(13);myTree.insert(7);myTree.insert(9);myTree.insert(15);myTree.insert(14);myTree.insert(42);myTree.insert(22);myTree.insert(21);myTree.insert(24);myTree.insert(57);console.log(myTree.levelOrder()); // 20 13 42 7 15 22 57 9 14 21 24
前序遍历
遍历顺序:
- 访问根节点。
- 前序遍历左子树。
- 前序遍历右子树。
前序递归法
// 前序递归遍历, 1:访问根节点。2:前序遍历左子树。3:前序遍历右子树。preOrderRec(node = this.root) {// 先根,后左,再右let result = "";if (node !== null) {// 先显示根result += node === this.root ? `${node.data}` : `->${node.data}`;// 显示左子树result += this.preOrderRec(node.left);// 显示右子树result += this.preOrderRec(node.right);}return result;}
前序非递归法
非递归的遍历时,需要借助一个栈。stack
首先访问根节点,然后将其入栈,如果此节点的左子树不为空,则再次访问此节点左子树的根节点,然后将其入栈……直到节点的左子树为空时,从堆栈中弹出一个节点,再按照相同的方法访问出栈节点的右子树。
非递归算法的效率要高于递归算法。preOrderNonRec(node = this.root) {//非递归的遍历时,算法需要借助一个栈let stack = [];let result = "";// 当节点存在或者栈不空时while (node || stack.length > 0) {if (node) {// 访问根节点result += `->${node.data} `;// 根节点入栈stack.push(node);// 根之后先遍历左子树node = node.left;} else {// 从栈中取出根节点node = stack.pop();// 遍历根节点的右子树node = node.right;}}return result;}
中序遍历
中序遍历,先左再根后右。中序递归法
inOrderRec(node = this.root) {// 先左,后根,再右let result = "";if (node !== null) {result += this.inOrderRec(node.left);result += `->${node.data}`;result += this.inOrderRec(node.right);}return result;}
中序非递归法
非递归遍历需要借助栈数据结构实现。
首先访问根节点 的所有左子节点,并将它们依次进栈,然后出栈顶层节点【左子节点】,打印该节点【左子节点或者暂时的根】。然后扫描该节点的右子节点,将其进栈,再扫描该右子节点的所有左节点并依次进栈,如此反复,直到栈为空时结束。
inOrderNonRec(node = this.root) {// 非递归遍历借助栈结构let stack = [];let result = "";while (node || stack.length) {if (node) {// 节点存在,先将节点入栈stack.push(node);// 如果node存在,使用节点的左子节点 更新节点,然后继续入栈node = node.left;} else {// 左子节点不存在了。执行出栈,后进先出node = stack.pop();result += `->${node.data} `;// 使用节点的右子节点 更新节点,然后入栈node = node.right;}}return result;}
测试
console.log(myTree.inOrderRec()); // 7 9 13 14 15 20 21 22 24 42 57console.log(myTree.inOrderNonRec()); // 7 9 13 14 15 20 21 22 24 42 57
后序遍历
后续递归法
把打印操作放到最后
postOrderRec(node = this.root) {// 先左,后右,再根let result = "";if (node !== null) {result += this.postOrderRec(node.left);result += this.postOrderRec(node.right);result += `->${node.data}`;}return result;}
后序非递归法
后序遍历的非递归算法比较复杂。
非递归遍历二叉树的顺序是 先访问左子树, 再访问右子树, 最后访问根节点。
用栈来存储节点,必须分清楚返回根节点时,是从左子树返回的,还是从右子树返回的。所以变量指针ret,其指向最近访问过的节点。
postOrderNonRec(node = this.root) {// 左右根let stack = [];let ret = node;let result = "";while (node || stack.length) {// 第一步现将根节点以及左节点依次入栈if (node) {// 根节点存在,将节点入栈stack.push(node);// 更新node节点,为左子节点,存在的话继续入栈,不存在就走else操作node = node.left;} else {// 获取栈顶节点,首次获取的值为7节点node = stack[stack.length - 1];// 如果node有右节点且未访问过if (node.right && node.right != ret) {// node.right != ret说明是从左子节点返回的根,不同才进入右子节点入栈操作,// 如果相同,已经处理过,说明是右子节点返回到的根,就不能进入,否则会死循环node = node.right;// 将右节点入栈stack.push(node);node = node.left; // 再次查找此时右节点上是否有左节点} else {// 首先会进入这里开始遍历左子节点// 取出栈结构中的节点node = stack.pop();result += `->${node.data} `;// 记录下节点,防止进入无限循环ret = node;node = null;}}}return result;}
测试
console.log(myTree.postOrderRec()); // 9 7 14 15 13 21 24 22 57 42 20console.log(myTree.postOrderNonRec()); // 9 7 14 15 13 21 24 22 57 42 20
重建一颗二叉树
给出前序和中序的值,求出整个树的结构?重建出该二叉树
分析思路:
- 前序遍历中,第一个值一定是树的根。
- 中序遍历中,根节点一定在树的左子树和右子树中间,通过第一步找到的根,将中序的值可以划分三份,左子树,根,右子树。同时计算出左子树和右子树的个数
- 用第二步的左右子节点个数,对前序遍历的值进行分割,划分成左右子树。
- 通过节点数量对前序遍历分割处理的左右子树,它们【前序分割出的左右子树】第一节点还是根节点。
- 用根节点的值重复执行第一步。
如此递归地进行下去,便能唯一地确定这棵二叉树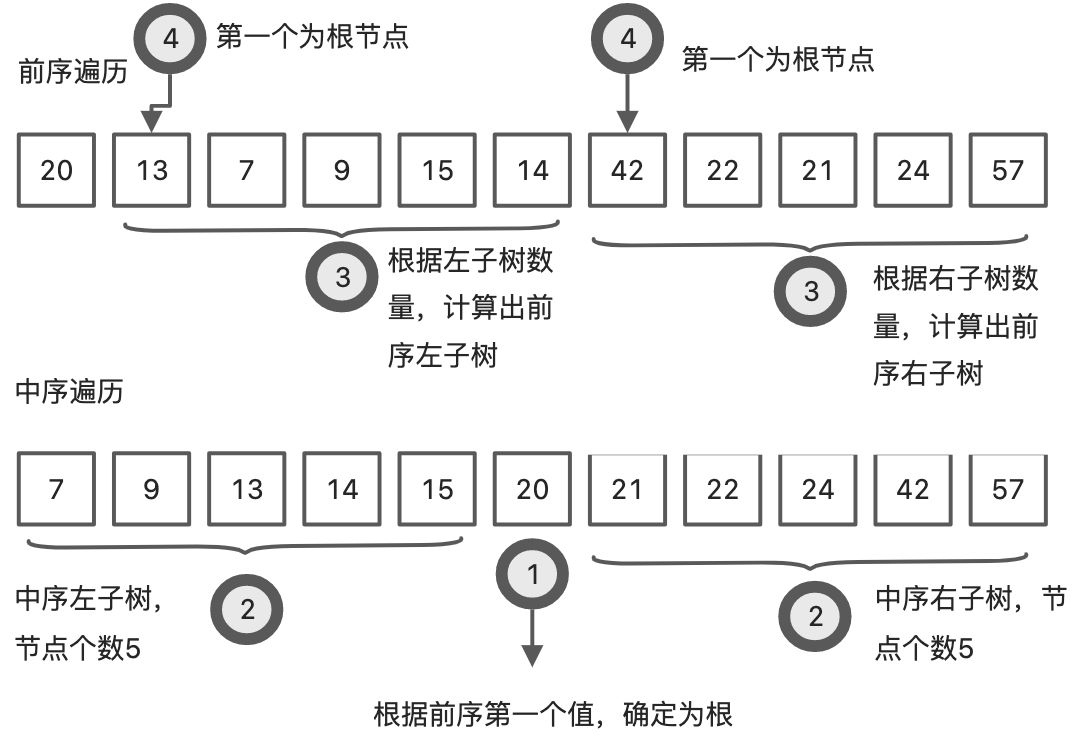
/*** @param {Array} preArr 先序序列* @param {Array} midArr 中序序列* @param {Number} pBeg 先序序列的第一个下标* @param {Number} pEnd 先序序列的最后一个下标* @param {Number} mBeg 中序序列的第一个下标* @param {Number} mEnd 中序序列的最后一个下标*/preInCreate(preArr, midArr, pBeg, pEnd, mBeg, mEnd) {let lLen = 0,rLen = 0;let splitIdx = -1;// 建立根节点,先序的开头就是根let node = new Node(preArr[pBeg], null, null);if (!this.root) {this.root = node;}// 利用根节点即【20】 在中序序列中进行划分// 先序序列 20 ->13 ->7 ->9 ->15 ->14 ->42 ->22 ->21 ->24 ->57// 中序序列 7 ->9 ->13 ->14 ->15 ->20 ->21 ->22 ->24 ->42 ->57for (let i = mBeg; i <= mEnd; i++) {// 用先序的根【20】,在中序列查找,查出索引位置,即20所处的位置if (midArr[i] == preArr[pBeg]) {splitIdx = i;break;}}// 根据20所处的索引位置,求出左右子树的长度if (splitIdx > -1) {lLen = splitIdx - mBeg; // 左子树的长度 5, 【7 ->9 ->13 ->14 ->15】rLen = mEnd - splitIdx; // 右子树的长度 5, 【21 ->22 ->24 ->42 ->57】}// 递归建立左子树if (lLen) {node.left = this.preInCreate(preArr,midArr,pBeg + 1,pBeg + lLen,mBeg,mBeg + lLen - 1);} else {node.left = null;}// 递归建立右子树if (rLen) {node.right = this.preInCreate(preArr,midArr,pEnd - rLen + 1,pEnd,mEnd - rLen + 1,mEnd);} else {node.right = null;}return node;}
测试
// 前序序列为:20, 13, 7, 9, 15, 14, 42, 22, 21, 24, 57// 中序序列为:7, 9, 13, 14, 15, 20, 21, 22, 24, 42, 57let preOrder = [20, 13, 7, 9, 15, 14, 42, 22, 21, 24, 57];let inOrder = [7, 9, 13, 14, 15, 20, 21, 22, 24, 42, 57];let inLstIdx = inOrder.length - 1;let preLstIdx = preOrder.length - 1;let myTree = new BSTree();myTree.preInCreate(preOrder, inOrder, 0, preLstIdx, 0, inLstIdx);console.log(myTree.inOrderNonRec()); // 7 9 13 14 15 20 21 22 24 42 57console.log(myTree.preOrderNonRec()); // 20 13 7 9 15 14 42 22 21 24 57console.log(myTree.postOrderNonRec()); // 9 7 14 15 13 21 24 22 57 42 20
二叉树排序树其他常用操作
获取节点个数
//非递归计算节点操作,使用层序遍历的队列计数,只要在每次节点出队的时候计数 +1getNodeNumber(node = this.root) {let count = 0;if (node) {let queue = [];queue.push(node); // 根节点入队列while (queue.length) {node = queue.shift();count++; // 只要一个节点出队,计数就+1if (node.left) {queue.push(node.left);}if (node.right) {queue.push(node.right);}}return count;}}
getNodeNumber2(node = this.root) {let count = 0;if (node) {count++;count += this.getNodeNumber2(node.left);count += this.getNodeNumber2(node.right);}return count;}console.log(myTree.getNodeNumber());myTree.remove(42);console.log(myTree.getNodeNumber2());
获取叶子节点个数
统计叶子节点的个数也使用层序遍历。
统计叶子节点个数:只统计出队列的节点同时没有左右子树时,计数才+1;
// 非递归操作getLeafNodeNumber(node = this.root) {let count = 0;let queue = [];queue.push(node);while (queue.length) {node = queue.pop();if (node.left) {queue.push(node.left);}if (node.right) {queue.push(node.right);}if (!node.left && !node.right) {count++;}}return count;}//递归操作getLeafNodeNumber2(node = this.root) {// 每次递归的结束条件if (!node) {return 0;}if (!node.left && !node.right) {return 1;}let leftNum = this.getLeafNodeNumber2(node.left);let rightNum = this.getLeafNodeNumber2(node.right);return leftNum + rightNum;}
测试
console.log(myTree.getLeafNodeNumber()); // 5myTree.remove(57);console.log(myTree.getLeafNodeNumber()); // 4
获取二叉树深度
二叉树的深度指的是从根节点到叶子节点中最长路径的长度为树的深度。
使用递归的方法实现
- 一颗树只有一个节点,它的深度是1;
- 二叉树的根节点只有左子树而没有右子树,二叉树的深度应该是其左子树的深度加1;
- 二叉树的根节点只有右子树而没有左子树,二叉树的深度应该是其右子树的深度加1;
- 二叉树的根节点既有右子树又有左子树,那么二叉树的深度应该是其左右子树的深度较大值加1。
getTreeDepth(node = this.root) {let depth = 0;if (node) {depth++;if (node.left && !node.right) {depth = this.getTreeDepth(node.left) + 1;}if (node.right && !node.left) {depth = this.getTreeDepth(node.right) + 1;}if (node.left && node.right) {depth =this.getTreeDepth(node.left) > this.getTreeDepth(node.right)? this.getTreeDepth(node.left) + 1: this.getTreeDepth(node.right) + 1;}}return depth;}
测试
console.log(myTree.getTreeDepth()); // 4myTree.remove(9);myTree.remove(14);myTree.remove(21);myTree.remove(24);console.log(myTree.getTreeDepth()); // 3
计算指定层的节点数
使用层次遍历,使用一个变量来保存当前层数节点的个数,用这个变量作为内层循环结束的标识,当内层循环结束时,队列中保存的就是下一层的节点,这时判断是否等于给定层数,如果相等直接返回,不相等再进行下一轮循环// 计算指定层数节点的个数// 使用一个变量来保存当前层数节点的个数,用这个变量作为内层循环结束的标识getLevelNodeNumber(level, node = this.root) {if (node) {// depth保存查找的层级let depth = 1;let queue = [];queue.push(node);if (depth === level) {return queue.length;}while (true) {//使用size保存当前层级节点的个数let size = queue.length;if (size === 0) {return;}// size有值,说明还是在当前层级while (size) {node = queue.shift();if (node.left) {queue.push(node.left);}if (node.right) {queue.push(node.right);}size--;}depth++;if (depth === level) return queue.length;}}}
测试
console.log(myTree.getLevelNodeNumber(1)); // 1console.log(myTree.getLevelNodeNumber(2)); // 2console.log(myTree.getLevelNodeNumber(3)); // 4console.log(myTree.getLevelNodeNumber(4)); // 4
判断是不是完全二叉树
完全二叉树的定义若设二叉树的深度为h,除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~h-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第 h 层所有的结点都连续集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。
完全二叉树指的是除了最后一层可能不是满的,其他层都是满的二叉树
算法1
如果层次遍历时遇到一个空节点后,再向后的遍历的时候依然还有节点,则这个二叉树肯定不是完全二叉树。
//采用层序遍历,如果遇到一个空节点,则后边的节点都是空节点才是完全二叉树,否则就不是完全二叉树isCompleteTree1(node = this.root) {let queue = [];let flag = false;queue.push(node);while (queue.length) {node = queue.shift();// 如果节点存在if (node) {if (flag) {return false;}queue.push(node.left);queue.push(node.right);} else {// 节点不存在,说明出现了空节点,空节点就设置flag为true,如果后边没有任何节点,则为完全二叉树// 如果后边还有节点,再次进入到if(node)中,则是非完全二叉树flag = true;}}return true;}
算法2
- 如果一个节点只有右子节点,则不是完全二叉树。
- 当遍历到一个不是叶子节点的节点【说明该节点存在子节点】时,如果其前面的节点没有右孩子节点【前面节点有空的节点】,则不是完全二叉树。
isCompleteTree2(node = this.root) {let queue = [];let noRight = false;queue.push(node);while (queue.length) {node = queue.shift();// 对应注释《1》if (!node.left && node.right) {return false;}//遇到一个非叶子节点 且其前面的节点没有右孩子节点if ((node.left || node.right) && noRight) {return false;}if (node.left) {queue.push(node.left);}if (node.right) {queue.push(node.right);} else {// 没右子节点,但是后续的节点还是有子节点的枪口noRight = true;}}return true;}
二叉树镜像
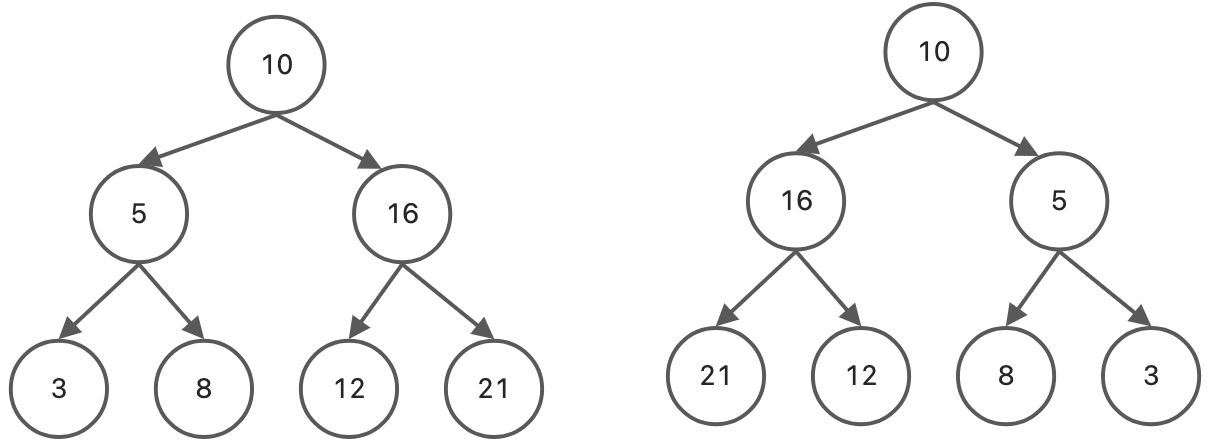
将左右子树交换
invertTree(node = this.root) {if (!node) {return;}// 建立一个临时存放节点的变量let tempNode = node.left;node.left = node.right;node.right = tempNode;this.invertTree(node.left);this.invertTree(node.right);}